Abstract
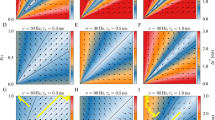
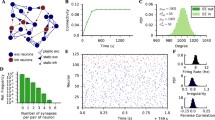
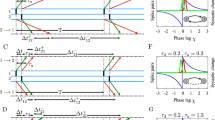
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) determines the evolution of the synaptic weights according to their pre- and post-synaptic activity, which in turn changes the neuronal activity on a (much) slower time scale. This paper examines the effect of STDP in a recurrently connected network stimulated by external pools of input spike trains, where both input and recurrent synapses are plastic. Our previously developed theoretical framework is extended to incorporate weight-dependent STDP and dendritic delays. The weight dynamics is determined by an interplay between the neuronal activation mechanisms, the input spike-time correlations, and the learning parameters. For the case of two external input pools, the resulting learning scheme can exhibit a symmetry breaking of the input connections such that two neuronal groups emerge, each specialized to one input pool only. In addition, we show how the recurrent connections within each neuronal group can be strengthened by STDP at the expense of those between the two groups. This neuronal self-organization can be seen as a basic dynamical ingredient for the emergence of neuronal maps induced by activity-dependent plasticity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez VA, Sabatini BL (2007) Anatomical and physiological plasticity of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Neurosci 30: 79–97
Appleby PA, Elliott T (2006) Stable competitive dynamics emerge from multispike interactions in a stochastic model of spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Neural Comput 18(10): 2414–2464
Bell CC, Han VZ, Sugawara Y, Grant K (1997) Synaptic plasticity in a cerebellum-like structure depends on temporal order. Nature 387(6630): 278–281
Bi GQ, Poo MM (1998) Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: Dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type. J Neurosci 18(24): 10464–10472
Bi GQ, Poo MM (2001) Synaptic modification by correlated activity: Hebb’s postulate revisited. Annu Rev Neurosci 24: 139–166
Bienenstock EL, Cooper LN, Munro PW (1982) Theory for the development of neuron selectivity—orientation specificity and binocular interaction in visual-cortex. J Neurosci 2(1): 32–48
Boettiger CA, Doupe AJ (2001) Developmentally restricted synaptic plasticity in a songbird nucleus required for song learning. Neuron 31(5): 809–818
Burkitt AN (2006) A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: I. Homogeneous synaptic input. Biol Cybern 95(1): 1–19
Burkitt AN, Meffin H, Grayden DB (2004) Spike-timing-dependent plasticity: the relationship to rate-based learning for models with weight dynamics determined by a stable fixed point. Neural Comput 16(5): 885–940
Burkitt AN, Gilson M, van Hemmen JL (2007) Spike-timing-dependent plasticity for neurons with recurrent connections. Biol Cybern 96(5): 533–546
Butts DA, Kanold PO, Shatz CJ (2007a) A burst-based “Hebbian” learning rule at retinogeniculate synapses links retinal waves to activity-dependent refinement. PLoS Biol 5(3): 651–661
Butts DA, Weng C, Jin J, Yeh CI, Lesica NA, Alonso JM, Stanley GB (2007b) Temporal precision in the neural code and the timescales of natural vision. Nature 449: 92–95
Butz M, Wörgötter F, van Ooyen A (2009) Activity-dependent structural plasticity. Brain Res Rev 60(2): 287–305
Caporale N, Dan Y (2008) Spike timing-dependent plasticity: a Hebbian learning rule. Annu Rev Neurosci 31: 25–46
Câteau H, Kitano K, Fukai T (2008) Interplay between a phase response curve and spike-timing-dependent plasticity leading to wireless clustering. Phys Rev E 77(5): 051909
Choe Y, Miikkulainen R (1998) Self-organization and segmentation in a laterally connected orientation map of spiking neurons. Neurocomputing 21(1–3): 139–157
Dahmen JC, Hartley DE, King AJ (2008) Stimulus-timing-dependent plasticity of cortical frequency representation. J Neurosci 28(50): 13629–13639
Dan Y, Poo MM (2006) Spike timing-dependent plasticity: from synapse to perception. Physiol Rev 86(3): 1033–1048
Debanne D, Gahwiler BH, Thompson SM (1998) Long-term synaptic plasticity between pairs of individual CA3 pyramidal cells in rat hippocampal slice cultures. J Physiol (Lond) 507(1): 237–247
deCharms RC, Zador A (2000) Neural representation and the cortical code. Annu Rev Neurosci 23: 613–647
Delorme A, Perrinet L, Thorpe SJ (2001) Networks of integrate-and-fire neurons using rank order coding B: Spike timing dependent plasticity and emergence of orientation selectivity. Neurocomputing 38: 539–545
Egger V, Feldmeyer D, Sakmann B (1999) Coincidence detection and changes of synaptic efficacy in spiny stellate neurons in vat barrel cortex. Nat Neurosci 2(12): 1098–1105
