Abstract
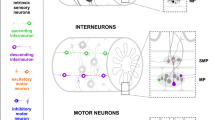
Light- and electron-microscopic studies were used to investigate connections between specific subgroups of neurons in the myenteric plexus of the guineapig small intestine. Inputs to two classes of calretinin-immunoreactive (IR) nerve cells, longitudinal muscle motor neurons and ascending interneurons, were examined. Inputs from calbindin-IR primary sensory neurons and from three classes of descending interneurons were studied. Electron-microscopic analysis showed that calbindin-IR axons formed two types of inputs, synapses and close contacts, on calretinin-IR neurons. About 40% of inputs to the longitudinal muscle motor neurons and 70% to ascending interneurons were calbindin-IR. Approximately 50% of longitudinal muscle motor neurons were surrounded by bombesin-IR dense pericellular baskets and 40% by closely apposed varicosities. At the electron-microscope level, the bombesin-IR varicosities were found to form synapses and close contacts with the motor neurons. Dense pericellular baskets with bombesin-IR surrounded 36% of all ascending interneurons, and a further 17% had closely apposed varicosities. Somatostatin-and 5-HT-IR descending interneurons provided no dense pericellular baskets to calretinin-IR nerve cells. Thus, calretinin-IR, longitudinal muscle motor neurons and ascending interneurons receive direct synaptic inputs from intrinsic primary sensory neurons and from non-cholinergic, bombesin-IR, descending interneurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bornstein JC, Furness JB, Smith TK, Trussell DC (1991a) Synaptic responses evoked by mechanical stimulation of the mucosa in morphologically characterised myenteric neurons of the guinea-pig ileum. J Neurosci 11:505–518
Bornstein JC, Hendriks R, Furness JB, Trussell DC (1991b) Ramifications of the axons of AH-neurons injected with the intracellular marker biocytin in the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig small intestine. J Comp Neurol 314:437–451
Brookes SJH, Steele PA, Costa M (1991) Calretinin immunoreactivity in cholinergic motor neurones, interneurones and vasomotor neurones in the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 263:471–481
Brookes SJH, Ramsay GA, Neville T, Costa M (1994) Dogiel type II neurones are a source of fast excitatory potentials to inhibitory motor neurones in the guinea-pig small intestine. Proc Aust Neuroscience Soc 5:54
Buchan AMJ, McIntosh CHS, Dyck I, Brown JC, Sikova LKJ, Levy JG (1985) An immunocytochemical investigation with monoclonal antibodies to somatostatin. Histochemistry 83:175–180
Costa M, Furness JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Davies B, Oliver J (1980) An immunohistochemical study of the projections of somatostatin-containing neurons in the guinea-pig intestine. Neuroscience 5:841–852
Costa M, Furness JB, Cuello AC, Verhofstad AAJ, Steinbusch HWM, Elde RP (1982) Neurons with 5-hydroxytryptamine-like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system: their visualisation and reactions to drug treatment. Neuroscience 7:351–363
Costa M, Brookes SA, Waterman S, Mayo R (1992) Enteric neuronal circuitry and transmitters controlling intestinal motor function. In: Holle GE (ed) Advances in the innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 115–121
Cuttita F, Carney DN, Mulshine J, Moody TW, Fedorko J, Fischler A, Minna JD (1985) Bombesin-like peptides can function as autocrine growth factors in human small-cell lung cancer. Nature 316:823–826
Dogiel AS (1899) Über den Bau der Ganglien in den Geflechten des Darmes und der Gallenblase des Menschen und der Säugetiere. Arch Anat Physiol (Leipzig) Anat Abt Jg 1899:130–158
Furness JB, Costa M (1982) Neurons with 5-hydroxytryptamine-like immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system: their projections in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 7:341–349
Furness JB, Costa M, Walsh JH (1981) Evidence for and significance of the projection of VIP neurons from the myenteric plexus to the taenia coli in the guinea-pig. Gastroenterology 80:1557–1561
Furness JB, Keast JR, Pompolo S, Bornstein JC, Costa M, Emson PC, Lawson DEM (1988) Immunohistochemical evidence for the presence of calcium binding proteins in enteric neurons. Cell Tissue Res 252:79–87
Furness JB, Pompolo S, Murphy R, Giraud A (1989) Projections of neurons with neuromedin U-like immunoreactivity in the small intestine of the guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res 257:415–422
Furness JB, Trussell DC, Pompolo S, Bornstein JC, Smith TK (1990) Calbindin neurons of the guinea-pig small intestine: Quantitative analysis of their numbers and projections. Cell Tissue Res 260:261–272
Furness JB, Bornstein JC, Pompolo S, Young HM, Kunze WAA, Kelly H (1994) The circuitry of the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterology and Motility 6:241–253
Galligan JJ, Bertrand PP (1995) ATP mediates fast synaptic potentials in enteric neurons. J Neurosci (in press)
Hirst GDS, Holman ME, Spence I (1974) Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol (Lond) 236:303–326
