Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effectiveness of personal protective measures in a dismantling plant for chemical weapons from World War I of the Belgian Defence.
Methods
Seventeen NIOSH level B-equipped plant workers exposed to arsenic trichloride (AsCl3) in combination with phosgene or hydrogen cyanide (HCN) were compared to 24 NIOSH level C-protected field workers occasionally exposed to genotoxic chemicals (including AsCl3-phosgene/HCN) when collecting chemical ammunition, and 19 matched referents. Chromosomal aberrations (CA), micronuclei (MNCB and MNMC), sister chromatid exchanges (SCE) and high frequency cells (HFC) were analysed in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Urinary arsenic levels and genetic polymorphisms in major DNA repair enzymes (hOGG1 326 , XRCC1 399 , XRCC3 241) were also assessed.
Results
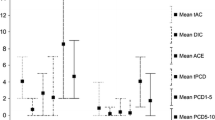
SCE and HFC levels were significantly higher in plant-exposed versus referent subjects, but MNCB and MNMC were not different. MNCB, SCE and HFC levels were significantly higher and MNMC levels significantly lower in field-exposed workers versus referents. AsCl3 exposure was not correlated with genotoxicity biomarkers.
Conclusions
Protective measures for plant-exposed workers appear adequate, but protection for field-exposed individuals could be improved.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertini RJ, Anderson D, Douglas GR, Hagmar L, Hemminki K, Merlo F, Natarajan AT, Norppa H, Shuker DE, Tice R, Waters MD, Aitio A (2000) IPCS guidelines for the monitoring of genotoxic effects of carcinogens in humans. Mutat Res 463(2):111–172
Au WW, Salama SA, Sierra-Torres CH (2003) Functional characterization of polymorphisms in DNA repair genes using cytogenetic challenge assays. Environ Health Perspect 111(15):1843–1850
Barrett JC, Lamb PW, Wang TC, Lee TC (1989) Mechanisms of arsenic-induced cell transformation. Biol Trace Elem Res 21:421–429
Basu A, Mahata J, Gupta S, Giri AK (2001) Genetic toxicology of a paradoxical human carcinogen, arsenic: a review. Mutat Res 488(2):171–194
Basu A, Mahata J, Roy AK, Sarkar JN, Poddar G, Nandy AK, Sarkar PK, Dutta PK, Banerjee A, Das M, Ray K, Roychaudhury S, Natarajan AT, Nilsson R, Giri AK (2002) Enhanced frequency of micronuclei in individuals exposed to arsenic through drinking water in West Bengal, India. Mutat Res 516(1–2):29–40
Basu A, Ghosh P, Das JK, Banerjee A, Ray K, Giri AK (2004) Micronuclei as biomarkers of carcinogen exposure in populations exposed to arsenic through drinking water in West Bengal, India: a comparative study in three cell types. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13(5):820–827
Bonassi S, Hagmar L, Stromberg U, Montagud AH, Tinnerberg H, Forni A, Heikkila P, Wanders S, Wilhardt P, Hansteen IL, Knudsen LE, Norppa H (2000) Chromosomal aberrations in lymphocytes predict human cancer independently of exposure to carcinogens. European Study Group on Cytogenetic Biomarkers and Health. Cancer Res 60(6):1619–1625
Bonassi S, Lando C, Ceppi M, Landi S, Rossi AM, Barale R (2004) No association between increased levels of high-frequency sister chromatid exchange cells (HFCs) and the risk of cancer in healthy individuals. Environ Mol Mutagen 43(2):134–136
Bonassi S, Znaor A, Ceppi M, Lando C, Chang WP, Holland N, Kirsch-Volders M, Zeiger E, Ban S, Barale R, Bigatti MP, Bolognesi C, Cebulska-Wasilewska A, Fabianova E, Fucic A, Hagmar L, Joksic G, Martelli A, Migliore L, Mirkova E, Scarfi MR, Zijno A, Norppa H, Fenech M (2007) An increased micronucleus frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes predicts the risk of cancer in humans. Carcinogenesis 28(3):625–631
Bonassi S, Norppa H, Ceppi M, Stromberg U, Vermeulen R, Znaor A, Cebulska-Wasilewska A, Fabianova E, Fucic A, Gundy S, Hansteen IL, Knudsen LE, Lazutka J, Rossner P, Sram RJ, Boffetta P (2008) Chromosomal aberration frequency in lymphocytes predicts the risk of cancer: results from a pooled cohort study of 22 358 subjects in 11 countries. Carcinogenesis 29(6):1178–1183
Buchet JP, Lison D, Ruggeri M, Foa V, Elia G (1996) Assessment of exposure to inorganic arsenic, a human carcinogen, due to the consumption of seafood. Arch Toxicol 70(11):773–778
