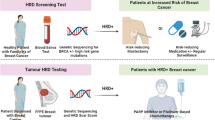
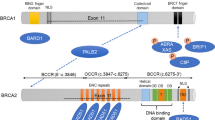
Abstract
Purpose
Few and small studies have been reported about multigene testing usage by massively parallel sequencing in European cancer families. There is an open debate about what genes should be tested, and the actionability of some included genes is under research.
Methods
We investigated a panel of 34 known high/moderate-risk cancer genes, including 16 related to breast or ovarian cancer (BC/OC) genes, and 63 candidate genes to BC/OC in 192 clinically suspicious of hereditary breast/ovarian cancer (HBOC) Spanish families without pathogenic variants in BRCA1 or BRCA2 (BRCA1/2).
Results
We identified 16 patients who carried a high- or moderate-risk pathogenic variant in eight genes: 4 PALB2, 3 ATM, 2 RAD51D, 2 TP53, 2 APC, 1 BRIP1, 1 PTEN and 1 PMS2. These findings led to increased surveillance or prevention options in 12 patients and predictive testing in their family members. We detected 383 unique variants of uncertain significance in known cancer genes, of which 35 were prioritized in silico. Eighteen loss-of-function variants were detected in candidate BC/OC genes in 17 patients (1 BARD1, 1 ERCC3, 1 ERCC5, 2 FANCE, 1 FANCI, 2 FANCL, 1 FANCM, 1 MCPH1, 1 PPM1D, 2 RBBP8, 3 RECQL4 and 1 with SLX4 and XRCC2), three of which also carry pathogenic variants in known cancer genes.
Conclusions
Eight percent of the BRCA1/2 negative patients carry pathogenic variants in other actionable genes. The multigene panel usage improves the diagnostic yield in HBOC testing and it is an effective tool to identify potentially new candidate genes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balmaña J, Balaguer F, Cervantes A, Arnold D (2013) Familial risk-colorectal cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines. Ann Oncol 24:vi73–vi80. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt209
Borràs E, Pineda M, Cadiñanos J et al (2013) Refining the role of pms2 in Lynch syndrome: germline mutational analysis improved by comprehensive assessment of variants. J Med Genet 50:552–563. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101511
Bouaoun L, Sonkin D, Ardin M et al (2016) TP53 variations in human cancers: new lessons from the IARC TP53 database and genomics data. Hum Mutat 37:865–876. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23035
Buys SS, Sandbach JF, Gammon A et al (2017) A study of over 35,000 women with breast cancer tested with a 25-gene panel of hereditary cancer genes. Cancer 123:1721–1730. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30498
Cardoso M, Paulo P, Maia S, Teixeira MR (2016) Truncating and missense PPM1D mutations in early-onset and/or familial/hereditary prostate cancer patients. Genes Chromosom Cancer 55:954–961. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22393
Castéra L, Krieger S, Rousselin A et al (2014) Next-generation sequencing for the diagnosis of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer using genomic capture targeting multiple candidate genes. Eur J Hum Genet 22:1305–1313. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.16
Chinnadurai G (2006) CtIP, a candidate tumor susceptibility gene is a team player with luminaries. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1765:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2005.09.002
Couch FJ, Shimelis H, Hu C et al (2017) Associations between cancer predisposition testing panel genes and breast cancer. JAMA Oncol 3:1190–1196. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0424
Duran-Lozano L, Montalban G, Bonache S et al (2018) Alternative transcript imbalance underlying breast cancer susceptibility in a family carrying PALB2 c.3201+5G>T. Breast Cancer Res Treat (under second revision)
Easton DF, Pharoah P, Antoniou AC et al (2015) Gene-panel sequencing and the prediction of breast-cancer risk. N Engl J Med 372:2243–2257. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3121
Easton DF, Lesueur F, Decker B et al (2016) No evidence that protein truncating variants in BRIP1 are associated with breast cancer risk: implications for gene panel testing. J Med Genet 53:298–309. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103529
Eliade M, Skrzypski J, Baurand A et al (2017) The transfer of multigene panel testing for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer to healthcare: what are the implications for the management of patients and families ? Oncotarget 8:1957–1971. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12699
Espenschied CR, LaDuca H, Li S et al (2017) Multigene panel testing provides a new perspective on lynch syndrome. J Clin Oncol 35:2568–2575. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.71.9260
