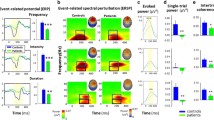
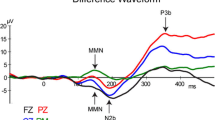
Abstract
Our sensory systems actively predict sensory information based on previously learnt patterns, which are continuously updated with information from the actual sensory input via prediction errors. Individuals with schizophrenia consistently show reduced auditory prediction errors as well as altered fractional anisotropy (indicative of white matter changes) in the arcuate fasciculus and the auditory interhemispheric pathway, both of which are auditory white matter pathways associated with prediction errors. However, it is not clear if healthy individuals with psychotic-like experiences exhibit similar deficits. Participants underwent electroencephalography (EEG) recordings while listening to a classical two-tone duration deviant oddball paradigm (n = 103) and a stochastic oddball paradigm (n = 89). A subset of participants (n = 89) also underwent diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Fractional anisotropy (FA), was extracted from the arcuate fasciculi and the auditory interhemispheric pathway. While prediction errors evoked by the classical oddball paradigm failed to reveal significant effects, the stochastic oddball paradigm elicited significant clusters at the typical mismatch negativity time window. Furthermore, we observed that FA of the arcuate fasciculi and auditory interhemispheric pathway significantly improved predictive models of psychotic-like experiences in healthy individuals over and above predictions made by auditory prediction error responses alone. Specifically, we observed that decreasing FA in the auditory interhemispheric pathway and reducing ability to learn stochastic irregularities are associated with increasing CAPE + scores. To the extent that these associations have previously been reported in patients with schizophrenia, the findings from this study suggest that both, auditory prediction errors and white matter changes in the auditory interhemispheric pathway, may have the potential to be translated into early screening markers for psychosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson JLR, Sotiropoulos SN (2016) An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 125:1063–1078
Atkinson RJ, Michie PT, Schall U (2012) Duration mismatch negativity and P3a in first-episode psychosis and individuals at ultra-high risk of psychosis. Biol Psychiatry 71:98–104
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571
Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA (1988) An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 56:893–897
Belger A, Yucel GH, Donkers FCL (2012) In search of psychosis biomarkers in high-risk populations: is the mismatch negativity the one we’ve been waiting for? Biol Psychiat 71:94–95
Berg P, Scherg M (1994) A multiple source approach to the correction of eye artifacts. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 90:229–241
Bodatsch M, Ruhrmann S, Wagner M, Muller R, Schultze-Lutter F, Frommann I, Brinkmeyer J, Gaebel W, Maier W, Klosterkotter J, Brockhaus-Dumke A (2011) Prediction of psychosis by mismatch negativity. Biol Psychiatry 69:959–966
Bodatsch M, Brockhaus-Dumke A, Klosterkotter J, Ruhrmann S (2015) Forecasting psychosis by event-related potentials-systematic review and specific meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry 77:951–958
Brainard DH (1997) The psychophysics toolbox. Spat Vis 10:433–436
Broyd SJ, Michie PT, Bruggemann J, van Hell HH, Greenwood LM, Croft RJ, Todd J, Lenroot R, Solowij N (2016) Schizotypy and auditory mismatch negativity in a non-clinical sample of young adults. Psychiatry Res 254:83–91
Catani M, Thiebaut de Schotten M (2008) A diffusion tensor imaging tractography atlas for virtual in vivo dissections. Cortex 44:1105–1132
Cheng CH, Hsu WY, Lin YY (2013) Effects of physiological aging on mismatch negativity: a meta-analysis. Int J Psychophysiol 90:165–171
Corlett P, Fletcher P (2012) The neurobiology of schizotypy: fronto-striatal prediction error signal correlates with delusion-like beliefs in healthy people. Neuropsychologia 50:3612–3620
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 9:179–194
Di Biase MA, Cropley VL, Baune BT, Olver J, Amminger GP, Phassouliotis C, Bousman C, McGorry PD, Everall I, Pantelis C, Zalesky A (2017) White matter connectivity disruptions in early and chronic schizophrenia. Psychol Med 47:1–14
