Abstract
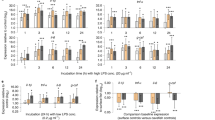
While parasites are likely to encounter several potential intermediate hosts in natural communities, a parasite’s actual range of compatible hosts is limited by numerous biological factors ranging from behaviour to immunology. In crustaceans, two major components of immunity are haemocytes and the prophenoloxidase system involved in the melanisation of foreign particles. Here, we analysed metazoan parasite prevalence and loads in the two sympatric crab species Hemigrapsus crenulatus and Macrophthalmus hirtipes at two sites. In parallel, we analysed the variation in haemocyte concentration and amount of circulating phenoloxidase (PO) in the haemolymph of the same individuals in an attempt to (a) explain differences in parasite prevalence and loads in the two species at two sites and (b) assess the impact of parasites on these immune parameters. M. hirtipes harboured more parasites but also exhibited higher haemocyte concentrations than H. crenulatus independent of the study site. Thus, higher investment in haemocyte production for M. hirtipes does not seem to result in higher resistance to parasites. Analyses of variation in immune parameters for the two crab species between the two sites that differed in parasite prevalence showed common trends. (a) In general, haemocyte concentrations were higher at the site experiencing higher parasitic pressure while circulating PO activity was lower and (b) haemocyte concentrations were influenced by microphallid trematode metacercariae in individuals from the site with higher parasitic pressure. We suggest that the higher haemocyte concentrations observed in both crab species exposed to higher parasitic pressure may represent an adaptive response to the impact of parasites on this immune parameter.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson ML, Caira JN (1994) Evolutionary factors influencing the nature of parasite specificity. Parasitology 109:S85–S95
Brockerhoff AM, Smales LR (2002) Profilicolllis novaezelandensis n. sp. (Polymorphidae) and two other acanthocephalan parasites from shore birds (Haematopodidae and Scolopacidae) in New Zealand, with records of two species in intertidal crabs (Decapoda: Grapsidae and Ocypodidae). Syst Parasitol 52:55–65
Bryan-Walker K, Leung TLF, Poulin R (2007) Local adaptation of immunity against a trematode parasite in marine amphipod populations. Mar Biol 152:687–695
Cerenius L, Söderhäll K (2004) The prophenoloxidase-activating system in invertebrates. Immunol Rev 198:116–126
Cerenius L, Lee BL, Söderhäll K (2008) The proPO-System: pros and cons for its role in invertebrate immunity. Trends Immunol 29:263–271
Cerenius L, Babu R, Söderhäll K, Jiravanichpaisal P (2010) In vitro effects on bacterial growth of phenoloxidase reaction products. J Invertebr Pathol 103:21–23
Chisholm JRS, Smith VJ (1992) Antibacterial activity in the haemocytes of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 72:529–542
Combes C (2001) Parasitism. The ecology and evolution of intimate interactions. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Cornet S, Biard C, Moret Y (2009) Variation in immune defence among populations of Gammarus pulex (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Oecologia 159:257–269
Damian RT (1997) Parasite immune evasion and exploitiation: reflections and projections. Parasitology 115:S169–S175
Destoumieux D, Bulet P, Loew D, Van Dorsselaer A, Rodriguez G, Bachère E (1997) Penaeidins, a new family of antimicrobial peptides isolated from the shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Decapoda). J Biol Chem 272:28398–28406
Destoumieux D, Muñoz M, Cosseau C, Rodriguez J, Bulet P, Comps M, Bachère E (2000) Penaeidins, antimicrobial peptides with chitin-binding activity, are produced and stored in shrimp granulocytes and released after microbial challenge. J Cell Sci 113:461–469
Euzet L, Combes C (1980) Les problèmes de l’espèce chez les animaux parasites. In: Boquet C, Genermont J, Lamotte M (eds) Les problèmes de l’espèce dans le règne animal. Tome III. Mémoires de la Société Zoologique Française 40:239–285
Fagutao FF, Koyama T, Kaizu A, Saito-Taki T, Kondo H, Aoki T, Hirono I (2009) Increased bacterial load in the shrimp hemolymph in the absence of prophenoloxidase. FEBS J 276:5298–5306
Fredensborg BL, Poulin R (2006) Parasitism shaping host life-history evolution: adaptive responses in a marine gastropod to infection by trematodes. J Anim Ecol 75:44–53
Fredensborg BL, Mouritsen KN, Poulin R (2004) Intensity-dependent mortality of Paracalliope novizealandiae (Amphipoda: Crustacea) infected by a trematode: experimental infections and field observations. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 311:253–265
Galaktionov KV, Malkova II, Irwin SWB, Saville DH, Maguire JG (1996) Developmental changes in the tegument of four microphallid metacercariae in their second (crustacean) intermediate hosts. J Helminthol 70:201–210