Esteban I, Vilaró M, Adrover E et al (2018) Psychological impact of multigene cancer panel testing in patients with a clinical suspicion of hereditary cancer across Spain. Psychooncology 27(6):1530–1537. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.4686
Esteban-Jurado C, Franch-Expósito S, Muñoz J et al (2016) The Fanconi anemia DNA damage repair pathway in the spotlight for germline predisposition to colorectal cancer. Eur J Hum Genet 24:1501–1505. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.44
Fachal L, Dunning AM (2015) From candidate gene studies to GWAS and post-GWAS analyses in breast cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 30:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2015.01.004
Feliubadaló L, Tonda R, Gausachs M et al (2017) Benchmarking of whole exome sequencing and ad hoc designed panels for genetic testing of hereditary cancer. Sci Rep 7:37984. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37984
Frey MK, Sandler G, Sobolev R et al (2017) Multigene panels in Ashkenazi Jewish patients yield high rates of actionable mutations in multiple non-BRCA cancer-associated genes. Gynecol Oncol 146:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.04.009
Fu W, Ligabue A, Rogers KJ et al (2017) Human RECQ helicase pathogenic variants, population variation and “Missing” diseases. Hum Mutat 38:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23148
Gutiérrez-Enríquez S, Bonache S, Ruíz De Garibay G et al (2014) About 1% of the breast and ovarian Spanish families testing negative for BRCA1 and BRCA2 are carriers of RAD51D pathogenic variants. Int J Cancer 134:2088–2097. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28540
Han FF, Guo CL, Liu LH (2013) The effect of CHEK2 variant I157T on cancer susceptibility: evidence from a meta-analysis. DNA Cell Biol 32:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2013.1970
Kraus C, Hoyer J, Vasileiou G et al (2017) Gene panel sequencing in familial breast/ovarian cancer patients identifies multiple novel mutations also in genes others than BRCA1/2. Int J Cancer 140:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30428
Kurian AW, Hughes E, Handorf EA et al (2017) Breast and ovarian cancer penetrance estimates derived from germline multiple-gene sequencing results in women. JCO Precis Oncol 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO.16.00066
Leshno A, Shapira S, Liberman E et al (2016) The APC I1307K allele conveys a significant increased risk for cancer. Int J Cancer 138:1361–1367. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29876
Lhota F, Zemankova P, Kleiblova P et al (2016) Hereditary truncating mutations of DNA repair and other genes in BRCA1/BRCA2/PALB2-negatively tested breast cancer patients. Clin Genet 90:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12748
Liang J, Lin C, Hu F et al (2013) APC polymorphisms and the risk of colorectal neoplasia: a huge review and meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol 177:1169–1179. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kws382
Lipton L, Tomlinson I (2004) The multiple colorectal adenoma phenotype and MYH, a excision repair gene. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:633–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00286-1
Llort G, Chirivella I, Morales R et al (2015) SEOM clinical guidelines in Hereditary Breast and ovarian cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 17:956–961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1435-3
Mantere T, Winqvist R, Kauppila S et al (2016) Targeted next-generation sequencing identifies a recurrent mutation in MCPH1 associating with hereditary breast cancer susceptibility. PLoS Genet 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005816
Nakonechny QB, Gilks CB (2016) Ovarian cancer in hereditary cancer susceptibility syndromes. Surg Pathol Clin 9:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.path.2016.01.003
Nielsen M, Morreau H, Vasen HF, Hes FJ (2011) MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP). Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 79:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2010.05.011
Paluch-Shimon S, Cardoso F, Sessa C et al (2016) Prevention and screening in BRCA mutation carriers and other breast/ovarian hereditary cancer syndromes: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for cancer prevention and screening. Ann Oncol 27:v103–v110. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw327
Pharoah PDP, Song H, Dicks E et al (2016) PPM1D mosaic truncating variants in ovarian cancer cases may be treatment-related somatic mutations. J Natl Cancer Inst 108:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv347
