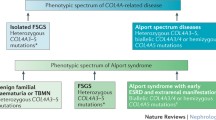
Abstract
Recent expert guidelines recommend genetic testing for the diagnosis of Alport syndrome. Here, we describe current best practice and likely future developments. In individuals with suspected Alport syndrome, all three COL4A5, COL4A3 and COL4A4 genes should be examined for pathogenic variants, probably by high throughput-targeted next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, with a customised panel for simultaneous testing of the three Alport genes. These techniques identify up to 95% of pathogenic COL4A variants. Where causative pathogenic variants cannot be demonstrated, the DNA should be examined for deletions or insertions by re-examining the NGS sequencing data or with multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA). These techniques identify a further 5% of variants, and the remaining few changes include deep intronic splicing variants or cases of somatic mosaicism. Where no pathogenic variants are found, the basis for the clinical diagnosis should be reviewed. Genes in which mutations produce similar clinical features to Alport syndrome (resulting in focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis, complement pathway disorders, MYH9-related disorders, etc.) should be examined. NGS approaches have identified novel combinations of pathogenic variants in Alport syndrome. Two variants, with one in COL4A3 and another in COL4A4, produce a more severe phenotype than an uncomplicated heterozygous change. NGS may also identify further coincidental pathogenic variants in genes for podocyte-expressed proteins that also modify the phenotype. Our understanding of the genetics of Alport syndrome is evolving rapidly, and both genetic and non-genetic factors are likely to contribute to the observed phenotypic variability.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gubler M, Levy M, Broyer M, Naizot C, Gonzales G, Perrin D, Habib R (1981) Alport’s syndrome. A report of 58 cases and a review of the literature. Am J Med 70:493–505
Habib R, Gubler MC, Hinglais N, Noel LH, Droz D, Levy M, Mahieu P, Foidart JM, Perrin D, Bois E, Grunfeld JP (1982) Alport’s syndrome: experience at Hopital Necker. Kidney Int Suppl 11:S20–S28
Grunfeld JP, Joly D (1997) Hereditary kidney diseases in adults. Rev Prat 47:1566–1569
Barker DF, Hostikka SL, Zhou J, Chow LT, Oliphant AR, Gerken SC, Gregory MC, Skolnick MH, Atkin CL, Tryggvason K (1990) Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science 248:1224–1227
Mochizuki T, Lemmink HH, Mariyama M, Antignac C, Gubler MC, Pirson Y, Verellen-Dumoulin C, Chan B, Schroder CH, Smeets HJ, Reeders ST (1994) Identification of mutations in the alpha 3(IV) and alpha 4(IV) collagen genes in autosomal recessive Alport syndrome. Nat Genet 8:77–81
Feingold J, Bois E, Chompret A, Broyer M, Gubler MC, Grunfeld JP (1985) Genetic heterogeneity of Alport syndrome. Kidney Int 27:672–677
Savige J, Gregory M, Gross O, Kashtan C, Ding J, Flinter F (2013) Expert guidelines for the management of Alport syndrome and thin basement membrane nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:364–375
Jais JP, Knebelmann B, Giatras I, De Marchi M, Rizzoni G, Renieri A, Weber M, Gross O, Netzer KO, Flinter F, Pirson Y, Dahan K, Wieslander J, Persson U, Tryggvason K, Martin P, Hertz JM, Schroder C, Sanak M, Carvalho MF, Saus J, Antignac C, Smeets H, Gubler MC (2003) X-linked Alport syndrome: natural history and genotype-phenotype correlations in girls and women belonging to 195 families: a “European Community Alport Syndrome Concerted Action” study. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2603–2610
