Abstract
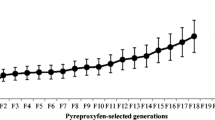
Imidacloprid, a neonicotinoid insecticide, has been used frequently for the management of Musca domestica L., (Diptera: Muscidae) worldwide. To design the strategy for resistance management, life history traits were established for imidacloprid-resistant, susceptible counterpart, and reciprocal crosses M. domestica strains based on laboratory observations. Bioassay results showed that the imidacloprid-selected strain developed a resistance ratio of 106-fold to imidacloprid, 19-fold to nitenpyram, 29-fold to chlorpyrifos, and 3.8-fold to cypermethrin compared to that of the susceptible counterpart strain. The imidacloprid-selected strain showed very low cross-resistance against nitenpyram and cypermethrin and a lack of cross-resistance to chlorpyrifos. Resistance to imidacloprid, nitenpyram, and chlorpyrifos was unstable, while resistance to cypermethrin was stable in Imida-SEL strain of M. domestica. The imidacloprid-selected strain had a relative fitness of 0.61 and lower fecundity, hatchability, number of next-generation larvae, and net reproductive rate compared with the susceptible counterpart strain. Mean population growth rates, such as intrinsic rate of population increase and biotic potential, were lower for the imidacloprid-selected strain compared with the susceptible counterpart strain. Development of resistance can cost considerable fitness for the imidacloprid-selected strain. The present study provided useful information for making potential management strategies to overcome development of resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas N, Shad SA, Razaq M (2012) Fitness cost, cross resistance and realized heritability of resistance to imidacloprid in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pestic Biochem Physiol 103:181–188
Abbas N, Khan HAA, Shad SA (2014a) Cross-resistance, genetics, and realized heritability of resistance to fipronil in the house fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae): a potential vector for disease transmission. Parasitol Res 113:1343–1352
Abbas N, Khan HAA, Shad SA (2014b) Resistance of the house fly Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) to lambda-cyhalothrin: mode of inheritance, realized heritability, and cross-resistance to other insecticides. Ecotoxicology 23:791–801
Abbas N, Shad SA, Razaq M, Waheed A, Aslam M (2014c) Resistance of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to profenofos: relative fitness and cross resistance. Crop Prot 58:49–54
Abbott W (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Acevedo GR, Zapater M, Toloza AC (2009) Insecticide resistance of house fly, Musca domestica (L.) from Argentina. Parasitol Res 105:489–493
Alyokhin A, Dively G, Patterson M, Castaldo C, Rogers D, Mahoney M, Wollam J (2007) Resistance and cross-resistance to imidacloprid and thiamethoxam in the Colorado potato beetle Leptinotarsa decemlineata. Pest Manag Sci 63:32–41
Anonymous (2005) Statistix for Windows. Analytical Software, Tallahassee
Basit M, Sayyed AH, Saleem MA, Saeed S (2011) Cross-resistance, inheritance and stability of resistance to acetamiprid in cotton whitefly, Bemisia tabaci Genn (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Crop Prot 30:705–712
Bell HA, Robinson KA, Weaver RJ (2010) First report of cyromazine resistance in a population of UK house fly (Musca domestica) associated with intensive livestock production. Pest Manag Sci 66:693–695
Birch L (1948) The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J Anim Ecol 15–26
Bourguet D, Guillemaud T, Chevillon C, Raymond M (2004) Fitness costs of insecticide resistance in natural breeding sites of the mosquito Culex pipiens. Evolution 58:128–135
Butler SM, Gerry AC, Mullens BA (2007) House fly (Diptera: Muscidae) activity near baits containing (Z)-9-tricosene and efficacy of commercial toxic fly baits on a Southern California dairy. J Econ Entomol 100:1489–1495
Cao G, Han Z (2006) Tebufenozide resistance selected in Plutella xylostella and its cross-resistance and fitness cost. Pest Manag Sci 62:746–751
Carriere Y, Deland J-P, Roff D, Vincent C (1994) Life-history costs associated with the evolution of insecticide resistance. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B Biol Sci 258:35–40
