Abstract
Background
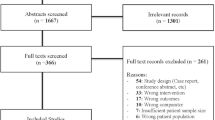
Medical, endoscopic, and open/laparoscopic surgical methods are used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This study aimed to perform a systematic review of randomized controlled trials comparing medical and surgical treatments of GERD in adult patients.
Methods
For the study, MEDLINE and EMBASE (1980–2012) were searched. Two reviewers independently assessed methodologic aspects and extracted data from eligible studies, focusing on patient-relevant outcomes. The primary outcomes were health-related and GERD-specific quality-of-life aspects. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) between treatment groups were calculated and combined using random-effect meta-analysis.
Results
The study identified 11 publications reporting on 7 trials comparing surgical (open or laparoscopic) and medical treatment of GERD. Meta-analysis of both quality-of-life aspects showed a pooled-effect estimate in favor of fundoplication (SMD 0.18; 95 % confidence interval [CI] 0.01–0.35; SMD 0.33; 95 % CI 0.13–0.54). Heartburn and regurgitation were less frequent after surgical intervention. However, a considerable proportion of patients still needed antireflux medication after fundoplication. Nevertheless, the surgical patients were significantly more satisfied with their symptom control and showed higher satisfaction with the treatment received.
Conclusions
This systematic review showed that surgical management of GERD is more effective than medical management with respect to patient-relevant outcomes in the short and medium term. However, long-term studies still are needed to determine whether antireflux surgery is an equivalent alternative to lifelong medical treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dent J, El-Serag H, Wallander MA, Johansson S (2005) Epidemiology of gastrooesoghageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut 54:710–717
Moller Hansen J, Wildner-Christensen M, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB (2009) Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in a Danish Population: a prospective follow-up analysis of symptoms, quality-of-life, and health-care use. Am J Gastroenterol 104:2394–2403
Katz PO, Gerson LB, Vela MF (2013) Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 108:308–328
Khalili H, Huang ES, Jacobson BC, Camargo CA, Feskanich D, Chan AT (2012) Use of proton pump inhibitors and risk of hip fracture in relation to dietary and lifestyle factors: a prospective cohort study. BMJ 344:e372
Gray SL, LACroix AZ, Larson J, Robbins J, Cauley JA, Manson JE, Chen Z (2010) Proton pump inhibitor use, hip fracture, and change in bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: results from the Women’s Health Initiative. Arch Int Med 170:765–771
Neufel M, Graham A (2007) Levels of evidence available for techniques in antireflux surgery. Dis Esophagus 20:161–167
Koch OO, Kaindlstorfer A, Antoniou SA, Luketina RR, Emmanuel K, Pointner R (2013) Comparison of results from a randomized trial 1 year after laparoscopic Nissen and Toupet fundoplications. Surg Endosc 27(7):2383–2390
Behar J, Sheahan DG, Biancani P, Spiro HM, Storer EH (1975) Medical and surgical management of reflux esophagitis: a 38-month report of a prospective clinical trial. N Eng J Med 293:263–268
Spechler SJ (1992) Comparison of medical and surgical therapy for complicated gastroesophageal reflux disease in veterans. The Department of Veterans Affairs Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Study Group. N Engl J Med 326:786–792
Allgood PC, Bachmann M (2000) Medical or surgical treatment for chronic gastrooesophageal reflux? A systematic review of published evidence of effectiveness. Eur J Surg 166:713–721
Urbach DR, Horvath KD, Baxter NN, Jobe BA, Madan AK, Pryor AD, Khaitan L, Torquati A, Brower ST, Trus TL, Schwaitzberg S (2007) A research agenda for gastrointestinal and endoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc 21:1518–1525
Frazzoni M, Piccoli M, Conigliaro R, Manta R, Frazzoni L, Melotti G (2013) Refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease as diagnosed by impedance-pH monitoring can be cured by laparoscopic fundoplication. Surg Endosc 27(8):2940–2946
Juni P, Altman DG, Egger M (2001) Systematic reviews in health care: assessing the quality of controlled clinical trials. BMJ 323:42–46
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Spechler SJ, Lee E, Ahnen D, Goyal RK, Hirano I, Ramirez F, Raufman JP, Sampliner R, Schnell T, Sontag S, Vlahcevic ZR, Young R, Williford W (2001) Long-term outcome of medical and surgical therapies for gastroesophageal reflux disease: follow-up of a randomized con-trolled trial. JAMA 285:2331–2338
Lundell L, Miettinen P, Myrvold HE, Pedersen SA, Liedman B, Hatlebakk JG, Julkonen R, Levander K, Carlsson J, Lamm M, Wiklund I (2001) Continued (5-year) follow-up of a randomized clinical study comparing antireflux surgery and omeprazole in gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 192:172–179
