Abstract
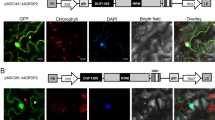
A family of Golgi-localised molecules was recently described in animals and fungi possessing extensive coiled regions and a short (~40 residues) conserved C-terminal domain, called the GRIP domain, which is responsible for their location to this organelle. Using the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, we identified a gene (AtGRIP) encoding a putative GRIP protein. We demonstrated that the C-terminal domain from AtGRIP functions as a Golgi-targeting sequence in plant cells. Localisation studies in living cells expressing the AtGRIP fused to a DsRed2 fluorescent probe, showed extensive co-location with the Golgi marker α-mannosidase I in transformed tobacco protoplasts. GRIP-like sequences were also found in genomic databases of rice, maize, wheat and alfalfa, suggesting that this domain may be a useful Golgi marker for immunolocalisation studies. Despite low sequence identity amongst GRIP domains, the plant GRIP sequence was able to target to the Golgi of mammalian cells. Taken together, these data indicate that GRIP domain proteins might be implicated in a targeting mechanism that is conserved amongst eukaryotes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α-ManI:
-
α-Mannosidase I
- AtGRIP:
-
Arabidopsis GRIP domain protein
- GCC:
-
Golgi-localized coiled-coil protein
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- MES:
-
2-(N-Morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid
- TGN:
-
Trans-Golgi network
References
Barr F (1999) A novel Rab6-interacting domain defines a family of Golgi-targeted coiled-coil proteins. Curr Biol 9:381–384
Brown D, Heimann K, Lock J, Kjer-Nielsen L, Vliet K van, Stow J, Gleeson P (2001) The GRIP domain is a specific targeting sequence for a population of trans-Golgi network derived tubulo-vesicular carriers. Traffic 2:336–344
Clague M (1999) Membrane transport: take your fusion partners. Curr Biol 9:R258–R260
Davis S, Vierstra R (1998) Soluble, highly fluorescent variants of green fluorescent protein (GFP) for use in higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 36:521–528
Erlich R, Gleeson P, Campbell P, Dietzsch E, Toh B (1996) Molecular characterization of trans-Golgi p230. A human peripheral membrane protein encoded by a gene on chromosome 6p12-22 contains extensive coiled-coil alpha-helical domains and a granin motif. J Biol Chem 271:8328–8337
Essl D, Dirnberger D, Gomord V, Strasser R, Faye L, Glossl J, Steinkellner H (1999) The N-terminal 77 amino acids from tobacco N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I are sufficient to retain a reporter protein in the Golgi apparatus of Nicotiana benthamiana cells. FEBS Lett 453:169–173
Fitchette A, Cabanes-Macheteau M, Marvin L, Martin B, Satiat-Jeunemaitre B, Gomord V, Crooks K, Lerouge P, Faye L, Hawes C (1999) Biosynthesis and immunolocalization of Lewis a-containing N-glycans in the plant cell. Plant Physiol 121:333–344
Fritzler M, Lung C, Hamel J, Griffith K, Chan E (1995) Molecular characterization of Golgin-245, a novel Golgi complex protein containing a granin signature. J Biol Chem 270:31262–31268
Gangi Setty SR, Shin ME, Yoshino A, Marks MS, Burd CG (2003) Golgi recruitment of GRIP domain proteins by Arf-like GTPase 1 is regulated by Arf-like GTPase 3. Curr Biol 13:401–404
Gish W, States D (1993) Identification of protein coding regions by database similarity search. Nat Genet 3:266–272
Gleeson P, Anderson T, Stow J, Griffiths G, Toh B, Matheson F (1996) p230 is associated with vesicles budding from the trans-Golgi network. J Cell Sci 109:2811–2821
Goodin M, Dietzgen RG, Schichnes D, Ruzin S, Jackson AO (2002) PGD vectors: versitile tools for the expression of green and red fluorescent protein fusions in agroinfiltrated plant leaves. Plant J 31:375–383
Kim DH, Eu Y-J, Yoo CM, Kim Y-W, Pih KT, Jin JB, Kim SJ, Stenmark H, Hwang I (2001) Trafficking of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate from the trans-Golgi network to the lumen of the central vacuole in plant cells. Plant Cell 13:287–301