Jais JP, Knebelmann B, Giatras I, De Marchi M, Rizzoni G, Renieri A, Weber M, Gross O, Netzer KO, Flinter F, Pirson Y, Verellen C, Wieslander J, Persson U, Tryggvason K, Martin P, Hertz JM, Schroder C, Sanak M, Krejcova S, Carvalho MF, Saus J, Antignac C, Smeets H, Gubler MC (2000) X-linked Alport syndrome: natural history in 195 families and genotype-phenotype correlations in males. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:649–657
Gross O, Netzer KO, Lambrecht R, Seibold S, Weber M (2002) Meta-analysis of genotype-phenotype correlation in X-linked Alport syndrome: impact on clinical counselling. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17:1218–1227
Savige J, Storey H, Il Cheong H, Gyung Kang H, Park E, Hilbert P, Persikov A, Torres-Fernandez C, Ars E, Torra R, Hertz JM, Thomassen M, Shagam L, Wang D, Wang Y, Flinter F, Nagel M (2016) X-linked and autosomal recessive Alport syndrome: pathogenic variant features and further genotype-phenotype correlations. PLoS One 11:e0161802
Zhou J, Mochizuki T, Smeets H, Antignac C, Laurila P, de Paepe A, Tryggvason K, Reeders ST (1993) Deletion of the paired alpha 5(IV) and alpha 6(IV) collagen genes in inherited smooth muscle tumors. Science 261:1167–1169
Kashtan CE, Butkowski RJ, Kleppel MM, First MR, Michael AF (1990) Posttransplant anti-glomerular basement membrane nephritis in related males with Alport syndrome. J Lab Clin Med 116:508–515
Ding J, Zhou J, Tryggvason K, Kashtan CE (1994) COL4A5 deletions in three patients with Alport syndrome and posttransplant antiglomerular basement membrane nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 5:161–168
Deltas C, Pierides A, Voskarides K (2013) Molecular genetics of familial hematuric diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:2946–2960
Fallerini C, Dosa L, Tita R, Del Prete D, Feriozzi S, Gai G, Clementi M, La Manna A, Miglietti N, Mancini R, Mandrile G, Ghiggeri GM, Piaggio G, Brancati F, Diano L, Frate E, Pinciaroli AR, Giani M, Castorina P, Bresin E, Giachino D, De Marchi M, Mari F, Bruttini M, Renieri A, Ariani F (2014) Unbiased next generation sequencing analysis confirms the existence of autosomal dominant Alport syndrome in a relevant fraction of cases. Clin Genet 86:252–257
Fallerini C, Baldassarri M, Trevisson E, Morbidoni V, La Manna A, Lazzarin R, Pasini A, Barbano G, Pinciaroli AR, Garosi G, Frullanti E, Pinto AM, Mencarelli MA, Mari F, Renieri A, Ariani F (2017) Alport syndrome: impact of digenic inheritance in patients management. Clin Genet 92:34–44
Mencarelli MA, Heidet L, Storey H, van Geel M, Knebelmann B, Fallerini C, Miglietti N, Antonucci MF, Cetta F, Sayer JA, van den Wijngaard A, Yau S, Mari F, Bruttini M, Ariani F, Dahan K, Smeets B, Antignac C, Flinter F, Renieri A (2015) Evidence of digenic inheritance in Alport syndrome. J Med Genet 52:163–174
Voskarides K, Stefanou C, Pieri M, Demosthenous P, Felekkis K, Arsali M, Athanasiou Y, Xydakis D, Stylianou K, Daphnis E, Goulielmos G, Loizou P, Savige J, Hohne M, Volker LA, Benzing T, Maxwell PH, Gale DP, Gorski M, Boger C, Kollerits B, Kronenberg F, Paulweber B, Zavros M, Pierides A, Deltas C (2017) A functional variant in NEPH3 gene confers high risk of renal failure in primary hematuric glomerulopathies. Evidence for predisposition to microalbuminuria in the general population. PLoS One 12:e0174274
Savige J, Colville D, Rheault M, Gear S, Lennon R, Lagas S, Finlay M, Flinter F (2016) Alport syndrome in women and girls. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11:1713–1720