Carrière Y, Ellers-kirk C, Patin AL, Sims MA, Meyer S, Y-b L, Dennehy TJ, Tabashnik BE (2001) Overwintering cost associated with resistance to transgenic cotton in the pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J Econ Entomol 94:935–941
Castle S, Prabhaker N (2013) Monitoring changes in Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) susceptibility to neonicotinoid insecticides in Arizona and California. J Econ Entomol 106:1404–1413
Crow JF (1957) Genetics of insect resistance to chemicals. Annu Rev Entomol 2:227–246
Crowder DW, Ellers-Kirk C, Tabashnik BE, Carriere Y (2009) Lack of fitness costs associated with pyriproxyfen resistance in the B biotype of Bemisia tabaci. Pest Manag Sci 65:235–240
Deacutis JM, Leichter CA, Gerry AC, Rutz DA, Watson WD, Geden CJ, Scott JG (2006) Susceptibility of field collected house flies to spinosad before and after a season of use. J Agric Urban Entomol 23:105–110
EPA (1999) LC50 Software Program. Version 1.50, Cincinnati, OH, USA, Ecological Monitoring Research Division, Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, EPA, USA
Ferré J, Van Rie J (2002) Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Entomol 47:501–533
Finney D (1971) A statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve. Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, London, p 333
Förster M, Klimpel S, Mehlhorn H, Sievert K, Messler S, Pfeffer K (2007) Pilot study on synanthropic flies (e.g. Musca, Sarcophaga, Calliphora, Fannia, Lucilia, Stomoxys) as vectors of pathogenic microorganisms. Parasitol Res 101:243–246
Foster S, Young S, Williamson M, Duce I, Denholm I, Devine G (2003) Analogous pleiotropic effects of insecticide resistance genotypes in peach–potato aphids and houseflies. Heredity 91:98–106
Gazave É, Chevillon C, Lenormand T, Marquine M, Raymond M (2001) Dissecting the cost of insecticide resistance genes during the overwintering period of the mosquito Culex pipiens. Heredity 87:441–448
Georghiou GP, Taylor CE (1977) Genetic and biological influences in the evolution of insecticide resistance. J Econ Entomol 70:319–323
Groeters FR, Tabashnik BE, Finson N, Johnson MW (1994) Fitness costs of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in the diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella). Evolution 197–201
Jia B, Liu Y, Zhu YC, Liu X, Gao C, Shen J (2009) Inheritance, fitness cost and mechanism of resistance to tebufenozide in Spodoptera exigua (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest Manag Sci 65:996–1002
Kaufman PE, Scott JG, Rutz DA (2001) Monitoring insecticide resistance in house flies (Diptera: Muscidae) from New York dairies. Pest Manag Sci 57:514–521
Kaufman PE, Gerry AC, Rutz DA, Scott JG (2006) Monitoring susceptibility of house flies (Musca domestica L.) in the United States to imidacloprid. J Agric Urban Entomol 23:195–200
Kaufman PE, Nunez SC, Geden CJ, Scharf ME (2010a) Selection for resistance to imidacloprid in the house fly (Diptera: Muscidae). J Econ Entomol 103:1937–1942
Kaufman PE, Nunez SC, Mann RS, Geden CJ, Scharf ME (2010b) Nicotinoid and pyrethroid insecticide resistance in houseflies (Diptera: Muscidae) collected from Florida dairies. Pest Manag Sci 66:290–294
Kavi LA, Kaufman PE, Scott JG (2014) Genetics and mechanisms of imidacloprid resistance in house flies. Pestic Biochem Physiol 109:64–69
Khan HAA, Shad SA, Akram W (2012) Effect of livestock manures on the fitness of house fly, Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Parasitol Res 111:1165–1171
Khan HAA, Akram W, Shad SA (2013a) Resistance to conventional insecticides in Pakistani populations of Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae): a potential ectoparasite of dairy animals. Ecotoxicology 22:522–527
Khan HAA, Shad SA, Akram W (2013b) Resistance to new chemical insecticides in the house fly, Musca domestica L., from dairies in Punjab, Pakistan. Parasitol Res 112:2049–2054
Khan HAA, Akram W, Shad SA (2014) Genetics, cross-resistance and mechanism of resistance to spinosad in a field strain of Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Acta Trop 130:148–154