Kjer-Nielsen L, Teasdale R, Vliet C van, Gleeson P (1999) A novel Golgi-localisation domain shared by a class of coiled coil peripheral membrane proteins. Curr Biol 9:385–388
Kooy J, Toh B, Pettitt J, Erlich R, Gleeson P (1992) Human autoantibodies as reagents to conserved Golgi components. Characterization of a peripheral, 230-kDa compartment-specific Golgi protein. J Biol Chem 267:20255–20263
Lu L, Hong W (2003) Interaction of Arl1-GTP with GRIP domains recruits autoantigens Golgin-97 and Golgin-245/p230 onto the Golgi. Mol Biol Cell 14:3767–3781
Luke M, Kjer-Nielsen L, Brown D, Stow J, Gleeson P (2003) GRIP domain-mediated targeting of two new coiled-coil proteins, GCC88 and GCC185, to subcompartments of the trans-Golgi Network. J Biol Chem 278:4216–4226
Lupas A (1996) Colied coils: new structures and new functions. Trends Biochem Sci 21:375–382
Mathur J, Szabados L, Schaefer S, Grunenberg B, Lossow A, Jonas-Straube E, Schell J, Koncz C, Koncz-Kalman Z (1998) Gene identification with sequenced T-DNA tags generated by transformation of Arabidopsis cell suspension. Plant J 13:707–716
Matz MV, Fradkov AF, Labas YA, Savitsky AP, Zaraisky AG, Markelov ML, Lukyanov SA (1999) Fluorescent proteins from nonbioluminescent Anthozoa species. Nat Biotechnol 17:969–973
McConville M, Ilgoutz S, Teasdale R, Foth B, Matthews A, Mullin K, Gleeson P (2002) Targeting of the GRIP domain to the trans-Golgi network is conserved from protists to animals. Eur J Cell Biol 81:485–495
Munro S, Nichols B (1999) The GRIP domain—novel Golgi-targeting domain found in several coiled coil proteins. Curr Biol 9:377–380
Nebenführ A, Staehelin L (2001) Mobile factories: Golgi dynamics in plant cells. Trends Plant Sci 6:160–167
Nebenführ A, Gallagher LA, Dunahahay TG, Frohlick JA, Mazurkiewicz AM, Meehl JB, Staehelin A (1999) Stop-and-go movements of plant Golgi stacks are mediated by the acto-myosin system. Plant Physiol 121:1127–1141
Nebenführ A, Frohlick J, Staehelin L (2000) Redistribution of Golgi stacks and other organelles during mitosis and cytokinesis in plant cells. Plant Physiol 124:135–151
Panic B, Whyte J, Munro S (2003) The ARF-like GTPases Arl1p and Arll3p act in a pathway that interacts with vesicle-tethering factors at the Golgi apparatus. Curr Biol 13:405–410
Sheen J (2002) A transient expression assay using Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. http://genetics.mgh.harvard.edu/sheenweb/
Tsukuda M, Will E, Gallwitz D (1999) Structural and functional analysis of a novel coiled coil protein involved in Ypt6 GTPase-regulated protein transport in yeast. Mol Cell Biol 10:63–75
Waters M, Hughson F (2000) Membrane tethering in intracellular transport. Traffic 1:588–597
Waters M, Pfeffer S (1999) Membrane tethering and fusion in the secretory and endocytic pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:453–459
Acknowledgements
Paul R. Gilson and Claudia E. Vergara contributed equally to this work. We acknowledge the financial support of the Australian Research Council. We thank A.-C. Fitchette, Université de Rouen, for providing us with the anti-Lewis antigen antibody and thank Ross Waller and Tim Spurck, University of Melbourne, for assistance with confocal microscopy. We also thank Andrew Staehelin, University of Colorado, Boulder, for providing us with the α-Mannosidase I-GFP clone, Inhwan Hwang, Pohang University of Science and Technology, for the H+ATPase-GFP clone and Michael Goodin, University of California, Berkeley, for providing us with the pGD vectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilson, P.R., Vergara, C.E., Kjer-Nielsen, L. et al. Identification of a Golgi-localised GRIP domain protein from Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 219, 1050–1056 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1311-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1311-9