Wang YY, Rana K, Tonna S, Lin T, Sin L, Savige J (2004) COL4A3 mutations and their clinical consequences in thin basement membrane nephropathy (TBMN). Kidney Int 65:786–790
Hanson H, Storey H, Pagan J, Flinter F (2011) The value of clinical criteria in identifying patients with X-linked Alport syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:198–203
Gast C, Pengelly RJ, Lyon M, Bunyan DJ, Seaby EG, Graham N, Venkat-Raman G, Ennis S (2016) Collagen (COL4A) mutations are the most frequent mutations underlying adult focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 31:961–970
Voskarides K, Damianou L, Neocleous V, Zouvani I, Christodoulidou S, Hadjiconstantinou V, Ioannou K, Athanasiou Y, Patsias C, Alexopoulos E, Pierides A, Kyriacou K, Deltas C (2007) COL4A3/COL4A4 mutations producing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and renal failure in thin basement membrane nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:3004–3016
Savige J, Rana K, Tonna S, Buzza M, Dagher H, Wang YY (2003) Thin basement membrane nephropathy. Kidney Int 64:1169–1178
Usui T, Ichibe M, Hasegawa S, Miki A, Baba E, Tanimoto N, Abe H (2004) Symmetrical reduced retinal thickness in a patient with Alport syndrome. Retina 24:977–979
Savige J, Sheth S, Leys A, Nicholson A, Mack HG, Colville D (2015) Ocular features in Alport syndrome: pathogenesis and clinical significance. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:703–709
Ahmed F, Kamae KK, Jones DJ, Deangelis MM, Hageman GS, Gregory MC, Bernstein PS (2013) Temporal macular thinning associated with X-linked Alport syndrome. JAMA Ophthalmol 131:777–782
Kashtan CE (1999) Alport syndrome: is diagnosis only skin-deep? Kidney Int 55:1575–1576
Yoshioka K, Hino S, Takemura T, Maki S, Wieslander J, Takekoshi Y, Makino H, Kagawa M, Sado Y, Kashtan CE (1994) Type IV collagen alpha 5 chain. Normal distribution and abnormalities in X-linked Alport syndrome revealed by monoclonal antibody. Am J Pathol 144:986–996
Tan R, Colville D, Wang YY, Rigby L, Savige J (2010) Alport retinopathy results from “severe” COL4A5 mutations and predicts early renal failure. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:34–38
Persikov AV, Pillitteri RJ, Amin P, Schwarze U, Byers PH, Brodsky B (2004) Stability related bias in residues replacing glycines within the collagen triple helix (Gly-Xaa-Yaa) in inherited connective tissue disorders. Hum Mutat 24:330–337
Rheault MN, Kren SM, Hartich LA, Wall M, Thomas W, Mesa HA, Avner P, Lees GE, Kashtan CE, Segal Y (2010) X-inactivation modifies disease severity in female carriers of murine X-linked Alport syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:764–769
Storey H, Savige J, Sivakumar V, Abbs S, Flinter FA (2013) COL4A3/COL4A4 mutations and features in individuals with autosomal recessive Alport syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1945–1954
Murray LS, Lu Y, Taggart A, Van Regemorter N, Vilain C, Abramowicz M, Kadler KE, Van Agtmael T (2014) Chemical chaperone treatment reduces intracellular accumulation of mutant collagen IV and ameliorates the cellular phenotype of a COL4A2 mutation that causes haemorrhagic stroke. Hum Mol Genet 23:283–292
Bateman JF, Freddi S, Nattrass G, Savarirayan R (2003) Tissue-specific RNA surveillance? Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay causes collagen X haploinsufficiency in Schmid metaphyseal chondrodysplasia cartilage. Hum Mol Genet 12:217–225
