Abstract
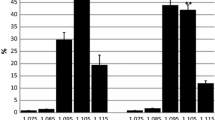
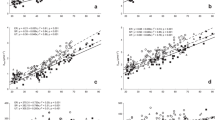
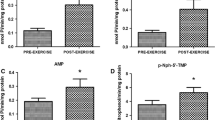
In this study we examined the time course of changes in the plasma concentration of oxypurines [hypoxanthine (Hx), xanthine and urate] during prolonged cycling to fatigue. Ten subjects with an estimated maximum oxygen uptake (V˙O2max) of 54 (range 47–67) ml · kg−1 · min−1 cycled at [mean (SEM)] 74 (2)% of V˙O2max until fatigue [79 (8) min]. Plasma levels of oxypurines increased during exercise, but the magnitude and the time course varied considerably between subjects. The plasma concentration of Hx ([Hx]) was 1.3 (0.3) μmol/l at rest and increased eight fold at fatigue. After 60 min of exercise plasma [Hx] was >10 μmol/l in four subjects, whereas in the remaining five subjects it was <5 μmol/l. The muscle contents of total adenine nucleotides (TAN = ATP+ADP+AMP) and inosine monophosphate (IMP) were measured before and after exercise in five subjects. Subjects with a high plasma [Hx] at fatigue also demonstrated a pronounced decrease in muscle TAN and increase in IMP. Plasma [Hx] after 60 min of exercise correlated significantly with plasma concentration of ammonia ([NH3], r = 0.90) and blood lactate (r = 0.66). Endurance, measured as time to fatigue, was inversely correlated to plasma [Hx] at 60 min (r = −0.68, P < 0.05) but not to either plasma [NH3] or blood lactate. It is concluded that during moderate-intensity exercise, plasma [Hx] increases, but to a variable extent between subjects. The present data suggest that plasma [Hx] is a marker of adenine nucleotide degradation and energetic stress during exercise. The potential use of plasma [Hx] to assess training status and to identify overtraining deserves further attention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 11 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahlin, K., Tonkonogi, M. & Söderlund, K. Plasma hypoxanthine and ammonia in humans during prolonged exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 80, 417–422 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050613
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050613