Abstract
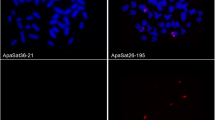
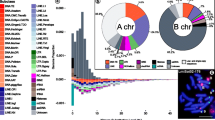
The origin of supernumerary (B) chromosomes is clearly conditioned by their ancestry from the standard (A) chromosomes. Sequence similarity between A and B chromosomes is thus crucial to determine B chromosome origin. For this purpose, we compare here the DNA sequences from A and B chromosomes in the characid fish Characidium gomesi using two main approaches. First, we found 59 satellite DNA (satDNA) families constituting the satellitome of this species and performed FISH analysis for 18 of them. This showed the presence of six satDNAs on the B chromosome: one shared with sex chromosomes and autosomes, two shared with sex chromosomes, one shared with autosomes and two being B-specific. This indicated that B chromosomes most likely arose from the sex chromosomes. Our second approach consisted of the analysis of five repetitive DNA families: 18S and 5S ribosomal DNA (rDNA), the H3 histone gene, U2 snDNA and the most abundant satDNA (CgoSat01-184) on DNA obtained from microdissected B chromosomes and from B-lacking genomes. PCR and sequence analysis of these repetitive sequences was successful for three of them (5S rDNA, H3 histone gene and CgoSat01-184), and sequence comparison revealed that DNA sequences obtained from the B chromosomes displayed higher identity with C. gomesi genomic DNA than with those obtained from other Characidium species. Taken together, our results support the intraspecific origin of B chromosomes in C. gomesi and point to sex chromosomes as B chromosome ancestors, which raises interesting prospects for future joint research on the genetic content of sex and B chromosomes in this species.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
We deposited the 0B and + B genomic libraries in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database with accession numbers SRR9613702 and SRR9613703, respectively.
References
Ahmad SF, Martins C (2019) The modern view of B chromosomes under the impact of high scale omics analyses. Cells 8(2):156
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Banaei-Moghaddam AM, Meier K, Karimi-Ashtiyani R, Houben A (2013) Formation and expression of pseudogenes on the B chromosome of rye. Plant Cell 25:2536–2544
Bao W, Kojima KK, Kohany O (2015) Repbase update, a database of repetitive elements in eukaryotic genomes. Mob DNA 6:11
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Burt A, Trivers R (2006) Genes in conflict: the biology of selfish genetic elements. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Camacho JPM (2005) B chromosomes. The evolution of the genome. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 223–286
Camacho JPM, Sharbel TF, Beukeboom LW (2000) B-chromosome evolution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 355:163–178
Carmello BO, Coan RLB, Cardoso AL et al (2017) The hnRNP Q-like gene is retroinserted into the B chromosomes of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata. Chromosome Res 25:277–290
Clark FE, Conte MA, Ferreira-Bravo IA et al (2016) Dynamic sequence evolution of a sex-associated B chromosome in Lake Malawi cichlid fish. J Hered 108:53–62
Clark FE, Conte MA, Kocher TD (2018) Genomic characterization of a B chromosome in Lake Malawi cichlid fishes. Genes 9:610
Coan RLB, Martins C (2018) Landscape of transposable elements focusing on the B chromosome of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata. Genes 9:269
Colgan DJ, McLauchlan A, Wilson GDF et al (1998) Histone H3 and U2 snRNA DNA sequences and arthropod molecular evolution. Aust J Zool 46:419–437
Dalla Benetta E, Akbari OS, Ferree PM (2019) Sequence expression of supernumerary B chromosomes: function or fluff? Genes 10:123
Dhar MK, Gurmeet Kour G, Kaul S (2017) B chromosome in Plantago lagopus Linnaeus, 1753 shows preferential transmission and accumulation through unusual processes. Comp Cytogenet 11:375–392
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567
Foresti F, Almeida-Toledo LF, Toledo-Filho SA (1981) Polymorphic nature of nucleolus organizer regions in fishes. Cytogenet Genome Res 31:137–144
Gribble S, Ng BL, Prigmore E et al (2004) Chromosome paints from single copies of chromosomes. Chromosome Res 12:143–151
Hanlon SL, Miller DE, Eche S et al (2018) Origin, composition, and structure of the supernumerary B chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 210(4):1197–1212
Houben A (2017) B chromosomes—a matter of chromosome drive. Front Plant Sci 8:210
Huang W, Du Y, Zhao X et al (2016) B chromosome contains active genes and impacts the transcription of A chromosomes in maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Plant Biol 16:88
