Abstract
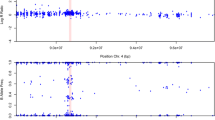
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is the most common mitochondrially inherited disease causing blindness, preferentially in young adult males. Most of the patients carry the G11778A mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutation. However, the marked incomplete penetrance and the gender bias indicate some additional genetic and/or environmental factors to disease expression. Herein, we first conducted a genome-wide linkage scan with 400 microsatellite markers in 9 large Thai LHON G11778A pedigrees. Using an affecteds-only nonparametric linkage analysis, 4 regions on chromosomes 3, 12, 13 and 18 showed Zlr scores greater than 2 (P < 0.025), which is consistently significant across several linkage statistics. The most suggestive marker D3S1565 (Zlr > 2 in 10 of 16 allele sharing models tested) was then expanded to include the region 3q26.2–3q28 covering SLC7A14 (3q26.2), MFN1 (3q26.32), MRPL47 (3q26.33), MCCC1 (3q27.1), PARL (3q27.1) and OPA1 (3q28–q29). All of these candidate genes were selected from the Maestro database and had known to be localized in mitochondria. Sixty tag SNPs were genotyped in 86 cases, 211 of their relatives and 32 unrelated Thai controls, by multiplex-PCR-based Invader assay. Analyses using a powerful association testing tool that adjusts for relatedness (the MQLS statistic) showed the most evidence of association between two SNPs, rs3749446 and rs1402000 (located in PARL presenilins-associated rhomboid-like) and LHON expression (both P = 8.8 × 10−5). The mitochondrial PARL protease has been recently known to play a role with a dynamin-related OPA1 protein in preventing apoptotic events by slowing down the release of cytochrome c out of mitochondrial cristae junctions. Moreover, PARL is required to activate the intramembranous proteolyses resulting in the degradation of an accumulated pro-apoptotic protein in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Under these circumstances, variants of PARL are suggested to influence cell death by apoptosis which has long been believed to intrigue the neurodegeneration of LHON.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2002) Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30:97–101
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21:263–265
Brown MD (1999) The enigmatic relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. J Neurol Sci 165:1–5
Bu XD, Rotter JI (1991) X chromosome-linked and mitochondrial gene control of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: evidence from segregation analysis for dependence on X chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8198–8202
Calvo S, Jain M, Xie X, Sheth SA, Chang B, Goldberger OA, Spinazzola A, Zeviani M, Carr SA, Mootha VK (2006) Systematic identification of human mitochondrial disease genes through integrative genomics. Nat Genet 38:576–582
Chan DC (2006) Mitochondria: dynamic organelles in disease, aging, and development. Cell 125:1241–1252
Chao JR, Parganas E, Boyd K, Hong CY, Opferman JT, Ihle JN (2008) Hax1-mediated processing of HtrA2 by Parl allows survival of lymphocytes and neurons. Nature 452:98–102
Chuenkongkaew WL, Lertrit P, Limwongse C, Nilanont Y, Boonyapisit K, Sangruchi T, Chirapapaisan N, Suphavilai R (2005) An unusual family with Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy and facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Eur J Neurol 12:388–391
Cipolat S, Rudka T, Hartmann D, Costa V, Serneels L, Craessaerts K, Metzger K, Frezza C, Annaert W, D’Adamio L, Derks C, Dejaegere T, Pellegrini L, D’Hooge R, Scorrano L, De Strooper B (2006) Mitochondrial rhomboid PARL regulates cytochrome c release during apoptosis via OPA1-dependent cristae remodeling. Cell 126:163–175
