Abstract
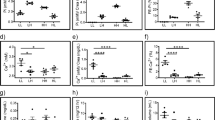
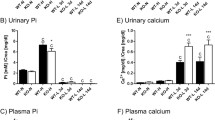
Renal reabsorption of inorganic phosphate (Pi) is mediated by the phosphate transporters NaPi-IIa, NaPi-IIc, and Pit-2 in the proximal tubule brush border membrane (BBM). Dietary Pi intake regulates these transporters; however, the contribution of the specific isoforms to the rapid and slow phase is not fully clarified. Moreover, the regulation of PTH and FGF23, two major phosphaturic hormones, during the adaptive phase has not been correlated. C57/BL6 and NaPi-IIa−/− mice received 5 days either 1.2 % (HPD) or 0.1 % (LPD) Pi-containing diets. Thereafter, some mice were acutely switched to LPD or HPD. Plasma Pi concentrations were similar under chronic diets, but lower when mice were acutely switched to LPD. Urinary Pi excretion was similar in C57/BL6 and NaPi-IIa−/− mice under HPD. During chronic LPD, NaPi-IIa−/− mice lost phosphate in urine compensated by higher intestinal Pi absorption. During the acute HPD-to-LPD switch, NaPi-IIa−/− mice exhibited a delayed decrease in urinary Pi excretion. PTH was acutely regulated by low dietary Pi intake. FGF23 did not respond to low Pi intake within 8 h whereas the phospho-adaptator protein FRS2α necessary for FGF-receptor cell signaling was downregulated. BBM Pi transport activity and NaPi-IIa but not NaPi-IIc and Pit-2 abundance acutely adapted to diets in C57/BL6 mice. In NaPi-IIa−/−, Pi transport activity was low and did not adapt. Thus, NaPi-IIa mediates the fast adaptation to Pi intake and is upregulated during the adaptation to low Pi despite persistently high FGF23 levels. The sensitivity to FGF23 may be regulated by adapting FRS2α abundance and phosphorylation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almaden Y, Canalejo A, Hernandez A, Ballesteros E, Garcia-Navarro S, Torres A, Rodriguez M (1996) Direct effect of phosphorus on PTH secretion from whole rat parathyroid glands in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 11:970–976
Almaden Y, Hernandez A, Torregrosa V, Canalejo A, Sabate L, Fernandez Cruz L, Campistol JM, Torres A, Rodriguez M (1998) High phosphate level directly stimulates parathyroid hormone secretion and synthesis by human parathyroid tissue in vitro. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:1845–1852
Andrukhova O, Zeitz U, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Lanske B, Erben RG (2012) FGF23 acts directly on renal proximal tubules to induce phosphaturia through activation of the ERK1/2-SGK1 signaling pathway. Bone 51(3):621–628. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2012.05.015
Bacic D, Capuano P, Baum M, Zhang J, Stange G, Biber J, Kaissling B, Moe OW, Wagner CA, Murer H (2005) Activation of dopamine D1-like receptors induces acute internalization of the renal Na+/phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIa in mouse kidney and OK cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F740–F747
Bacic D, Lehir M, Biber J, Kaissling B, Murer H, Wagner CA (2006) The renal Na+/phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIa is internalized via the receptor-mediated endocytic route in response to parathyroid hormone. Kidney Int 69:495–503
Baum M, Schiavi S, Dwarakanath V, Quigley R (2005) Effect of fibroblast growth factor-23 on phosphate transport in proximal tubules. Kidney Int 68:1148–1153
Beck L, Karaplis AC, Amizuka N, Hewson AS, Ozawa H, Tenenhouse HS (1998) Targeted inactivation of Npt2 in mice leads to severe renal phosphate wasting, hypercalciuria, and skeletal abnormalities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5372–5377
Bergwitz C, Juppner H (2010) Regulation of phosphate homeostasis by PTH, vitamin D, and FGF23. Annu Rev Med 61:91–104
Bergwitz C, Roslin NM, Tieder M, Loredo-Osti JC, Bastepe M, Abu-Zahra H, Frappier D, Burkett K, Carpenter TO, Anderson D, Garabedian M, Sermet I, Fujiwara TM, Morgan K, Tenenhouse HS, Juppner H (2006) SLC34A3 mutations in patients with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria predict a key role for the sodium-phosphate cotransporter NaP(i)-IIc in maintaining phosphate homeostasis. Am J Hum Genet 78:179–192