Kliot A, Ghanim M (2012) Fitness costs associated with insecticide resistance. Pest Manag Sci 68:1431–1437
Li J, Wang Q, Zhang L, Gao X (2012) Characterization of imidacloprid resistance in the housefly Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). Pestic Biochem Physiol 102:109–114
Litchfield J, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose–effect experiments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 96:99–113
Liu Z, Han Z (2006) Fitness costs of laboratory-selected imidacloprid resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål. Pest Manag Sci 62:279–282
Matsuda K, Sattelle DB (2005) Mechanism of selective actions of neonicotinoids on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. New discoveries in agrochemicals. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 172–182
Millar NS, Denholm I (2007) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: targets for commercially important insecticides. Invertebr Neurosci 7:53–66
Nauen R, Denholm I (2005) Resistance of insect pests to neonicotinoid insecticides: current status and future prospects. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 58:200–215
Peck SL, Gould F, Ellner SP (1999) Spread of resistance in spatially extended regions of transgenic cotton: implications for management of Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Econ Entomol 92:1–16
Rabinovich JE (1972) Vital statistics of Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) under laboratory conditions. J Med Entomol 9:351–370
Radford P (1967) Growth analysis formulae—their use and abuse. Crop Sci 7:171–175
Roush RT, McKenzie JA (1987) Ecological genetics of insecticide and acaricide resistance. Annu Rev Entomol 32:361–380
Roush R, Plapp F (1982) Effects of insecticide resistance on biotic potential of the house fly (Diptera: Muscidae). J Econ Entomol 75:708–713
Roush RT, Daly JC (1990) The role of population genetics in resistance research and management. In: Roush RT, Tabashnik BE (eds) Pesticide resistance in arthropods. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 97–152
Saeed S, Sayyed AH, Ahmad I (2010) Effect of host plants on life-history traits of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Pest Sci 83:165–172
Sayyed AH, Attique MNR, Khaliq A, Wright DJ (2005) Inheritance of resistance and cross-resistance to deltamethrin in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) from Pakistan. Pest Manag Sci 61:636–642
Schuster DJ, Mann RS, Toapanta M, Cordero R, Thompson S, Cyman S, Shurtleff A, Morris I, Roy F (2010) Monitoring neonicotinoid resistance in biotype B of Bemisia tabaci in Florida. Pest Manag Sci 66:186–195
Scott JG, Alefantis TG, Kaufman PE, Rutz DA (2000) Insecticide resistance in house flies from caged-layer poultry facilities. Pest Manag Sci 56:147–153
Srigiriraju L, Semtner PJ, Bloomquist JR (2010) Monitoring for imidacloprid resistance in the tobacco adapted form of the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae), in the eastern United States. Pest Manag Sci 66:676–685
Tabashnik BE (1994) Evolution of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Entomol 39:47–79
Tabashnik BE, Carrière Y, Dennehy TJ, Morin S, Sisterson MS, Roush RT, Shelton AM, Zhao J-Z (2003) Insect resistance to transgenic Bt crops: lessons from the laboratory and field. J Econ Entomol 96:1031–1038
Wang Z, Yao M, Wu Y (2009) Cross-resistance, inheritance and biochemical mechanisms of imidacloprid resistance in B-biotype Bemisia tabaci. Pest Manag Sci 65:1189–1194
Zaka SM, Abbas N, Shad SA, Shah RM (2014) Effect of emamectin benzoate on life history traits and relative fitness of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Phytoparasitica 1–9
Acknowledgments
The authors are highly thankful to Marie Varloud, Global Technical Manager (Parasitology, Companion Animal), France, for critical review of the manuscript to improve its English language and for technical improvement.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, N., Khan, H. & Shad, S.A. Cross-resistance, stability, and fitness cost of resistance to imidacloprid in Musca domestica L., (Diptera: Muscidae). Parasitol Res 114, 247–255 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4186-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4186-0