Curran JE, Jowett JB, Abraham LJ, Diepeveen LA, Elliott KS, Dyer TD, Kerr-Bayles LJ, Johnson MP, Comuzzie AG, Moses EK, Walder KR, Collier GR, Blangero J, Kissebah AH (2009) Genetic variation in PARL influences mitochondrial content. Hum Genet 127(2):183–190
Dredge BK, Darnell RB (2003) Nova regulates GABA(A) receptor gamma2 alternative splicing via a distal downstream UCAU-rich intronic splicing enhancer. Mol Cell Biol 23:4687–4700
Dredge BK, Polydorides AD, Darnell RB (2001) The splice of life: alternative splicing and neurological disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:43–50
Frezza C, Cipolat S, Martins de Brito O, Micaroni M, Beznoussenko GV, Rudka T, Bartoli D, Polishuck RS, Danial NN, De Strooper B, Scorrano L (2006) OPA1 controls apoptotic cristae remodeling independently from mitochondrial fusion. Cell 126:177–189
Gottlieb E (2006) OPA1 and PARL keep a lid on apoptosis. Cell 126:27–29
Gudbjartsson DF, Jonasson K, Frigge ML, Kong A (2000) Allegro, a new computer program for multipoint linkage analysis. Nat Genet 25:12–13
Harding AE, Sweeney MG, Govan GG, Riordan-Eva P (1995) Pedigree analysis in Leber hereditary optic neuropathy families with a pathogenic mtDNA mutation. Am J Hum Genet 57:77–86
Heiduschka P, Schnichels S, Fuhrmann N, Hofmeister S, Schraermeyer U, Wissinger B, Alavi MV (2010) Electrophysiological and histologic assessment of retinal ganglion cell fate in a mouse model for OPA1-associated autosomal dominant optic atrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:1424–1431
Hotta Y, Fujiki K, Hayakawa M, Nakajima A, Kanai A, Mashima Y, Hiida Y, Shinoda K, Yamada K, Oguchi Y et al (1995) Clinical features of Japanese Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy with 11778 mutation of mitochondrial DNA. Jpn J Ophthalmol 39:96–108
Howell N (1998) Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: respiratory chain dysfunction and degeneration of the optic nerve. Vis Res 38:1495–1504
Hudson G, Keers S, Yu Wai Man P, Griffiths P, Huoponen K, Savontaus ML, Nikoskelainen E, Zeviani M, Carrara F, Horvath R, Karcagi V, Spruijt L, de Coo IF, Smeets HJ, Chinnery PF (2005) Identification of an X-chromosomal locus and haplotype modulating the phenotype of a mitochondrial DNA disorder. Am J Hum Genet 77:1086–1091
Hudson G, Carelli V, Spruijt L, Gerards M, Mowbray C, Achilli A, Pyle A, Elson J, Howell N, La Morgia C, Valentino ML, Huoponen K, Savontaus ML, Nikoskelainen E, Sadun AA, Salomao SR, Belfort R Jr, Griffiths P, Man PY, de Coo RF, Horvath R, Zeviani M, Smeets HJ, Torroni A, Chinnery PF (2007) Clinical expression of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy is affected by the mitochondrial DNA-haplogroup background. Am J Hum Genet 81:228–233
Jeyaraju DV, Xu L, Letellier MC, Bandaru S, Zunino R, Berg EA, McBride HM, Pellegrini L (2006) Phosphorylation and cleavage of presenilin-associated rhomboid-like protein (PARL) promotes changes in mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18562–18567
Ju WK, Misaka T, Kushnareva Y, Nakagomi S, Agarwal N, Kubo Y, Lipton SA, Bossy-Wetzel E (2005) OPA1 expression in the normal rat retina and optic nerve. J Comp Neurol 488:1–10
Kirkman MA, Yu-Wai-Man P, Korsten A, Leonhardt M, Dimitriadis K, De Coo IF, Klopstock T, Chinnery PF (2009) Gene-environment interactions in Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Brain 132:2317–2326
Kong A, Cox NJ (1997) Allele-sharing models: LOD scores and accurate linkage tests. Am J Hum Genet 61:1179–1188
Lander E, Kruglyak L (1995) Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet 11:241–247
Lessing D, Bonini NM (2009) Maintaining the brain: insight into human neurodegeneration from Drosophila melanogaster mutants. Nat Rev Genet 10(6):359–370
Mackey DA, Oostra RJ, Rosenberg T, Nikoskelainen E, Bronte-Stewart J, Poulton J, Harding AE, Govan G, Bolhuis PA, Norby S (1996) Primary pathogenic mtDNA mutations in multigeneration pedigrees with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet 59:481–485