Berndt T, Thomas LF, Craig TA, Sommer S, Li X, Bergstralh EJ, Kumar R (2007) Evidence for a signaling axis by which intestinal phosphate rapidly modulates renal phosphate reabsorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:11085–11090
Berndt TJ, Bielesz B, Craig TA, Tebben PJ, Bacic D, Wagner CA, O’Brien S, Schiavi S, Biber J, Murer H, Kumar R (2006) Secreted frizzled-related protein-4 reduces sodium-phosphate co-transporter abundance and activity in proximal tubule cells. Pflugers Arch 451:579–587
Biber J, Hernando N, Forster I, Murer H (2009) Regulation of phosphate transport in proximal tubules. Pflugers Arch 458:39–52
Biber J, Stieger B, Stange G, Murer H (2007) Isolation of renal proximal tubular brush-border membranes. Nat Protoc 2:1356–1359
Biber J, Stieger B, Haase W, Murer H (1981) A high yield preparation for rat kidney brush border membranes. Different behaviour of lysosomal markers. Biochim Biophys Acta 647:169–176
Breusegem SY, Takahashi H, Giral-Arnal H, Wang X, Jiang T, Verlander JW, Wilson P, Miyazaki-Anzai S, Sutherland E, Caldas Y, Blaine JT, Segawa H, Miyamoto K, Barry NP, Levi M (2009) Differential regulation of the renal sodium-phosphate cotransporters NaPi-IIa, NaPi-IIc, and PiT-2 in dietary potassium deficiency. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F350–F361
Capuano P, Bacic D, Stange G, Hernando N, Kaissling B, Pal R, Kocher O, Biber J, Wagner CA, Murer H (2005) Expression and regulation of the renal Na/phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIa in a mouse model deficient for the PDZ protein PDZK1. Pflugers Arch 449:392–402
Capuano P, Radanovic T, Wagner CA, Bacic D, Kato S, Uchiyama Y, St-Arnoud R, Murer H, Biber J (2005) Intestinal and renal adaptation to a low-Pi diet of type II NaPi cotransporters in vitamin D receptor- and 1alphaOHase-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C429–C434
Christov M, Koren S, Yuan Q, Baron R, Lanske B (2011) Genetic ablation of sfrp4 in mice does not affect serum phosphate homeostasis. Endocrinology 152:2031–2036
Custer M, Lötscher M, Biber J, Murer H, Kaissling B (1994) Expression of Na-Pi cotransport in rat kidney: localization by RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. Am J Physiol 266:F767–F774
David V, Martin A, Hedge AM, Rowe PS (2009) Matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein (MEPE) is a new bone renal hormone and vascularization modulator. Endocrinology 150:4012–4023
Dobbie H, Unwin RJ, Faria NJ, Shirley DG (2008) Matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein causes phosphaturia in rats by inhibiting tubular phosphate reabsorption. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:730–733
Farrow EG, Davis SI, Summers LJ, White KE (2009) Initial FGF23-mediated signaling occurs in the distal convoluted tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:955–960
Fiske CH, SubbaRow Y (1925) The colorometric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66:375–400
Hu MC, Shi M, Zhang J, Pastor J, Nakatani T, Lanske B, Shawkat Razzaque M, Rosenblatt KP, Baum MG, Kuro OM, Moe OW (2010) Klotho: a novel phosphaturic substance acting as an autocrine enzyme in the renal proximal tubule. FASEB J 24(9):3438–3450. doi:10.1096/fj.10-154765
Ito N, Fukumoto S, Takeuchi Y, Takeda S, Suzuki H, Yamashita T, Fujita T (2007) Effect of acute changes of serum phosphate on fibroblast growth factor (FGF)23 levels in humans. J Bone Miner Metab 25:419–422
Keusch I, Traebert M, Lötscher M, Kaissling B, Murer H, Biber J (1998) Parathyroid hormone and dietary phosphate provoke a lysosomal routing of the proximal tubular Na/Pi-cotransporter type II. Kidney Int 54:1224–1232
Kurosu H, Ogawa Y, Miyoshi M, Yamamoto M, Nandi A, Rosenblatt KP, Baum MG, Schiavi S, Hu MC, Moe OW, Kuro-o M (2006) Regulation of fibroblast growth factor-23 signaling by klotho. J Biol Chem 281:6120–6123