Barker DF, Pruchno CJ, Jiang X, Atkin CL, Stone EM, Denison JC, Fain PR, Gregory MC (1996) A mutation causing Alport syndrome with tardive hearing loss is common in the western United States. Am J Hum Genet 58:1157–1165
Voskarides K, Patsias C, Pierides A, Deltas C (2008) COL4A3 founder mutations in Greek-Cypriot families with thin basement membrane nephropathy and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis dating from around 18th century. Genet Test 12:273–278
Slajpah M, Gorinsek B, Berginc G, Vizjak A, Ferluga D, Hvala A, Meglic A, Jaksa I, Furlan P, Gregoric A, Kaplan-Pavlovcic S, Ravnik-Glavac M, Glavac D (2007) Sixteen novel mutations identified in COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5 genes in Slovenian families with Alport syndrome and benign familial hematuria. Kidney Int 71:1287–1295
Miner JH, Baigent C, Flinter F, Gross O, Judge P, Kashtan CE, Lagas S, Savige J, Blatt D, Ding J, Gale DP, Midgley JP, Povey S, Prunotto M, Renault D, Skelding J, Turner AN, Gear S (2014) The 2014 International workshop on Alport syndrome. Kidney Int 86:679–684
Moriniere V, Dahan K, Hilbert P, Lison M, Lebbah S, Topa A, Bole-Feysot C, Pruvost S, Nitschke P, Plaisier E, Knebelmann B, Macher MA, Noel LH, Gubler MC, Antignac C, Heidet L (2014) Improving mutation screening in familial hematuric nephropathies through next generation sequencing. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2740–2751
Hertz JM, Thomassen M, Storey H, Flinter F (2015) Clinical utility gene card for: Alport syndrome - update 2014. Eur J Hum Genet 23 (9)
Baleato RM, Guthrie PL, Gubler MC, Ashman LK, Roselli S (2008) Deletion of CD151 results in a strain-dependent glomerular disease due to severe alterations of the glomerular basement membrane. Am J Pathol 173:927–937
Kovacs G, Kalmar T, Endreffy E, Ondrik Z, Ivanyi B, Rikker C, Haszon I, Turi S, Sinko M, Bereczki C, Maroti Z (2016) Efficient targeted next generation sequencing-based workflow for differential diagnosis of Alport-related disorders. PLoS One 11:e0149241
Artuso R, Fallerini C, Dosa L, Scionti F, Clementi M, Garosi G, Massella L, Epistolato MC, Mancini R, Mari F, Longo I, Ariani F, Renieri A, Bruttini M (2012) Advances in Alport syndrome diagnosis using next-generation sequencing. Eur J Hum Genet 20:50–57
King K, Flinter FA, Nihalani V, Green PM (2002) Unusual deep intronic mutations in the COL4A5 gene cause X linked Alport syndrome. Hum Genet 111:548–554
Nakazato H, Hattori S, Ushijima T, Matsuura T, Koitabashi Y, Takada T, Yoshioka K, Endo F, Matsuda I (1994) Mutations in the COL4A5 gene in Alport syndrome: a possible mutation in primordial germ cells. Kidney Int 46:1307–1314
Hertz JM, Thomassen M, Storey H, Flinter F (2012) Clinical utility gene card for: Alport syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 20 (6)
King K, Flinter FA, Green PM (2006) A two-tier approach to mutation detection in the COL4A5 gene for Alport syndrome. Hum Mutat 27:1061
Tazon-Vega B, Ars E, Burset M, Santin S, Ruiz P, Fernandez-Llama P, Ballarin J, Torra R (2007) Genetic testing for X-linked Alport syndrome by direct sequencing of COL4A5 cDNA from hair root RNA samples. Am J Kidney Dis 50:257 e251–214
Zhang H, Ding J, Wang F, Zhao D (2011) Mutation detection of COL4An gene based on mRNA of peripheral blood lymphocytes and prenatal diagnosis of Alport syndrome in China. Nephrology (Carlton) 16:377–380