Mahasirimongkol S, Chantratita W, Promso S, Pasomsab E, Jinawath N, Jongjaroenprasert W, Lulitanond V, Krittayapoositpot P, Tongsima S, Sawanpanyalert P, Kamatani N, Nakamura Y, Sura T (2006) Similarity of the allele frequency and linkage disequilibrium pattern of single nucleotide polymorphisms in drug-related gene loci between Thai and northern East Asian populations: implications for tagging SNP selection in Thais. J Hum Genet 51:896–904
Man PY, Turnbull DM, Chinnery PF (2002) Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. J Med Genet 39:162–169
Man PY, Griffiths PG, Brown DT, Howell N, Turnbull DM, Chinnery PF (2003) The epidemiology of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy in the North East of England. Am J Hum Genet 72:333–339
McPeek MS (1999) Optimal allele-sharing statistics for genetic mapping using affected relatives. Genet Epidemiol 16:225–249
McPeek MS, Sun L (2000) Statistical tests for detection of misspecified relationships by use of genome-screen data. Am J Hum Genet 66:1076–1094
McPeek MS, Wu X, Ober C (2004) Best linear unbiased allele-frequency estimation in complex pedigrees. Biometrics 60:359–367
McQuibban GA, Lee JR, Zheng L, Juusola M, Freeman M (2006) Normal mitochondrial dynamics requires rhomboid-7 and affects Drosophila lifespan and neuronal function. Curr Biol 16:982–989
Moraes CT, Ricci E, Bonilla E, DiMauro S, Schon EA (1992) The mitochondrial tRNA(Leu(UUR)) mutation in mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke like episodes (MELAS): genetic, biochemical, and morphological correlations in skeletal muscle. Am J Hum Genet 50:934–949
Nikoskelainen EK, Savontaus ML, Wanne OP, Katila MJ, Nummelin KU (1987) Leber’s hereditary optic neuroretinopathy, a maternally inherited disease. A genealogic study in four pedigrees. Arch Ophthalmol 105:665–671
Nishioka T, Soemantri A, Ishida T (2004) mtDNA/nDNA ratio in 14484 LHON mitochondrial mutation carriers. J Hum Genet 49:701–705
Nyholt DR (2004) A simple correction for multiple testing for single-nucleotide polymorphisms in linkage disequilibrium with each other. Am J Hum Genet 74:765–769
O’Connell JR, Weeks DE (1998) PedCheck: a program for identification of genotype incompatibilities in linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 63:259–266
Ohnishi Y, Tanaka T, Ozaki K, Yamada R, Suzuki H, Nakamura Y (2001) A high-throughput SNP typing system for genome-wide association studies. J Hum Genet 46:471–477
Pellegrini L, Scorrano L (2007) A cut short to death: Parl and Opa1 in the regulation of mitochondrial morphology and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 14:1275–1284
Pesch UE, Fries JE, Bette S, Kalbacher H, Wissinger B, Alexander C, Kohler K (2004) OPA1, the disease gene for autosomal dominant optic atrophy, is specifically expressed in ganglion cells and intrinsic neurons of the retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:4217–4225
Phasukkijwatana N, Chuenkongkaew WL, Suphavilai R, Suktitipat B, Pingsuthiwong S, Ruangvaravate N, Atchaneeyasakul LO, Warrasak S, Poonyathalang A, Sura T, Lertrit P (2006) The unique characteristics of Thai Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: analysis of 30 G11778A pedigrees. J Hum Genet 51:298–304
Qu J, Li R, Zhou X, Tong Y, Lu F, Qian Y, Hu Y, Mo JQ, West CE, Guan MX (2006) The novel A4435G mutation in the mitochondrial tRNAMet may modulate the phenotypic expression of the LHON-associated ND4 G11778A mutation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:475–483
Riordan-Eva P, Sanders MD, Govan GG, Sweeney MG, Da Costa J, Harding AE (1995) The clinical features of Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy defined by the presence of a pathogenic mitochondrial DNA mutation. Brain 118(Pt 2):319–337