Lanzano L, Lei T, Okamura K, Giral H, Caldas Y, Masihzadeh O, Gratton E, Levi M, Blaine J (2011) Differential modulation of the molecular dynamics of the type IIa and IIc sodium phosphate cotransporters by parathyroid hormone. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 301:C850–C861
Levi M, Lötscher M, Sorribas V, Custer M, Arar M, Kaissling B, Murer H, Biber J (1994) Cellular mechanisms of acute and chronic adaptation of rat renal Pi transporter to alterations in dietary Pi. Am J Physiol 267:F900–F908
Lötscher M, Wilson P, Nguyen S, Kaissling B, Biber J, Murer H, Levi M (1996) New aspects of adaptation of rat renal Na-Pi cotransporter to alterations in dietary phosphate. Kidney Int 49:1012–1018
Marks J, Churchill LJ, Debnam ES, Unwin RJ (2008) Matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein inhibits phosphate transport. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:2313–2320
Matsumoto N, Hemmi A, Yamato H, Ohnishi R, Segawa H, Ohno S, Miyamoto K (2010) Immunohistochemical analyses of parathyroid hormone-dependent downregulation of renal type II Na-Pi cotransporters by cryobiopsy. J Med Invest 57:138–145
Miyamoto K, Haito-Sugino S, Kuwahara S, Ohi A, Nomura K, Ito M, Kuwahata M, Kido S, Tatsumi S, Kaneko I, Segawa H (2011) Sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters: lessons from gene knockout and mutation studies. J Pharm Sci 100:3719–3730
Miyamoto KI, Itho M (2001) Transcriptional regulation of the NPT2 gene by dietary phosphate. Kidney Int 60:412–415
Mohebbi N, Kovacikova J, Nowik M, Wagner CA (2007) Thyroid hormone deficiency alters expression of acid–base transporters in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F416–F427
Muhlbauer RC, Bonjour JP, Fleisch H (1977) Tubular localization of adaptation to dietary phosphate in rats. Am J Physiol 233:F342–F348
Murer H, Biber J (2010) Phosphate transport in the kidney. J Nephrol 23(Suppl 16):S145–S151
Murer H, Forster I, Biber J (2004) The sodium phosphate cotransporter family SLC34. 7 447:763
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2000) Proximal tubular phosphate reabsorption: molecular mechanisms. Physiol Rev 80:1373–1409
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2003) Regulation of Na/Pi transporter in the proximal tubule. Annu Rev Physiol 65:531–542
Nielsen PK, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Olgaard K (1996) A direct effect in vitro of phosphate on PTH release from bovine parathyroid tissue slices but not from dispersed parathyroid cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant 11:1762–1768
Nowik M, Picard N, Stange G, Capuano P, Tenenhouse HS, Biber J, Murer H, Wagner CA (2008) Renal phosphaturia during metabolic acidosis revisited: molecular mechanisms for decreased renal phosphate reabsorption. Pflugers Arch 457:539–549
Ohkido I, Segawa H, Yanagida R, Nakamura M, Miyamoto K (2003) Cloning, gene structure and dietary regulation of the type-IIc Na/Pi cotransporter in the mouse kidney. Pflugers Arch 446:106–115
Picard N, Capuano P, Stange G, Mihailova M, Kaissling B, Murer H, Biber J, Wagner CA (2010) Acute parathyroid hormone differentially regulates renal brush border membrane phosphate cotransporters. Pflugers Arch 460:677–687
Quentin F, Chambrey R, Trinh-Trang-Tan MM, Fysekidis M, Cambillau M, Paillard M, Aronson PS, Eladari D (2004) The Cl−/HCO3 − exchanger pendrin in the rat kidney is regulated in response to chronic alterations in chloride balance. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F1179–F1188
Ravera S, Virkki LV, Murer H, Forster IC (2007) Deciphering PiT transport kinetics and substrate specificity using electrophysiology and flux measurements. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293:C606–C620
Razzaque MS (2009) The FGF23-Klotho axis: endocrine regulation of phosphate homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5:611–619