Lundell L, Miettinen P, Myrvold HE, Hatlebakk JG, Wallin L, Engström C, Julkunen R, Montgomery M, Malm A, Lind T, Walan A, Nordic GERD Study Group (2009) Comparison of outcomes twelve years after antireflux surgery or omeprazole maintenance therapy for reflux esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:1292–1298
Mahon D, Rhodes M, Decadt B, Hindmarsh A, Lowndes R, Beckingham I, Koo B, Newcombe RG (2005) Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication compared with proton pump inhibitors for treatment of chronic gastroesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 92:695–699
Mehta S, Bennett J, Mahon D, Rhodes M (2006) Prospective trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication versus proton pump inhibitor therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease: seven-year follow-up. J Gastrointest Surg 10:1312–1317
Anvari M, Allen C, Marshall J, Armstrong D, Goeree R, Ungar W, Goldsmith C (2006) A randomized controlled trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication versus proton pump inhibitors for treatment of patients with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease: one-year follow-up. Surg Innov 13:238–249
Anvari M, Allen C, Marshall J, Armstrong D, Goeree R, Ungar W, Goldsmith C (2011) A randomized controlled trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication versus proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of patients with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): 3-year outcomes. Surg Endosc 25:2547–2554
Grant AM, Wileman SM, Ramsay CR, Mowat NA, Krukowski ZH, Heading RC, Thursz MR, Campbell MK, REFLUX Trial Group (2008) Minimal access surgery compared with medical management for chronic gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: UK collaborative randomised trial. BMJ 337:a2664
Grant AM, Cotton SC, Boachie C, Ramsay CR, Krukowski ZH, Heading RC, Campbell MK, REFLUX Trial Group (2013) Minimal access surgery compared with medical management for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: five year follow-up of a randomised controlled trial (REFLUX). BMJ 346:f1908
Lundell L, Attwood S, Ell C, Fiocca R, Galmiche JP, Hatlebakk J, Lind T, Junghard O, LOTUS trial collaborators (2008) Comparing laparoscopic antireflux surgery with esomeprazole in the management of patients with chronic gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a 3-year interim analysis of the LOTUS trial. Gut 57:1207–1213
Galmiche JP, Hatlebakk J, Attwood S, Ell C, Fiocca R, Eklund S, Långström G, Lind T, Lundell L, LOTUS Trial Collaborators (2011) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery vs. esomeprazole treatment for chronic GERD: the LOTUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA 305:1969–1977
Egger M (2001) Systematic reviews in health care: meta-analysis in context. BMJ, London
Higgins JPT, Green S (2009) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, version 5.0.2. at www.cochrane-handbook.org. Accessed 18 Mar 2013
Noble LJ, Dalzell AM, El-Matary W (2012) The relationship between percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children: a systematic review. Surg Endosc 26:2504–2512
Wileman SM, McCann S, Grant AM, Krukowski ZH, Bruce J (2010) Medical versus surgical management for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 17(3):CD003243
Miholic J, Hafez J, Lenglinger J, Wrba F, Wischin C, Schütz K, Hudec M (2012) Hiatal hernia, Barrett’s esophagus, and long-term symptom control after laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux. Surg Endosc 26:3225–3231
Ip S, Tatsioni A, Conant A, Karagozian R, Fu L, Chew P, Raman G, Lau J, Bonis P (2009) Predictors of clinical outcomes following fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease remain insufficiently defined: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol 104:752
NICE (2004) Dyspepsia: managing dyspepsia in adults in primary care: clinical guidelines, CG17. at http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/pdf/CG017fullguideline.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2013
Stefanidis D, Hope WW, Kohn GP, Reardon PR, Richardson WS, Fanelli RD, SAGES Guidelines Committee (2010) Guidelines for surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 24:2647–2669
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Michaela Hänsel, Department of Primary Medical Care, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, for her help in performing the literature search and screening of eliglible articles. This work was conducted only with the resources of the Institute for Social Medicine and Epidemiology, University of Lübeck, Germany, and the Department of Primary Medical Care, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Germany.
Disclosures
Nadja Rickenbacher, Thomas Kötter, Michael M. Kochen, Martin Scherer, and Eva Blozik have no conflicts of interests or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rickenbacher, N., Kötter, T., Kochen, M.M. et al. Fundoplication versus medical management of gastroesophageal reflux disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 28, 143–155 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3140-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3140-z