Dima D, Frangou S, Burge L, Braeutigam S, James AC (2012) Abnormal intrinsic and extrinsic connectivity within the magnetic mismatch negativity brain network in schizophrenia: a preliminary study. Schizophr Res 135:23–27
Erickson MA, Ruffle A, Gold JM (2016) A meta-analysis of mismatch negativity in schizophrenia: from clinical risk to disease specificity and progression. Biol Psychiatry 79:980–987
Ettinger U, Mohr C, Gooding DC, Cohen AS, Rapp A, Haenschel C, Park S (2015) Cognition and brain function in schizotypy: a selective review. Schizophrenia Bull. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbu190
Fitzsimmons J, Schneiderman JS, Whitford TJ, Swisher T, Niznikiewicz MA, Pelavin PE, Terry DP, Mesholam-Gately RI, Seidman LJ, Goldstein JM, Kubicki M (2014) Cingulum bundle diffusivity and delusions of reference in first episode and chronic schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 224:124–132
Ford JM, Mathalon DH, Kalba S, Marsh L, Pfefferbaum A (2001) N1 and P300 abnormalities in patients with schizophrenia, epilepsy, and epilepsy with schizophrenialike features. Biol Psychiatry 49:848–860
Ford TC, Woods W, Crewther DP (2017) Spatio-temporal source cluster analysis reveals fronto-temporal auditory change processing differences within a shared autistic and schizotypal trait phenotype. NeuroImage Clin 16:383–389
Friedman JI, Tang C, Carpenter D, Buchsbaum M, Schmeidler J, Flanagan L, Golembo S, Kanellopoulou I, Ng J, Hof PR, Harvey PD, Tsopelas ND, Stewart D, Davis KL (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging findings in first-episode and chronic schizophrenia patients. Am J Psychiatry 165:1024–1032
Garrido MI, Friston KJ, Kiebel SJ, Stephan KE, Baldeweg T, Kilner JM (2008) The functional anatomy of the MMN: a DCM study of the roving paradigm. Neuroimage 42:936–944
Garrido MI, Sahani M, Dolan RJ (2013) Outlier responses reflect sensitivity to statistical structure in the human brain. PLoS Comput Biol 9:e1002999
Garrido MI, Teng CLJ, Taylor JA, Rowe EG, Mattingley JB (2016) Surprise responses in the human brain demonstrate statistical learning under high concurrent cognitive demand. Sci Learn 1:16006
Geoffroy PA, Houenou J, Duhamel A, Amad A, De Weijer AD, Curcic-Blake B, Linden DE, Thomas P, Jardri R (2014) The arcuate fasciculus in auditory-verbal hallucinations: a meta-analysis of diffusion-tensor-imaging studies. Schizophr Res 159:234–237
Greve DN, Fischl B (2009) Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary-based registration. Neuroimage 48:63–72
Haigh SM, Coffman BA, Salisbury DF (2016a) Mismatch negativity in first-episode schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Clin EEG Neurosci 48:3–10
Haigh SM, Coffman BA, Murphy TK, Butera CD, Salisbury DF (2016b) Abnormal auditory pattern perception in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 176:473–479
Horton J, Millar A, Labelle A, Knott VJ (2011) MMN responsivity to manipulations of frequency and duration deviants in chronic, clozapine-treated schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Res 126:202–211
Javitt DC, Grochowski S, Shelley AM, Ritter W (1998) Impaired mismatch negativity (MMN) generation in schizophrenia as a function of stimulus deviance, probability, and interstimulus/interdeviant interval. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 108:143–153
Jeurissen B, Tournier J-D, Dhollander T, Connelly A, Sijbers J (2014) Multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution for improved analysis of multi-shell diffusion MRI data. Neuroimage 103:411–426
Kawashima T, Nakamura M, Bouix S, Kubicki M, Salisbury DF, Westin CF, McCarley RW, Shenton ME (2009) Uncinate fasciculus abnormalities in recent onset schizophrenia and affective psychosis: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Schizophr Res 110:119–126
Kubicki M, Styner M, Bouix S, Gerig G, Markant D, Smith K, Kikinis R, McCarley R, Shenton M (2008) Reduced interhemispheric connectivity in schizophrenia-tractography based segmentation of the corpus callosum. Schizophr Res 106:125–131
Larsen KM, Morup M, Birknow MR, Fischer E, Hulme O, Vangkilde A, Schmock H, Baare WFC, Didriksen M, Olsen L, Werge T, Siebner HR, Garrido MI (2018) Altered auditory processing and effective connectivity in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Schizophr Res 197:328–336
Marques JP, Kober T, Krueger G, van der Zwaag W, Van de Moortele P-F, Gruetter R (2010) MP2RAGE, a self bias-field corrected sequence for improved segmentation and T1-mapping at high field. Neuroimage 49:1271–1281