Bonnet C, Krieger S, Vezain M, Rousselin A, Tournier I, Martins A, Berthet P, Chevrier A, Dugast C, Layet V, Rossi A, Lidereau R, Frebourg T, Hardouin A, Tosi M (2008) Screening BRCA1 and BRCA2 unclassified variants for splicing mutations using reverse transcription PCR on patient RNA and an ex vivo assay based on a splicing reporter minigene. J Med Genet 45:438–446
Sharma N, Sosnay PR, Ramalho AS, Douville C, Franca A, Gottschalk LB, Park J, Lee M, Vecchio-Pagan B, Raraigh KS, Amaral MD, Karchin R, Cutting GR (2014) Experimental assessment of splicing variants using expression minigenes and comparison with in silico predictions. Hum Mutat 35:1249–1259
Tournier I, Vezain M, Martins A, Charbonnier F, Baert-Desurmont S, Olschwang S, Wang Q, Buisine MP, Soret J, Tazi J, Frebourg T, Tosi M (2008) A large fraction of unclassified variants of the mismatch repair genes MLH1 and MSH2 is associated with splicing defects. Hum Mutat 29:1412–1424
Malone AF, Funk SD, Alhamad T, Miner JH (2017) Functional assessment of a novel COL4A5 splice region variant and immunostaining of plucked hair follicles as an alternative method of diagnosis in X-linked Alport syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 32:997–1003
Plant KE, Boye E, Green PM, Vetrie D, Flinter FA (2000) Somatic mosaicism associated with a mild Alport syndrome phenotype. J Med Genet 37:238–239
Bruttini M, Vitelli F, Meloni I, Rizzari G, Volpe MD, Mazzucco G, Marchi MD, Renieri A (2000) Mosaicism in Alport syndrome with genetic counselling. J Med Genet 37:717–719
Krol RP, Nozu K, Nakanishi K, Iijima K, Takeshima Y, Fu XJ, Nozu Y, Kaito H, Kanda K, Matsuo M, Yoshikawa N (2008) Somatic mosaicism for a mutation of the COL4A5 gene is a cause of mild phenotype male Alport syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:2525–2530
Beicht S, Strobl-Wildemann G, Rath S, Wachter O, Alberer M, Kaminsky E, Weber LT, Hinrichsen T, Klein HG, Hoefele J (2013) Next generation sequencing as a useful tool in the diagnostics of mosaicism in Alport syndrome. Gene 526:474–477
Fu XJ, Nozu K, Kaito H, Ninchoji T, Morisada N, Nakanishi K, Yoshikawa N, Ohtsubo H, Matsunoshita N, Kamiyoshi N, Matsumura C, Takagi N, Maekawa K, Taniguchi-Ikeda M, Iijima K (2016) Somatic mosaicism and variant frequency detected by next-generation sequencing in X-linked Alport syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 24:387–391
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17:405–424
Wallis Y, Payne S, McAnulty C, Bodmer D, Sistermans E, Robertson K, Moore D, Abbs S, Deans Z, Deverau A (2013) Practice guidelines for the evaluation of pathogenicity and reporting of sequence variants in clinical molecular genetics, Association for Clinical Genetic Science, UK, http://www.acgs.uk.com/
MacArthur DG, Manolio TA, Dimmock DP, Rehm HL, Shendure J, Abecasis GR, Adams DR, Altman RB, Antonarakis SE, Ashley EA, Barrett JC, Biesecker LG, Conrad DF, Cooper GM, Cox NJ, Daly MJ, Gerstein MB, Goldstein DB, Hirschhorn JN, Leal SM, Pennacchio LA, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Sunyaev SR, Valle D, Voight BF, Winckler W, Gunter C (2014) Guidelines for investigating causality of sequence variants in human disease. Nature 508:469–476
Parkin JD, San Antonio JD, Pedchenko V, Hudson B, Jensen ST, Savige J (2011) Mapping structural landmarks, ligand binding sites, and missense mutations to the collagen IV heterotrimers predicts major functional domains, novel interactions, and variation in phenotypes in inherited diseases affecting basement membranes. Hum Mutat 32:127–143
Malone AF, Funk SD, Alhamad T, Miner JH (2016) Functional assessment of a novel COL4A5 splice region variant and immunostaining of plucked hair follicles as an alternative method of diagnosis in X-linked Alport syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 32:997–1003