Carrano AV, Natarajan AT (1988) International commission for protection against environmental mutagens and carcinogens. ICPEMC publication no. 14. Considerations for population monitoring using cytogenetic techniques. Mutat Res 204(3):379–406
Carton C, Meert C, De Bisschop HC (2004) Destruction of clark munitions with a cold detonation chamber: aspects of workers protection. CWD, St Petersburg, Russia. Available at: http://www.dstl.gov.uk/conferences/cwd/2004/proceedings14.pdf. Accessed 20 Oct 2008
De Boeck M, Lardau S, Buchet JP, Kirsch-Volders M, Lison D (2000) Absence of significant genotoxicity in lymphocytes and urine from workers exposed to moderate levels of cobalt-containing dust: a cross-sectional study. Environ Mol Mutagen 36(2):151–160
Dean BJ, Danford N (1984) Assays for the detection of chemically-induced chromosome damage in cultured mammalian cells. In: Venitt S, Parry JM (eds) Mutagenicity testing—a practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 187–232
Deknudt G, Leonard A, Arany J, Jenar-Du Buisson G, Delavignette E (1986) In vivo studies in male mice on the mutagenic effects of inorganic arsenic. Mutagenesis 1(1):33–34
Donbak L, Rencuzogullari E, Yavuz A, Topaktas M (2005) The genotoxic risk of underground coal miners from Turkey. Mutat Res 588(2):82–87
European Standards EN 13274-1 (2001) Respiratory protective devices-methods of test-part I: determination of inward leakage and total inward leakage, British Standard, 1st edn, 32 p
Fenech M, Morley AA (1985) Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutat Res 147(1–2):29–36
Fenech M, Chang WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E (2003) HUMN project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res 534(1–2):65–75
Ghosh P, Basu A, Mahata J, Basu S, Sengupta M, Das JK, Mukherjee A, Sarkar AK, Mondal L, Ray K, Giri AK (2006) Cytogenetic damage and genetic variants in the individuals susceptible to arsenic-induced cancer through drinking water. Int J Cancer 118(10):2470–2478
Goode EL, Ulrich CM, Potter JD (2002) Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes and associations with cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11(12):1513–1530
Gurr JR, Liu F, Lynn S, Jan KY (1998) Calcium-dependent nitric oxide production is involved in arsenite-induced micronuclei. Mutat Res 416(3):137–148
Hagmar L, Brogger A, Hansteen IL, Heim S, Hogstedt B, Knudsen L, Lambert B, Linnainmaa K, Mitelman F, Nordenson I, Reuterwall C, Salomaa S, Skerfving S, Sorsa M (1994) Cancer risk in humans predicted by increased levels of chromosomal aberrations in lymphocytes: nordic study group on the health risk of chromosome damage. Cancer Res 54(11):2919–2922
Hagmar L, Bonassi S, Stromberg U, Brogger A, Knudsen LE, Norppa H, Reuterwall C (1998) Chromosomal aberrations in lymphocytes predict human cancer: a report from the European Study Group on Cytogenetic Biomarkers and Health (ESCH). Cancer Res 58(18):4117–4121
Han S, Zhang HT, Wang Z, Xie Y, Tang R, Mao Y, Li Y (2006) DNA repair gene XRCC3 polymorphisms and cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 48 case-control studies. Eur J Hum Genet 14(10):1136–1144
Heilier JF, Buchet JP, Haufroid V, Lison D (2005) Comparison of atomic absorption and fluorescence spectroscopic methods for the routine determination of urinary arsenic. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 78(1):51–59
Helleday T, Nilsson R, Jenssen D (2000) Arsenic[III] and heavy metal ions induce intrachromosomal homologous recombination in the hprt gene of V79 Chinese hamster cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 35(2):114–122
IARC (1980) Arsenic and arsenic compounds. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, vol 23. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, pp 39–141
IARC (1987) Arsenic. Overall evaluation of carcinogenicity: an updating of IARC monographs, Suppl 7. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, pp 100–106
IARC (2004) Some drinking—water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic. Arsenic in Drinking water. IARC monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk to humans, vol 84. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, pp 40–267
IPCS (1997) Environmental health criteria 193. Phosgene. International programme on chemical safety, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. Available at: http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc193.htm . Accessed 22 June 2009