McCarthy-Jones S, Oestreich LKL, Bank ASR, Whitford TJ (2015) Reduced integrity of the left arcuate fasciculus is specifically associated with hallucinations in the auditory verbal modality in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 162:1–6
Metzler-Baddeley C, Jones DK, Steventon J, Westacott L, Aggleton JP, O’Sullivan MJ (2012) Cingulum microstructure predicts cognitive control in older age and mild cognitive impairment. J Neurosci 32:17612–17619
Miller KM, Price CC, Okun MS, Montijo H, Bowers D (2009) Is the n-back task a valid neuropsychological measure for assessing working memory? Arch Clin Neuropsychol Off J Nat Acad Neuropsychol 24(7):711–717. https://doi.org/10.1093/arclin/acp063
Mossaheb N, Becker J, Schaefer MR, Klier CM, Schloegelhofer M, Papageorgiou K, Amminger GP (2012) The community assessment of psychic experience (CAPE) questionnaire as a screening-instrument in the detection of individuals at ultra-high risk for psychosis. Schizophr Res 141:210–214
Munoz Maniega S, Lymer GK, Bastin ME, Marjoram D, Job DE, Moorhead TW, Owens DG, Johnstone EC, McIntosh AM, Lawrie SM (2008) A diffusion tensor MRI study of white matter integrity in subjects at high genetic risk of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 106:132–139
Naatanen R (2000) The mismatch negativity as an index of the perception of speech sounds by the human brain. Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal Imeni I. M. Sechenova 86(11):1481–1501
Näätänen R (2014) The mismatch negativity (MMN)—a unitary biomarker for predicting schizophrenia onset. Int J Psychophysiol 94:120–120
Näätänen R, Shiga T, Asano S, Yabe H (2015) Mismatch negativity (MMN) deficiency: a break-through biomarker in predicting psychosis onset. Int J Psychophysiol 95:338–344
Nagai T, Tada M, Kirihara K, Yahata N, Hashimoto R, Araki T, Kasai K (2013) Auditory mismatch negativity and P3a in response to duration and frequency changes in the early stages of psychosis. Schizophr Res 150:547–554
Nelson MT, Seal ML, Phillips LJ, Merritt AH, Wilson R, Pantelis C (2011) An investigation of the relationship between cortical connectivity and schizotypy in the general population. J Nerv Ment Dis 199:348–353
Oestreich LK, Pasternak O, Shenton ME, Kubicki M, Gong X, McCarthy-Jones S, Whitford TJ (2016) Abnormal white matter microstructure and increased extracellular free-water in the cingulum bundle associated with delusions in chronic schizophrenia. NeuroImage Clin 12:405–414
Oestreich LKL, Randeniya R, Garrido MI (2018) White matter connectivity reductions in the pre-clinical continuum of psychosis: a connectome study. Hum Brain Mapp 40:529–537
Otten LJ, Alain C, Picton TW (2000) Effects of visual attentional load on auditory processing. NeuroReport 11:875–880
Pelli DG (1997) The VideoToolbox software for visual psychophysics: transforming numbers into movies. Spat Vis 10:437–442
Perez VB, Woods SW, Roach BJ, Ford JM, McGlashan TH, Srihari VH, Mathalon DH (2014) Automatic auditory processing deficits in schizophrenia and clinical high-risk patients: forecasting psychosis risk with mismatch negativity. Biol Psychiatry 75:459–469
Peter V, McArthur G, Thompson WF (2010) Effect of deviance direction and calculation method on duration and frequency mismatch negativity (MMN). Neurosci Lett 482:71–75
Peters BD, de Haan L, Dekker N, Blaas J, Becker HE, Dingemans PM, Akkerman EM, Majoie CB, van Amelsvoort T, den Heeten GJ, Linszen DH (2008) White matter fibertracking in first-episode schizophrenia, schizoaffective patients and subjects at ultra-high risk of psychosis. Neuropsychobiology 58:19–28
Qiu Y, Tang Y, Chan RCK, Sun X, He J (2014) P300 Aberration in first-episode schizophrenia patients: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 9:e97794
Rissling AJ, Park SH, Young JW, Rissling MB, Sugar CA, Sprock J, Mathias DJ, Pela M, Sharp RF, Braff DL, Light GA (2013) Demand and modality of directed attention modulate “pre-attentive” sensory processes in schizophrenia patients and nonpsychiatric controls. Schizophr Res 146:326–335
Rossell SL, Shapleske J, Fukuda R, Woodruff PW, Simmons A, David AS (2001) Corpus callosum area and functioning in schizophrenic patients with auditory–verbal hallucinations. Schizophr Res 50:9–17
Salisbury DF, McCathern AG (2016) Abnormal complex auditory pattern analysis in schizophrenia reflected in an absent missing stimulus mismatch negativity. Brain Topogr 29:867–874