Iyer V, Bornstein JC, Costa M, Furness JB, Takahashi Y, Iwanaga T (1988) Electrophysiology of guinea-pig myenteric neurons correlated with immunoreactivity for calcium binding proteins. J Auton Nerve Syst 22:141–150
Kirchgessner AL, Gershon MD (1988) Projections of submucosal neurons to the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig intestine: in vitro tracing of microcircuits by retrograde and anterograde transport. J Comp Neurol 277:487–498
Kirchgessner AL, Tamir H, Gershon MD (1992) Identification and stimulation by serotonin of intrinsic sensory neurons of the submucosal plexus of the guinea pig gut: activity-induced expression of Fos immunoreactivity. J Neurosci 12:235–248
Klemm M, Hirst GDS, Campbell G (1992) Structure of autonomic neuromuscular junctions in the sinus venosus of the toad. J Auton Nerv Syst 39:139–150
Kosterlitz HW, Robinson JA (1959) Reflex contractions of the longitudinal muscle coat of the isolated guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol (Lond) 146:369–379
Kunze WAA, Furness JB, Bornstein JC (1993) Simultaneous intracellular recordings from enteric neurons reveal that myenteric AH neurons transmit via slow excitatory postsynaptic potentials. Neuroscience 55:685–694
Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Costa M, Furness JB (1985) Light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of the same nerves from whole mount preparations. J Histochem Cytochem 33:857–866
Palmer JM, Wood JD, Zafirov DH (1987) Transduction of aminergic and peptidergic signals in enteric neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol (Lond) 387:371–383
Pompolo S, Furness JB (1988) Ultrastructure and synaptic relationships of calbindin-reactive, Dogiel type II neurons, in myenteric ganglia of guinea-pig small intestine. J Neurocytol 17:771–782
Pompolo S, Furness JB (1993) Origins of synaptic inputs to calretinin immunoreactive neurons in the guinea-pig small intestine. J Neurocytol 22:531–546
Pompolo S, Furness JB, Bornstein JC, Hendriks R, Trussell DC (1989) Dogiel type II neurons in the guinea-pig small intestine: Ultrastructure in relation to other characteristics. In: Singer MV, Goebell H (eds) Nerves in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Martin Lister, Carnforth, UK pp 57–67
Rogers JH (1989) Two calcium-binding proteins mark many chick sensory neurons. Neuroscience 31:697–709
Schmidt HHHW, Gagne GD, Nakane M, Pollock JS, Miller MF, Murad F (1992) Mapping of neural nitric oxide synthase in the rat suggest frequent co-localization with NADPH diaphorase but not with soluble guanylyl cyclase, and novel paraneural functions for nitrinergic signal transduction. J Histochem Cytochem 40:1439–1456
Smith TK, Furness JB (1988) Reflex changes in circular muscle activity elicited by stroking the mucosa: An electrophysiological analysis in the isolated guinea-pig ileum. J Auton Nerv Syst 25:205–218
Smith TK, Bornstein JC, Furness JB (1992) Convergence of reflex pathways excited by distension and mechanical stimulation of the mucosa onto the same myenteric neurons of the guinea pig small intestine. J Neurosci 12:1502–1510
Song Z-M, Brookes SJH, Costa M (1991) Identification of myenteric neurons which project to the mucosa of the guinea-pig small intestine. Neurosci Lett 129:294–298
Song Z-M, Brookes SJH, Costa M (1993) Identification of a subpopulation of anally-directed calbindin-immunoreactive neurons in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. Proc Aust Neuroscience Soc 4:76
Takaki M, Wood JD, Gershon MD (1985) Heterogeneity of ganglia of the guinea pig myenteric plexus: An in vitro study of the origin of terminals within single ganglia using a covalently bound fluorescent retrograde tracer. J Comp Neurol 235:488–502
Tamura K, Schemann M, Wood JD (1993) Actions of nitric oxidegenerating sodium nitroprusside in myenteric plexus of guinea pig small intestine. Am J Physiol 265:G887-G893
Tonini M, Costa M (1990) A pharmacological analysis of the neuronal circuitry involved in distension-evoked enteric excitatory reflex. Neuroscience 38:787–795
Williams JT, North RA (1979) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide excites neurones of the myenteric plexus. Brain Res 175:174–177
Young HM, Furness JB (1995) An ultrastructural examination of the targets of serotonin-immunoreactive descending interneurons in the guinea-pig small intestine. J Comp Neurol (in press)
Young HM, Furness JB, Sewell P, Burcher EF, Kandiah CJ (1993) Total numbers of neurons in myenteric ganglia of the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 272:197–200
Young HM, Kunze WAA, Pompolo S, Furness JB, Bornstein JC (1994) Combined intracellular injection of neurobiotin and pre-embedding immunocytochemistry using silver-intensified gold probes in myenteric neurons. J Neurosci Meth 51:39–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pompolo, S., Furness, J.B. Sources of inputs to longitudinal muscle motor neurons and ascending interneurons in the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 280, 549–560 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318359
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318359