Abstract
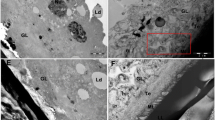
The aim of the present work was to evaluate the in vitro efficacy of the flubendazole (FLBZ) and ivermectin (IVM) combination against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces and metacestodes. Protoscoleces and groups of ten peritoneal cysts obtained from BALB/c mice were incubated with the two drugs, either separately or in combination, at the following final concentrations: 10 µg/mL FLBZ, 1 µg/mL FLBZ, 1 µg/mL IVM, 10 µg/mL FLBZ + 1 µg/mL IVM, and 1 µg/mL FLBZ + 1 µg/mL IVM. The maximum protoscolicidal effect was found with the combination 10 µg/mL FLBZ + 1 µg/mL IMV. After 1 day of incubation, the presence of numerous blebs in the tegument of protoscoleces was observed. Ultrastructural studies revealed that the primary site of damage was the tegument of the parasite. The effect of the two drugs on hydatid cysts obtained from mice was more rapidly detected in cysts treated with the combination of FLBZ + IVM than when drugs were used separately. Ultrastructural studies revealed that the germinal layer of treated cysts lost the multicellular structure feature and underwent considerable degenerative changes after in vitro treatment. The outcomes obtained demonstrated the favorable effect of the combination of FLBZ and IVM against E. granulosus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez L, Lifschitz A, Entrocasso C, Manazza J, Mottier L, Borda B, Virkel G, Lanusse C (2008) Understanding the pharmacokinetic interaction between ivermectin and albendazole following their combined use in lambs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 31:230–239
Bekhti A, Schaaps JP, Capron M, Dessaint JP, Santoro F, Capron A (1977) Treatment of hepatic hydatid disease with mebedazole: preliminary results in four cases. Br Med J 2:1047–1051
Campbell WC, Fisher MH, Stapley EO, Albers-Schonberg G, Jacob TA (1983) Ivermectin: a potent new antiparasitic agent. Science 221:823–828
Casado N, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F, Jiménez A, Criado A, De Armas C (1989) In vitro effects of levamisol and ivermectin against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces. Int J Parasitol 19:945–947
Casado N, Pérez Serrano J, Denegri G, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (1996) Development of a chemotherapeutic model for in vitro drug screening in Echinococcus granulosus cysts: assessment of the effects of albendazole and albendazole sulphoxide combination-therapy. Int J Parasitol 26:59–65
Casado N, Moreno MJ, Urrea-París MA, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (2002) Could ivermectin have a synergic effect with albendazole in hydatidosis therapy? 1. In vitro studies. Parasitol Res 88:153–159
Ceballos L, Álvarez L, Sánchez Bruni S, Elissondo C, Dopchiz M, Denegri G, Torrado J, Lanusse C (2006) Development of a cyclodextrin-based flubendazole formulation to control secondary echinococcosis: pharmacokinetics, hydatid cyst morphology and efficacy in mice. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 29:85–86
Chinnery JB, Morris DL (1986) Effect of albendazole sulphoxide on viability of hydatid protoscoleces in vitro. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 80:815–817
Cobo F, Yarnoz C, Sesma B, Fraile P, Aizcorbe M, Trujillo R (1998) Albendazole plus praziquantel versus albendazole alone as a pre-operative treatment in intra-abdominal hydatidosis caused by Echinococcus granulosus. Trop Med Int Health 3:462–466
Eckert J, Deplazes P (2004) Biological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects of echinococcosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:107–135
Elissondo MC, Dopchiz MC, Brasesco M, Denegri G (2004) Echinococcus granulosus: first report of microcysts formation from protoscoleces of cattle origin using the in vitro vesicular culture technique. Parasite 11:415–418
Elissondo MC, Dopchiz MC, Ceballos L, Alvarez L, Sánchez Bruni S, Lanusse C, Denegri G (2006) In vitro effects of flubendazole on Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces. Parasitol Res 98:317–323
Elissondo MC, Ceballos L, Dopchiz MC, Andresiuk MV, Alvarez L, Sánchez Bruni S, Lanusse C, Denegri G (2007) In vitro and in vivo effects of flubendazole on Echinococcus granulosus metacestodes. Parasitol Res 100:1003–1009
Fink E, Porras A (1989) Pharmacokinetics of ivermectin in animal and humans. In: Campbell W (ed) Ivermectin and abamectin. Springer, New York, pp 113–130
Kern P (2003) Echinococcus granulosus infection: clinical presentation, medical treatment and outcome. Langenbecks Arch Surg 388:413–420
Kern P (2006) Medical treatment of echinococcosis under the guidance of Good Clinical Practice (GCP/ICH). Parasitol Int 55:273–282
Martínez J, Pérez-Serrano J, Bernardina WE, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (1999) Echinococcus granulosus: in vitro effects of ivermectin and praziquantel on HSP60 and HSP70 levels. Exp Parasitol 93:171–180
McKellar Q, Benchaoui H (1996) Avermectins and milbemycins. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 19:331–351
Morris DL, Dykes PW, Dickson B, Marriner SE, Bogan JA, Burrows FG (1983) Albendazole in hydatid disease. Br Med J 286:103–104
Morris DL, Chinnery JB, Ubhi C (1987) A comparison of the effects al albendazole, its sulphone metabolite, and mebendazole on the viability of protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus in an in vitro culture system. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 81:804–806
Pérez Serrano J, Casado N, Denegri G, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (1994) The effects of albendazole and albendazole sulphoxide combination- therapy on Echinococcus granulosus in vitro. Int J Parasitol 24:219–224
Pérez-Serrano J, Denegri G, Casado N, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (1997) Treatment of experimental echinococcosis with albendazole and albendazole sulphoxide. Int J Parasitol 27:1341–1345
Pérez-Serrano J, Grossman C, Urrea-París MA, Denegri G, Casado N, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (2001) Depolarization of the tegument precedes morphological alterations in Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces incubated with ivermectin. Parasitol Res 87:804–807
Schantz PM, van den Bossche H, Eckert J (1982) Chemotherapy for larval 235 echinococcosis in animals and humans: report of a workshop. Z Parasitenkd 67:5–26
Urrea-Paris MA, Moreno MJ, Casado N, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (1999) Echinococcus granulosus: praziquantel treatment against the metacestode stage. Parasitol Res 85:999–1006
Urrea-Paris MA, Moreno MJ, Casado N, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (2000) In vitro effect of praziquantel and albendazole combination therapy of the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitol Res 86:957–964
Urrea-Paris MA, Moreno MJ, Casado N, Rodríguez-Caabeiro F (2002) Relationship between the efficacy of praziquantel treatment and the cystic differentiation in vivo of Echinococcus granulosus metacestode. Parasitol Res 88:26–31
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. Leo Van Leemput and Dr. Kathleen Vlaminck (Janssen Animal Health, Beerse, Belgium) and Dr. Gustavo Viana (Janssen, Buenos Aires, Argentina) for providing the FLBZ used in the present experimental work and for their critical review of this manuscript. The help of Dr. González and Sr. Chasma is gratefully appreciated. This work was supported by the PICT 02 No. 01-12535, BID 1201/OC-AR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elissondo, M.C., Ceballos, L., Alvarez, L. et al. Flubendazole and ivermectin in vitro combination therapy produces a marked effect on Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces and metacestodes. Parasitol Res 105, 835–842 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1469-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1469-y