Salisbury DF, Polizzotto NR, Nestor PG, Haigh SM, Koehler J, McCarley RW (2016) Pitch and duration mismatch negativity and premorbid intellect in the first hospitalized schizophrenia spectrum. Schizophr Bull 43:407–416
Sams M, Paavilainen P, Alho K, Näätänen R (1985) Auditory frequency discrimination and event-related potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 62:437–448
Shaikh M, Valmaggia L, Broome MR, Dutt A, Lappin J, Day F, Woolley J, Tabraham P, Walshe M, Johns L, Fusar-Poli P, Howes O, Murray RM, McGuire P, Bramon E (2012) Reduced mismatch negativity predates the onset of psychosis. Schizophr Res 134:42–48
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, De Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy RK, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, De Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S208–219
Smith RE, Tournier JD, Calamante F, Connelly A (2015) SIFT2: enabling dense quantitative assessment of brain white matter connectivity using streamlines tractography. Neuroimage 119:338–351
Solis-Vivanco R, Mondragon-Maya A, Leon-Ortiz P, Rodriguez-Agudelo Y, Cadenhead KS, de la Fuente-Sandoval C (2014) Mismatch Negativity reduction in the left cortical regions in first-episode psychosis and in individuals at ultra high-risk for psychosis. Schizophr Res 158:58–63
Stefanis NC, Hanssen M, Smirnis NK, Avramopoulos DA, Evdokimidis IK, Stefanis CN, Verdoux H, Van Os J (2002) Evidence that three dimensions of psychosis have a distribution in the general population. Psychol Med 32:347–358
Steinmann S, Leicht G, Mulert C (2014) Interhemispheric auditory connectivity: structure and function related to auditory verbal hallucinations. Front Hum Neurosci 8:55
Sur S, Sinha VK (2009) Event-related potential: an overview. Ind Psychiatry J 18:70–73
Sweet LH (2011) N-Back Paradigm. In: Kreutzer JS, DeLuca J, Caplan B (eds) Encyclopedia of clinical neuropsychology. Springer, New York, pp 1718–1719
Todd J, Michie PT, Schall U, Karayanidis F, Yabe H, Näätänen R (2008) Deviant matters: duration, frequency, and intensity deviants reveal different patterns of mismatch negativity reduction in early and late schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 63:58–64
Tournier JD, Calamante F, Connelly A (2012) MRtrix: diffusion tractography in crossing fiber regions. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 22:53–66
Wager TD, Keller MC, Lacey SC, Jonides J (2005) Increased sensitivity in neuroimaging analyses using robust regression. Neuroimage 26:99–113
Whitford TJ, Lee SW, Oh JS, de Luis-Garcia R, Savadjiev P, Alvarado JL, Westin CF, Niznikiewicz M, Nestor PG, McCarley RW, Kubicki M, Shenton ME (2014) Localized abnormalities in the cingulum bundle in patients with schizophrenia: a diffusion tensor tractography study. NeuroImage Clin 5:93–99
Wigand M, Kubicki M, Clemm von Hohenberg C, Leicht G, Karch S, Eckbo R, Pelavin PE, Hawley K, Rujescu D, Bouix S, Shenton ME, Mulert C (2015) Auditory verbal hallucinations and the interhemispheric auditory pathway in chronic schizophrenia. World J Biol Psychiatry 16:31–44
Winterer G, Egan MF, Raedler T, Sanchez C, Jones DW, Coppola R, Weinberger DR (2003) P300 and genetic risk for schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:1158–1167
Woodruff PW (2004) Auditory hallucinations: insights and questions from neuroimaging. Cogn Neuropsychiatry 9:73–91
Zhang Y, Brady M, Smith S (2001) Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:45–57
Acknowledgements
We thank John McGrath for helpful discussions; David Lloyd, Elise Rowe for support in EEG data acquisition. Aiman Al-Najjar and Nicole Atcheson for assisting in MRI data collection, and all participants for their time. M.I.G. was supported by a UQ Fellowship (2016000071), a UQ Foundation Research Excellence Award (2016001844), and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Integrative Brain Function (ARC CE140100007). R.R. was supported through a UQ International Research Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
L.K.L. Oestreich and R. Randeniya are co-first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oestreich, L.K.L., Randeniya, R. & Garrido, M.I. Auditory prediction errors and auditory white matter microstructure associated with psychotic-like experiences in healthy individuals. Brain Struct Funct 224, 3277–3289 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01972-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01972-z