Jones CR, Sepai O, Liu YY, Yan H, Sabbioni G (2005) Urinary metabolites of workers exposed to nitrotoluenes. Biomarkers 10(1):10–28
Kirsch-Volders M, Fenech M (2001) Inclusion of micronuclei in non-divided mononuclear lymphocytes and necrosis/apoptosis may provide a more comprehensive cytokinesis block micronucleus assay for biomonitoring purposes. Mutagenesis 16(1):51–58
Kirsch-Volders M, Mateuca RA, Roelants M, Tremp A, Zeiger E, Bonassi S, Holland N, Chang WP, Aka PV, De Boeck M, Godderis L, Haufroid V, Ishikawa H, Laffon B, Marcos R, Migliore L, Norppa H, Teixeira JP, Zijno A, Fenech M (2006) The effects of GSTM1 and GSTT1 polymorphisms on micronucleus frequencies in human lymphocytes in vivo. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15(5):1038–1042
Kopjar N, Garaj-Vrhovac V, Kasuba V, Rozgaj R, Ramic S, Pavlica V, Zeljezic D (2008) Assessment of genotoxic risks in Croatian health care workers occupationally exposed to cytotoxic drugs: a multi-biomarker approach. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212(4):414–431
Lerda D (1994) Sister-chromatid exchange (SCE) among individuals chronically exposed to arsenic in drinking water. Mutat Res 312(2):111–120
Lewinska D, Palus J, Stepnik M, Dziubaltowska E, Beck J, Rydzynski K, Natarajan AT, Nilsson R (2007) Micronucleus frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes and buccal mucosa cells of copper smelter workers, with special regard to arsenic exposure. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 80(5):371–380
Mahata J, Basu A, Ghoshal S, Sarkar JN, Roy AK, Poddar G, Nandy AK, Banerjee A, Ray K, Natarajan AT, Nilsson R, Giri AK (2003) Chromosomal aberrations and sister chromatid exchanges in individuals exposed to arsenic through drinking water in West Bengal, India. Mutat Res 534(1–2):133–143
Mateuca R, Aka PV, De Boeck M, Hauspie R, Kirsch-Volders M, Lison D (2005) Influence of hOGG1, XRCC1 and XRCC3 genotypes on biomarkers of genotoxicity in workers exposed to cobalt or hard metal dusts. Toxicol Lett 156(2):277–288
Mateuca RA, Roelants M, Iarmarcovai G, Aka PV, Godderis L, Tremp A, Bonassi S, Fenech M, Berge-Lefranc JL, Kirsch-Volders M (2008) hOGG1326, XRCC1399 and XRCC3241 polymorphisms influence micronucleus frequencies in human lymphocytes in vivo. Mutagenesis 23(1):35–41
Matullo G, Palli D, Peluso M, Guarrera S, Carturan S, Celentano E, Krogh V, Munnia A, Tumino R, Polidoro S, Piazza A, Vineis P (2001) XRCC1, XRCC3, XPD gene polymorphisms, smoking and (32)P-DNA adducts in a sample of healthy subjects. Carcinogenesis 22(9):1437–1445
Meert C, Carton C, De Bisschop HC (2006) Dismantling of mustard shells: evaluation of worker’s protection. CWD, Luneburg, Germany. Available at: http://www.dstl.gov.uk/conferences/cwd/2006/pres/carton.pdf. Accessed 22 June 2009
Muller WU, Streffer C, Fischer-Lahdo C (1986) Toxicity of sodium arsenite in mouse embryos in vitro and its influence on radiation risk. Arch Toxicol 59(3):172–175
Murgia E, Ballardin M, Bonassi S, Rossi AM, Barale R (2008) Validation of micronuclei frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes as early cancer risk biomarker in a nested case-control study. Mutat Res 639(1–2):27–34
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) (2004) NIOSH respirator selection logic, Cincinnati, OH: US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, CDC. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2005-100/. Accessed 22 June 2009
NRC (2002) acute exposure guideline levels for selected airborne chemicals, vol 2. Available at: http://www.nap.edu/catalog.php?record_id=10522 . Accessed 22 June 2009
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) (2006) Respiratory protection standard, 1910.134, U.S. Department of Labour. Available at: http://www.osha.gov/index.html . Accessed 22 June 2009
Pachkowski BF, Winkel S, Kubota Y, Swenberg JA, Millikan RC, Nakamura J (2006) XRCC1 genotype and breast cancer: functional studies and epidemiologic data show interactions between XRCC1 codon 280 His and smoking. Cancer Res 66(5):2860–2868
Paiva L, Martinez V, Creus A, Quinteros D, Marcos R (2006) Sister chromatid exchange analysis in smelting plant workers exposed to arsenic. Environ Mol Mutagen 47(4):230–235