Elliott T (2003) An analysis of synaptic normalization in a general class of Hebbian models. Neural Comput 15(4): 937–963
Elliott T, Shadbolt NR (1999) A neurotrophic model of the development of the retinogeniculocortical pathway induced by spontaneous retinal waves. J Neurosci 19(18): 7951–7970
Feldman DE (2000) Timing-based LTP and LTD at vertical inputs to layer II/III pyramidal cells in rat barrel cortex. Neuron 27(1): 45–56
Froemke RC, Dan Y (2002) Spike-timing-dependent synaptic modification induced by natural spike trains. Nature 416(6879): 433–438
Fusi S (2002) Hebbian spike-driven synaptic plasticity for learning patterns of mean firing rates. Biol Cybern 87(5–6): 459–470
Gerstner W, Ritz R, van Hemmen JL (1993) Why spikes? Hebbian learning and retrieval of time-resolved excitation patterns. Biol Cybern 69(5–6): 503–515
Gerstner W, Kempter R, van Hemmen JL, Wagner H (1996) A neuronal learning rule for sub-millisecond temporal coding. Nature 383(6595): 76–78
Gilson M, Burkitt AN, Grayden DB, Thomas DA, van Hemmen JL (2009a) Emergence of network structure due to spike-timing-dependent plasticity in recurrent neuronal networks I: input selectivity–strengthening correlated input pathways. Biol Cybern 101(2): 81–102
Gilson M, Burkitt AN, Grayden DB, Thomas DA, van Hemmen JL (2009b) Emergence of network structure due to spike-timing-dependent plasticity in recurrent neuronal networks II: input selectivity–symmetry breaking. Biol Cybern 101(2): 103–114
Gilson M, Burkitt AN, Grayden DB, Thomas DA, van Hemmen JL (2009c) Emergence of network structure due to spike-timing-dependent plasticity in recurrent neuronal networks III: Partially connected neurons driven by spontaneous activity. Biol Cybern 101(5–6): 411–426
Gilson M, Burkitt AN, Grayden DB, Thomas DA, van Hemmen JL (2009d) Emergence of network structure due to spike-timing-dependent plasticity in recurrent neuronal networks IV: structuring synaptic pathways among recurrent connections. Biol Cybern 101(5–6): 427–444
Gjorgjieva J, Toyoizumi T, Eglen SJ (2009) Burst-time-dependent plasticity robustly guides ON/OFF segregation in the lateral geniculate nucleus. PLoS Comput Biol 5(12): e1000618
Goodhill GJ (2007) Contributions of theoretical modeling to the understanding of neural map development. Neuron 56(2): 301–311
Goodhill GJ, Barrow HG (1994) The role of weight normalization in competitive learning. Neural Comput 6(2): 255–269
Graupner M, Brunel N (2007) STDP in a bistable synapse model based on CaMKII and associated signaling pathways. PLoS Comput Biol 3(11): 2299–2323
Gütig R, Aharonov R, Rotter S, Sompolinsky H (2003) Learning input correlations through nonlinear temporally asymmetric Hebbian plasticity. J Neurosci 23(9): 3697–3714
Hawkes AG (1971) Point spectra of some mutually exciting point processes. J R Statist Soc Ser B 33(3): 438–443
Hensch TK (2005) Critical period plasticity in local cortical circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(11): 877–888
Hirsch JA, Martinez LM (2006) Circuits that build visual cortical receptive fields. Trends Neurosci 29: 30–39
Holtmaat A, Svoboda K (2009) Experience-dependent structural synaptic plasticity in the mammalian brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(9): 647–658
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1962) Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in cats visual cortex. J Physiol (Lond) 160(1): 106–164
Iglesias J, Eriksson J, Grize F, Tomassini M, Villa A (2005) Dynamics of pruning in simulated large-scale spiking neural networks. Biosystems 79(1–3): 11–20
Izhikevich EM, Desai NS (2003) Relating STDP to BCM. Neural Comput 15(7): 1511–1523
Katz LC, Crowley JC (2002) Development of cortical circuits: lessons from ocular dominance columns. Nat Rev Neurosci 3(1): 34–42
Kempter R, Gerstner W, van Hemmen JL (1999) Hebbian learning and spiking neurons. Phys Rev E 59(4): 4498–4514
Kohonen T (1982) Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol Cybern 43(1): 59–69
Kriener B, Tetzlaff T, Aertsen A, Diesmann M, Rotter S (2008) Correlations and population dynamics in cortical networks. Neural Comput 20(9): 2185–2226
Leibold C, Kempter R, van Hemmen JL (2002) How spiking neurons give rise to a temporal-feature map: from synaptic plasticity to axonal selection. Phys Rev E 65(5): 051915
Lubenov EV, Siapas AG (2008) Decoupling through synchrony in neuronal circuits with propagation delays. Neuron 58(1): 118–131
Magee JC, Johnston D (1997) A synaptically controlled, associative signal for Hebbian plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Science 275(5297): 209–213
Malsburg CV (1973) Self-organization of orientation sensitive cells in striate cortex. Kybernetik 14(2): 85–100
Marinaro M, Scarpetta S, Yoshioka M (2007) Learning of oscillatory correlated patterns in a cortical network by a STDP-based learning rule. Math Biosci 207(2): 322–335