Jehangir M, Ahmad SF, Cardoso AL et al (2019) De novo genome assembly of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata reveals a higher level of genomic polymorphism and genes related to B chromosomes. Chromosoma 128(2):81–96
Jones RN (2018) Transmission and drive involving parasitic B chromosomes. Genes 9:388
Jones RN, Rees H (1982) B chromosomes. Academy Press, London
Kent WJ (2002) BLAT—the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res 12:656–664
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220
Li Y, Jing XA, Aldrich JC et al (2017) Unique sequence organization and small RNA expression of a “selfish” B chromosome. Chromosoma 126:753–768
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Ma W, Gabriel TS, Martis MM et al (2017) Rye B chromosomes encode a functional Argonaute-like protein with in vitro slicer activities similar to its A chromosome paralog. New Phytol 213:916–928
Makunin AI, Dementyeva PV, Graphodatsky AS et al (2014) Genes on B chromosomes of vertebrates. Mol Cytogenet 7:99
Makunin AI, Romanenko SA, Beklemisheva VR et al (2018) Sequencing of supernumerary chromosomes of red fox and raccoon dog confirms a non-random gene acquisition by B chromosomes. Genes 9:405
Martis MM, Klemme S, Banaei-Moghaddam AM et al (2012) Selfish supernumerary chromosome reveals its origin as a mosaic of host genome and organellar sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:13343–13346
McAllister BF, Werren JH (1997) Hybrid origin of a B chromosome (PSR) in the parasitic wasp Nasonia vitripennis. Chromosoma 106:243–253
Miao VP, Covert SF, VanEtten HD (1991) A fungal gene for antibiotic resistance on a dispensable (“B”) chromosome. Science 254:1773–1776
Milani D, Bardella VB, Ferretti ABSM et al (2018) Satellite DNAs unveil clues about the ancestry and composition of B chromosomes in three grasshopper species. Genes 9:523
Navarro-Domínguez B, Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Cabrero J et al (2017a) Protein-coding genes in B chromosomes of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Sci Rep 7:45200
Navarro-Domínguez B, Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Camacho JPM et al (2017b) Transcription of a B chromosome CAP-G pseudogene does not influence normal Condensin Complex genes in a grasshopper. Sci Rep 7:17650
Navarro-Domínguez B, Martín-Peciña M, Ruiz-Ruano FJ et al (2019) Gene expression changes elicited by a parasitic B chromosome in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans are consistent with its phenotypic effects. Chromosoma 128:53–67
Novák P, Neumann P, Pech J et al (2013) RepeatExplorer: a Galaxy-based web server for genome-wide characterization of eukaryotic repetitive elements from next-generation sequence reads. Bioinformatics 29:792–793
Pansonato-Alves JC, Serrano EA, Utsunomia R et al (2014) Single origin of sex chromosomes and multiple origins of B chromosomes in fish genus Characidium. PLoS One 9:e107169
Pendas AM, Moran P, Martinez JL, Garcia-Vazquez E (1995) Applications of 5S rDNA in Atlantic salmon, brown trout, and in Atlantic salmon brown trout hybrid identification. Mol Ecol 4:275–276
Perfectti F, Werren JH (2001) The interspecific origin of B chromosomes: experimental evidence. Evolution 55:1069–1073
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JW (1986) Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83:2934–2938
Ramos É, Cardoso AL, Brown J et al (2017) The repetitive DNA element BncDNA, enriched in the B chromosome of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata, transcribes a potentially noncoding RNA. Chromosoma 126:313–323
Rodrigues PHM, Santos RZ, Silva DMZA et al (2019) Chromosomal and genomic dynamics of satellite DNAs in Characidae (Characiformes, Teleostei) Species. Zebrafish 16:408–414
Ruiz-Estévez M, López-León M, Cabrero J et al (2013) Ribosomal DNA is active in different B chromosome variants of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Genetica 141:337–345
Ruiz-Estévez M, Badisco L, Broeck JV et al (2014) B chromosomes showing active ribosomal RNA genes contribute insignificant amounts of rRNA in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Mol Genet Genom 289:1209–1216
Ruiz-Ruano FJ, López-León MD, Cabrero J, Camacho JPM (2016) High-throughput analysis of the satellitome illuminates satellite DNA evolution. Sci Rep 6:28333
Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Cabrero J, López-León MD, Camacho JPM (2017) Satellite DNA content illuminates the ancestry of a supernumerary (B) chromosome. Chromosoma 126:487–500
Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Cabrero J, López-León MD et al (2018) Quantitative sequence characterization for repetitive DNA content in the supernumerary chromosome of the migratory locust. Chromosoma 127:45–57
Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison P (2000) Practical in situ hybridization. BIOS Scientific Publishers, Milton Park
Sharbel TF, Green DM, Houben A (1998) B-chromosome origin in the endemic New Zealand frog Leiopelma hochstetteri through sex chromosome devolution. Genome 41:14–22
Silva DMZA, Pansonato-Alves JC, Utsunomia R et al (2014) Delimiting the origin of a B chromosome by FISH mapping, chromosome painting and DNA sequence analysis in Astyanax paranae (Teleostei, Characiformes). PLoS One 9:e94896
Silva DMZA, Utsunomia R, Ruiz-Ruano FJ et al (2017) High-throughput analysis unveils a highly shared satellite DNA library among three species of fish genus Astyanax. Sci Rep 7:12726
Smit AFA, Hubley R (2008–2015) RepeatModeler Open-1.0. http://www.repeatmasker.org
Smit AFA, Hubley R, Green P (1996–2010) RepeatMasker Open-3.0. http://www.repeatmasker.org
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75:304–306
Teruel M, Cabrero J, Perfectti F, Camacho JPM (2010) B chromosome ancestry revealed by histone genes in the migratory locust. Chromosoma 119:217–225
Tosta VC, Marthe JB, Tavares MG et al (2014) Possible introgression of B chromosomes between Bee species (Genus Partamona). Cytogenet Genome Res 144:220–226
Trifonov VA, Dementyeva PV, Larkin DM et al (2013) Transcription of a protein-coding gene on B chromosomes of the Siberian roe deer (Capreolus pygargus). BMC Biol 11:90
Utsunomia R, Silva DMZA, Ruiz-Ruano FJ et al (2016) Uncovering the ancestry of B chromosomes in Moenkhausia sanctaefilomenae (Teleostei, Characidae). PLoS One 11:e0150573
Utsunomia R, Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Silva DMZA et al (2017) A glimpse into the satellite DNA library in characidae fish (Teleostei, Characiformes). Front Genet 8:103
Utsunomia R, Silva DMZA, Ruiz-Ruano FJ et al (2019) Satellitome landscape analysis of Megaleporinus macrocephalus (Teleostei, Anostomidae) reveals intense accumulation of satellite sequences on the heteromorphic sex chromosome. Sci Rep 9:5856
Valente GT, Conte MA, Fantinatti BEA et al (2014) Origin and evolution of B chromosomes in the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata based on integrated genomic analyses. Mol Biol Evol 31:2061–2072
Wei KHC, Lower SE, Caldas IV et al (2018) Variable rates of simple satellite gains across the Drosophila phylogeny. Mol Biol Evol 35:925–941
Wu D, Ruban A, Fuchs J et al (2019) Nondisjunction and unequal spindle organization accompany the drive of Aegilops speltoides B chromosomes. New Phytol 223:1340–1352
Yoshida K, Terai Y, Mizoiri S et al (2011) B chromosomes have a functional effect on female sex determination in lake victoria cichlid fishes. PLoS Genet 7(8):e1002203
Ziegler CG, Lamatsch DK, Steinlein C et al (2003) The giant B chromosome of the cyprinid fish Alburnus alburnus harbours a retrotransposon-derived repetitive DNA sequence. Chromosome Res 11:23
Acknowledgements
We are thankful Renato Devidé for his technical assistance and reviewers for the very helpful suggestions and corrections for improving the paper.
Funding
This study was funded by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) (Grant Number 2013/02143-3) and by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The animals were collected in accordance with Brazilian environmental protection legislation (Collection Permission MMA/IBAMA/SISBIO—number 3245), and the procedures for fish sampling, maintenance and analysis were performed in compliance with the Brazilian College of Animal Experimentation (COBEA) and approved (protocol 504) by the Bioscience Institute/Unesp Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals (CEUA).
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
438_2019_1615_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 2 Karyotypes of C. gomesi after FISH with 18S (red) and 5S rDNA (green) (a), U2 snDNA (b) and H3 histone (c) probes and metaphases of C. gomesi after chromosome painting with the probe from the microdissected B chromosome of the same species (d). Bar = 10 µm (TIFF 43 kb)
438_2019_1615_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Supplementary material 3 Metaphases of C. gomesi after FISH with satDNAs (a, c, e) and C-banding (b, d, f). Bar = 10 µm (JPEG 461 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serrano-Freitas, É.A., Silva, D.M.Z.A., Ruiz-Ruano, F.J. et al. Satellite DNA content of B chromosomes in the characid fish Characidium gomesi supports their origin from sex chromosomes. Mol Genet Genomics 295, 195–207 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01615-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01615-2