Palus J, Lewinska D, Dziubaltowska E, Stepnik M, Beck J, Rydzynski K, Nilsson R (2005) DNA damage in leukocytes of workers occupationally exposed to arsenic in copper smelters. Environ Mol Mutagen 46(2):81–87
Pashin Iu V, Kozachenko VI, Toroptsev SN (1984) Arsenic trioxide inhibition of the thiophosphamide induction of mutations in mouse germ and somatic cells. Genetika 20(2):365–366
Perry P, Wolff S (1974) New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature 251(5471):156–158
Ponzanelli I, Landi S, Bernacchi F, Barale R (1997) The nature of high frequency sister chromatid exchange cells (HFCs). Mutagenesis 12(5):329–333
Rossman TG (2003) Mechanism of arsenic carcinogenesis: an integrated approach. Mutat Res 533(1–2):37–65
Royal Decree of 11 March (2002) concerning the health protection and safety of workers against the risk of chemicals at the workplace. Available at: http://cdfc00.rug.ac.be/healthrisk/legislation/AR_11=03=2002.pdf. Accessed 22 June 2009
Savage JR (1976) Classification and relationships of induced chromosomal structural changes. J Med Genet 13(2):103–122
Schaumloffel N, Gebel T (1998) Heterogeneity of the DNA damage provoked by antimony and arsenic. Mutagenesis 13(3):281–286
Skjelbred CF, Svendsen M, Haugan V, Eek AK, Clausen KO, Svendsen MV, Hansteen IL (2006) Influence of DNA repair gene polymorphisms of hOGG1, XRCC1, XRCC3, ERCC2 and the folate metabolism gene MTHFR on chromosomal aberration frequencies. Mutat Res 602(1–2):151–162
Sram RJ, Rossner P, Smerhovsky Z (2004) Cytogenetic analysis and occupational health in the Czech Republic. Mutat Res 566(1):21–48
Sram RJ, Beskid O, Binkova B, Chvatalova I, Lnenickova Z, Milcova A, Solansky I, Tulupova E, Bavorova H, Ocadlikova D, Farmer PB (2007) Chromosomal aberrations in environmentally exposed population in relation to metabolic and DNA repair genes polymorphisms. Mutat Res 620(1–2):22–33
Tapio S, Grosche B (2006) Arsenic in the aetiology of cancer. Mutat Res 612(3):215–246
Tuimala J, Szekely G, Gundy S, Hirvonen A, Norppa H (2002) Genetic polymorphisms of DNA repair and xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes: role in mutagen sensitivity. Carcinogenesis 23(6):1003–1008
Vuyyuri SB, Ishaq M, Kuppala D, Grover P, Ahuja YR (2006) Evaluation of micronucleus frequencies and DNA damage in glass workers exposed to arsenic. Environ Mol Mutagen 47(7):562–570
Wan B, Christian RT, Soukup SW (1982) Studies of cytogenetic effects of sodium arsenicals on mammalian cells in vitro. Environ Mutagen 4(4):493–498
Weiss JM, Goode EL, Ladiges WC, Ulrich CM (2005) Polymorphic variation in hOGG1 and risk of cancer: a review of the functional and epidemiologic literature. Mol Carcinog 42(3):127–141
WHO (2004) Hydrogen cyanide and cyanides: human health aspects. concise international chemical assessment document 61. Available at: http://www.who.int/ipcs/publications/cicad/en/cicad61.pdf . Accessed 22 June 2009
Zanzoni F, Jung EG (1980) Arsenic elevates the sister chromatid exchange (SCE) rate in human lymphocytes in vitro. Arch Dermatol Res 267(1):91–95
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Belgian Defence (Department RS & TD and DOVO; VUB contract: WDGO251, study MS 03/01), and by ECNIS (Environmental Cancer Risk, Nutrition and Individual Susceptibility), a network of excellence operating within the European Union 6th Framework Programme, Priority 5: “Food Quality and Safety” (Contract No 513943). The authors are grateful to Ivan Hostens for his assistance in collecting the biological samples, and to Prof. Dr. Vincent Haufroid for his valuable scientific expertise in measuring the urinary arsenic concentrations. The authors also acknowledge Gina Plas for her excellent technical support. This study was partly funded by the Belgian Defence (Department RS & TD and DOVO; VUB contract: WDGO251, study MS 03/01), but the views expressed in this paper reflect the authors’ opinion and not the opinion of the Belgian Defence.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mateuca, R.A., Carton, C., Roelants, M. et al. Genotoxicity surveillance programme in workers dismantling World War I chemical ammunition. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 83, 483–495 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-010-0526-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-010-0526-2