Markram H, Lübke J, Frotscher M, Sakmann B (1997) Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 275(5297): 213–215
Masquelier T, Guyonneau R, Thorpe SJ (2008) Spike timing dependent plasticity finds the start of repeating patterns in continuous spike trains. PLoS ONE 3(1): e1377
Massoulie L (1998) Stability results for a general class of interacting point processes dynamics, and applications. Stoch Proc Appl 75(1): 1–30
Meffin H, Besson J, Burkitt AN, Grayden DB (2006) Learning the structure of correlated synaptic subgroups using stable and competitive spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Phys Rev E 73(4): 041911
Miller KD (1996) Synaptic economics: competition and cooperation in synaptic plasticity. Neuron 17(3): 371–374
Miller KD, Mackay DJC (1994) The role of constraints in Hebbian learning. Neural Comput 6(1): 100–126
Moreno-Bote R, Renart A, Parga N (2008) Theory of input spike auto- and cross-correlations and their effect on the response of spiking neurons. Neural Comput 20(7): 1651–1705
Morrison A, Aertsen A, Diesmann M (2007) Spike-timing-dependent plasticity in balanced random networks. Neural Comput 19(6): 1437–1467
Morrison A, Diesmann M, Gerstner W (2008) Phenomenological models of synaptic plasticity based on spike timing. Biol Cybern 98(6): 459–478
Neves G, Cooke SF, Bliss TVP (2008) Synaptic plasticity, memory and the hippocampus: a neural network approach to causality. Nat Rev Neurosci 9: 65–75
Pfister JP, Gerstner W (2006) Triplets of spikes in a model of spike timing-dependent plasticity. J Neurosci 26(38): 9673–9682
Pfister JP, Toyoizumi T, Barber D, Gerstner W (2006) Optimal spike-timing-dependent plasticity for precise action potential firing in supervised learning. Neural Comput 18(6): 1318–1348
Renart A, de la Rocha J, Bartho P, Hollender L, Parga N, Reyes A, Harris KD (2010) The asynchronous state in cortical circuits. Science 327(5965): 587–590
Rubin JE, Gerkin RC, Bi GQ, Chow CC (2005) Calcium time course as a signal for spike-timing-dependent plasticity. J Neurophysiol 93(5): 2600–2613
Sabatini BL, Oertner TG, Svoboda K (2002) The life cycle of Ca2+ ions in dendritic spines. Neuron 33(3): 439–452
Senn W (2002) Beyond spike timing: the role of nonlinear plasticity and unreliable synapses. Biol Cybern 87(5–6): 344–355
Shadlen MN, Newsome WT (1998) The variable discharge of cortical neurons: implications for connectivity, computation, and information coding. J Neurosci 18(10): 3870–3896
Sjöström PJ, Turrigiano GG, Nelson SB (2001) Rate, timing, and cooperativity jointly determine cortical synaptic plasticity. Neuron 32(6): 1149–1164
Song S, Abbott LF (2001) Cortical development and remapping through spike timing-dependent plasticity. Neuron 32(2): 339–350
Song S, Miller KD, Abbott LF (2000) Competitive Hebbian learning through spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Nat Neurosci 3(9): 919–926
Swindale NV (1996) The development of topography in the visual cortex: a review of models. Network 7(2): 161–247
Tzounopoulos T, Kim Y, Oertel D, Trussell LO (2004) Cell-specific, spike timing-dependent plasticities in the dorsal cochlear nucleus. Nat Neurosci 7(7): 719–725
van Hemmen JL (2001) Theory of synaptic plasticity. In: Moss F, Gielen S (eds), Handbook of biological physics, vol 4. Neuro-informatics and neural modelling. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 771–823
van Rossum MCW, Turrigiano GG (2001) Correlation based learning from spike timing dependent plasticity. Neurocomputing 38: 409–415
van Rossum MCW, Bi GQ, Turrigiano GG (2000) Stable Hebbian learning from spike timing-dependent plasticity. J Neurosci 20(23): 8812–8821
Wang HX, Gerkin RC, Nauen DW, Bi GQ (2005) Coactivation and timing-dependent integration of synaptic potentiation and depression. Nat Neurosci 8(2): 187–193
Wenisch OG, Noll J, van Hemmen JL (2005) Spontaneously emerging direction selectivity maps in visual cortex through STDP. Biol Cybern 93(4): 239–247
Wong RO (1999) Retinal waves and visual system development. Annu Rev Neurosci 22: 29–47
Zhang LI, Poo MM (2001) Electrical activity and development of neural circuits. Nat Neurosci 4: 1207–1214
Zou Q, Destexhe A (2007) Kinetic models of spike-timing dependent plasticity and their functional consequences in detecting correlations. Biol Cybern 97(1): 81–97
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilson, M., Burkitt, A.N., Grayden, D.B. et al. Emergence of network structure due to spike-timing-dependent plasticity in recurrent neuronal networks V: self-organization schemes and weight dependence. Biol Cybern 103, 365–386 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-010-0405-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-010-0405-7