Schug J (2003) Current protocols in bioinformatics. Wiley and Sons, New York
Shankar SP, Fingert JH, Carelli V, Valentino ML, King TM, Daiger SP, Salomao SR, Berezovsky A, Belfort R Jr, Braun TA, Sheffield VC, Sadun AA, Stone EM (2008) Evidence for a novel X-linked modifier locus for Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Ophthalmic Genet 29:17–24
Shibata A, Hattori M, Suda H, Sakaki Y (1996) Identification of cis-acting elements involved in an alternative splicing of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) gene. Gene 175:203–208
Thornton T, McPeek MS (2007) Case–control association testing with related individuals: a more powerful quasi-likelihood score test. Am J Hum Genet 81:321–337
Vilkki J, Ott J, Savontaus ML, Aula P, Nikoskelainen EK (1991) Optic atrophy in Leber hereditary optic neuroretinopathy is probably determined by an X-chromosomal gene closely linked to DXS7. Am J Hum Genet 48:486–491
Yen MY, Chen CS, Wang AG, Wei YH (2002) Increase of mitochondrial DNA in blood cells of patients with Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy with 11778 mutation. Br J Ophthalmol 86:1027–1030
Zhang Y, Chan DC (2007) New insights into mitochondrial fusion. FEBS Lett 581:2168–2173
Acknowledgments
The genome-wide linkage scan was performed with the assistance of Dr. Kelly Ewen-White in Australian Genome Research Facility (AGRF), Victoria, Australia. SNPs genotyping and all facilities to perform multiplex-PCR-based Invader assay were supported by Laboratory for Pharmacogenetics, RIKEN Center for Genomic Medicine, Yokohama, Japan, through the genotyping services supports and fellowships to Thai researchers and institutes executed on DMSc-RIKEN’s Center for Genomics Medicine (CGM) Collaboration. We acknowledge Sukanya Wattanapokayakit (DMSc, Thailand) for her assistance on collaboration process and SNPs genotyping at RIKEN. Also we sincerely thank Dr. Briony Patterson for the guidance on bioinformatics analyses and discussions. We are especially grateful to Dr. Komon Luangtrakool, Pattamon Tharaphan, Sarinee Pingsutthiwong, Thitima Sunpachudayan, Benjamas Intharabut, Treenud Suntisiri, Yutthana Joyjinda, Dr. Patchara Nantasri and the ophthalmologists for their great assistance in the field trip, DNA extraction and data manipulation. Finally, we thank all of the patients and families for their wonderful cooperation. This work was supported by the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) grant number BRG4580018 to P. Lertrit and PHD/0031/2546 through the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. Program to N. Phasukkijwatana and P. Lertrit, and by Siriraj Research and Development Fund, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University (Grant No. 014(II)/49). The SNPs genotyping and statistical genetics analyses were supported by grants from the Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University and from the National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (BIOTEC), Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
N. Phasukkijwatana and B. Kunhapan contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix
Appendix
For association testing using related individuals with the MQLS statistics refer http://www.stat.uchicago.edu/~mcpeek/software/MQLS/index.html. For bioinformatics tools to predict the transcription element binding sites refer http://www.cbil.upenn.edu/cgi-bin/tess/tess; http://regrna.mbc.nctu.edu.tw/html/prediction.html.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phasukkijwatana, N., Kunhapan, B., Stankovich, J. et al. Genome-wide linkage scan and association study of PARL to the expression of LHON families in Thailand. Hum Genet 128, 39–49 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-010-0821-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-010-0821-8