Ritthaler T, Traebert M, Lotscher M, Biber J, Murer H, Kaissling B (1999) Effects of phosphate intake on distribution of type II Na/Pi cotransporter mRNA in rat kidney. Kidney Int 55:976–983
Segawa H, Kaneko I, Takahashi A, Kuwahata M, Ito M, Ohkido I, Tatsumi S, Miyamoto K (2002) Growth-related renal type II Na/Pi cotransporter. J Biol Chem 277:19665–19672
Segawa H, Onitsuka A, Kuwahata M, Hanabusa E, Furutani J, Kaneko I, Tomoe Y, Aranami F, Matsumoto N, Ito M, Matsumoto M, Li M, Amizuka N, Miyamoto K (2009) Type IIc sodium-dependent phosphate transporter regulates calcium metabolism. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:104–113
Slatopolsky E, Finch J, Denda M, Ritter C, Zhong M, Dusso A, MacDonald PN, Brown AJ (1996) Phosphorus restriction prevents parathyroid gland growth. High phosphorus directly stimulates PTH secretion in vitro. J Clin Invest 97:2534–2540
Slot C (1965) Plasma creatinine determination. A new and specific Jaffe reaction method. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 17:381–387
Stoll R, Kinne R, Murer H (1979) Effect of dietary phosphate intake on phosphate transport by isolated rat renal brush-border vesicles. Biochem J 180:465–470
Suyama T, Okada S, Ishijima T, Iida K, Abe K, Nakai Y (2012) High phosphorus diet-induced changes in NaPi-IIb phosphate transporter expression in the rat kidney: DNA microarray analysis. PLoS One 7:e29483
Takahashi F, Morita K, Katai K, Segawa H, Fujioka A, Kouda T, Tatsumi S, Nii T, Taketani Y, Haga H, Hisano S, Fukui Y, Miyamoto KI, Takeda E (1998) Effects of dietary Pi on the renal Na+−dependent Pi transporter NaPi-2 in thyroparathyroidectomized rats. Biochem J 333(Pt 1):175–181
Tenenhouse HS, Martel J, Gauthier C, Segawa H, Miyamoto K (2003) Differential effects of Npt2a gene ablation and X-linked Hyp mutation on renal expression of Npt2c. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F1271–F1278
Verri T, Markovich D, Perego C, Norbis F, Stange G, Sorribas V, Biber J, Murer H (1995) Cloning of a rabbit renal Na-Pi cotransporter, which is regulated by dietary phosphate. Am J Physiol 268:F626–F633
Vervloet MG, van Ittersum FJ, Buttler RM, Heijboer AC, Blankenstein MA, ter Wee PM (2011) Effects of dietary phosphate and calcium intake on fibroblast growth factor-23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:383–389
Villa-Bellosta R, Ravera S, Sorribas V, Stange G, Levi M, Murer H, Biber J, Forster IC (2009) The Na+−Pi cotransporter PiT-2 (SLC20A2) is expressed in the apical membrane of rat renal proximal tubules and regulated by dietary Pi. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296:F691–F699
Virkki LV, Biber J, Murer H, Forster IC (2007) Phosphate transporters: a tale of two solute carrier families. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F643–F654
Weinman EJ, Biswas R, Steplock D, Wang P, Lau YS, Desir GV, Shenolikar S (2011) Increased renal dopamine and acute renal adaptation to a high-phosphate diet. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300:F1123–F1129
Woda C, Mulroney SE, Halaihel N, Sun L, Wilson PV, Levi M, Haramati A (2001) Renal tubular sites of increased phosphate transport and NaPi-2 expression in the juvenile rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 280:R1524–R1533
Acknowledgments
The authors thank N. Hernando for fruitful discussions. The use of the ZIRP Core facility for Rodent Physiology is acknowledged. The study was supported by the Swiss National Center for Competence in Research NCCR Kidney.CH to J. Biber and C.A. Wagner.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bourgeois, S., Capuano, P., Stange, G. et al. The phosphate transporter NaPi-IIa determines the rapid renal adaptation to dietary phosphate intake in mouse irrespective of persistently high FGF23 levels. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 465, 1557–1572 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1298-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1298-9