Rafnar T, Gudbjartsson DF, Sulem P et al (2011) Mutations in BRIP1 confer high risk of ovarian cancer. Nat Genet 43:1104–1107. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.955
Ramus SJ, Song H, Dicks E et al (2015) Germline mutations in the BRIP1, BARD1, PALB2, and NBN genes in women with ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 107:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv214
Rana HQ, Gelman R, LaDuca H et al (2018) Differences in TP53 mutation carrier phenotypes emerge from panel-based testing. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst 110:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djy001
Ruark E, Snape K, Humburg P et al (2013) Mosaic PPM1D mutations are associated with predisposition to breast and ovarian cancer. Nature 493:406–410. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11725
Schroeder C, Faust U, Sturm M et al (2015) HBOC multi-gene panel testing: comparison of two sequencing centers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 152:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3429-9
Slavin TP, Maxwell KN, Lilyquist J et al (2017) The contribution of pathogenic variants in breast cancer susceptibility genes to familial breast cancer risk. NPJ Breast Cancer 9:22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41523-017-0024-8
Suhasini AN, Brosh RMJ (2013) DNA helicases associated with genetic instability, cancer, and aging. Adv Exp Med Biol 767:123–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5037-5
Susswein LR, Marshall ML, Nusbaum R et al (2016) Pathogenic and likely pathogenic variant prevalence among the first 10,000 patients referred for next-generation cancer panel testing. Genet Med 18:823–832. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.166
Tavera-Tapia A, Pérez-Cabornero L, Macías JA et al (2017) Almost 2% of Spanish breast cancer families are associated to germline pathogenic mutations in the ATM gene. Breast Cancer Res Treat 161:597–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-4058-7
Tedaldi G, Tebaldi M, Zampiga V et al (2017) Multiple-gene panel analysis in a case series of 255 women with hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 8:47064–47075. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16791
Ten Broeke SW, Brohet RM, Tops CM et al (2015) Lynch syndrome caused by germline PMS2 mutations: delineating the cancer risk. J Clin Oncol 33:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.57.8088
Tinat J, Bougeard G, Baert-Desurmont S et al (2009) 2009 version of the Chompret criteria for Li Fraumeni Syndrome. J Clin Oncol 27:108–109. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.22.7967
Tung N, Domchek SM, Stadler Z et al (2016) Counselling framework for moderate-penetrance cancer-susceptibility mutations. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 13:581–588. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.90
Villani A, Shore A, Wasserman JD et al (2016) Biochemical and imaging surveillance in germline TP53 mutation carriers with Li–Fraumeni syndrome: 11 year follow-up of a prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 17:1295–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30249-2
Win AK, Reece JC, Dowty JG et al (2016) Risk of extracolonic cancers for people with biallelic and monoallelic mutations in MUTYH. Int J Cancer 139:1557–1563. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30197
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Cellex Foundation for providing research facilities and equipment.
Funding
This work was supported by Spanish Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII) funding, an initiative of the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Innovation partially supported by European Regional Development FEDER Funds: FIS PI12/02585 and PI15/00355 (to O Diez), PI13/01711 and PI16/01218 (to S. Gutiérrez-Enríquez). S. Gutiérrez-Enríquez and S. Bonache are supported by the Miguel Servet Progam (CPII16/00034) and AECC contract, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent, approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Vall d’Hebron Hospital from Barcelona, was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonache, S., Esteban, I., Moles-Fernández, A. et al. Multigene panel testing beyond BRCA1/2 in breast/ovarian cancer Spanish families and clinical actionability of findings. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144, 2495–2513 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2763-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2763-9