Hose JE, Martin GG, Gerard AS (1990) A decapod hemocyte classification scheme integrating morphology, cytochemistry and function. Biol Bull 178:33–45
Jaenicke E, Fraune S, May S, Irmak P, Augustin R, Meesters C, Decker H, Zimmer M (2009) Is activated hemocyanin instead of phenoloxidase involved in immune response in woodlice? Dev Comp Immunol 33:1055–1063
Jiravanichpaisal P, Lee BL, Söderhäll K (2006) Cell-mediated immunity in arthropods: hematopoiesis, coagulation, melanisation and opsonization. Immunobiology 211:213–236
Keeney DB, Waters JM, Poulin R (2007) Diversity of trematode genetic clones within amphipods and the timing of same-clone infections. Int J Parasitol 37:351–357
Kitaura J, Wada K, Nishida M (2002) Molecular phylogeny of grapsoid and ocypodoid crabs with special reference to the genera Metaplax and Macrophthalmus. J Crustac Biol 22:682–693
Koehler AV, Poulin R (2010) Host partitioning by parasites in an intertidal crustacean community. J Parasitol 96:862–868
Kostadinova A, Mavrodieva RS (2005) Microphallids in Gammarus insensibilis Stock, 1966 from a Black Sea lagoon: host response to infection. Parasitology 131:347–354
Latham ADM, Poulin R (2002a) Effect of acanthocephalan parasites on hiding behaviour in two species of shore crabs. J Helminthol 76:323–326
Latham ADM, Poulin R (2002b) Field evidence of the impact of two acanthocephalan parasites on the mortality of three species of New Zealand shore crabs (Brachyura). Mar Biol 141:1131–1139
Liu H, Jiravanichpaisal P, Cerenius L, Lee BL, Söderhäll I, Söderhäll K (2007) Phenoloxidase is an important component of the defense against Aeromonas hydrophila infection in a crustacean, Pacifastacus leniusculus. J Biol Chem 282:33593–33598
Lochmiller RL, Deerenberg C (2000) Trade-offs in evolutionary immunology: just what is the cost of immunity? Oikos 88:87–98
Matozzo V, Marin MG (2010) The role of haemocytes from the crab Carcinus aestuarii (Crustacea, Decapoda) in immune responses: a first survey. Fish Shellfish Immunol 28:534–541
Moravec F, Fredensborg BL, Latham ADM, Poulin R (2003) Larval Spirurida (Nematoda) from the crab Macrophthalmus hirtipes in New Zealand. Folia Parasitol 50:109–114
Perdomo-Morales R, Montero-Alejo V, Perera E, Pardo-Ruiz Z, Alonso-Jiménez E (2008) Hemocyanin-derived phenoloxidase activity in the spiny lobster Panulirus argus (Latreille, 1804). Biochim Biophys Acta 1780:652–658
Poulin R, Mouritsen KN (2006) Climate change, parasitism and the structure of intertidal ecosystems. J Helminthol 80:183–191
Schmid-Hempel P (2003) Variation in immune defence as a question of evolutionary ecology. Proc R Soc Lond B 270:357–366
Schmid-Hempel P (2008) Parasite immune evasion: a momentous molecular war. Trends Ecol Evol 23:318–326
Schnapp D, Kemp GD, Smith VJ (1996) Purification and characterization of a proline-rich antibacterial peptide, with sequence similarity to bactenecin-7, from the haemocytes of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. Eur J Biochem 240:532–539
Sheldon BC, Verhulst S (1996) Ecological immunology: costly parasite defences and trade-offs in evolutionary ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 11:317–321
Söderhäll K (1983) β-1,3 glucan enhancement of protease activity in crayfish hemocyte lysate. Comp Biochem Physiol B 74:221–224
Söderhäll K, Cerenius L (1998) Role of the prophenoloxidase-activating system in invertebrate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 10:23–28
Thomas F, Renaud F, de Meeûs T, Poulin R (1998) Manipulation of host behaviour by parasites: ecosystem engineering in the intertidal zone? Proc R Soc B 265:1091–1096
Thomas F, Poulin R, de Meeüs T, Guégan J-F, Renaud F (1999) Parasites and ecosystem engineering: what roles could they play? Oikos 84:167–171
Thomas F, Guldner E, Renaud F (2000) Differential parasite (Trematoda) encapsulation in Gammarus aequicauda (Amphipoda). J Parasitol 86:650–654
Vazquez L, Alpuche J, Maldonado G, Agundis C, Pereyra-Morales A, Zenteno E (2009) Immunity mechanisms in crustaceans. Innate Immun 15:179–188
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the entire parasitology research group at the University of Otago; Karen Judge for providing equipment; Charlotte Seifert for assistance during field work and Jean-Baptiste Ferdy as well as Ning Liu for help with the programming in R. This project was funded by the Erasmus Mundus Program “European Master in Applied Ecology” (EMAE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dittmer, J., Koehler, A.V., Richard, FJ. et al. Variation of parasite load and immune parameters in two species of New Zealand shore crabs. Parasitol Res 109, 759–767 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2319-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2319-2