Marcocci E, Uliana V, Bruttini M, Artuso R, Silengo MC, Zerial M, Bergesio F, Amoroso A, Savoldi S, Pennesi M, Giachino D, Rombola G, Fogazzi GB, Rosatelli C, Martinhago CD, Carmellini M, Mancini R, Di Costanzo G, Longo I, Renieri A, Mari F (2009) Autosomal dominant Alport syndrome: molecular analysis of the COL4A4 gene and clinical outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:1464–1471
Rosado C, Bueno E, Felipe C, Valverde S, Gonzalez-Sarmiento R (2015) Study of the true clinical progression of autosomal dominant Alport syndrome in a European population. Kidney Blood Press Res 40:435–442
Temme J, Peters F, Lange K, Pirson Y, Heidet L, Torra R, Grunfeld JP, Weber M, Licht C, Muller GA, Gross O (2012) Incidence of renal failure and nephroprotection by RAAS inhibition in heterozygous carriers of X-chromosomal and autosomal recessive Alport mutations. Kidney Int 81:779–783
Stefanou C, Pieri M, Savva I, Georgiou G, Pierides A, Voskarides K, Deltas C (2015) Co-inheritance of functional Podocin variants with heterozygous collagen IV mutations predisposes to renal failure. Nephron 130:200–212
Mohammad M, Nanra R, Colville D, Trevillian P, Wang Y, Storey H, Flinter F, Savige J (2014) A female with X-linked Alport syndrome and compound heterozygous COL4A5 mutations. Pediatr Nephrol 29:481–485
Lennon R, Stuart HM, Bierzynska A, Randles MJ, Kerr B, Hillman KA, Batra G, Campbell J, Storey H, Flinter FA, Koziell A, Welsh GI, Saleem MA, Webb NJ, Woolf AS (2015) Coinheritance of COL4A5 and MYO1E mutations accentuate the severity of kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 30:1459–1465
Tonna S, Wang YY, Wilson D, Rigby L, Tabone T, Cotton R, Savige J (2008) The R229Q mutation in NPHS2 may predispose to proteinuria in thin-basement-membrane nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 23:2201–2207
Bullich G, Trujillano D, Santin S, Ossowski S, Mendizabal S, Fraga G, Madrid A, Ariceta G, Ballarin J, Torra R, Estivill X, Ars E (2015) Targeted next-generation sequencing in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: mutations in multiple glomerular genes may influence disease severity. Eur J Hum Genet 23:1192–1199
Tsukaguchi H, Sudhakar A, Le TC, Nguyen T, Yao J, Schwimmer JA, Schachter AD, Poch E, Abreu PF, Appel GB, Pereira AB, Kalluri R, Pollak MR (2002) NPHS2 mutations in late-onset focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: R229Q is a common disease-associated allele. J Clin Invest 110:1659–1666
Savige J, Amos L, Ierino F, Mack HG, Symons RC, Hughes P, Nicholls K, Colville D (2016) Retinal disease in the C3 glomerulopathies and the risk of impaired vision. Ophthalmic Genet 37:369–376
Gale DP, de Jorge EG, Cook HT, Martinez-Barricarte R, Hadjisavvas A, McLean AG, Pusey CD, Pierides A, Kyriacou K, Athanasiou Y, Voskarides K, Deltas C, Palmer A, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, de Cordoba SR, Maxwell PH, Pickering MC (2010) Identification of a mutation in complement factor H-related protein 5 in patients of Cypriot origin with glomerulonephritis. Lancet 376:794–801
Heath KE, Campos-Barros A, Toren A, Rozenfeld-Granot G, Carlsson LE, Savige J, Denison JC, Gregory MC, White JG, Barker DF, Greinacher A, Epstein CJ, Glucksman MJ, Martignetti JA (2001) Nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA mutations define a spectrum of autosomal dominant macrothrombocytopenias: may-Hegglin anomaly and Fechtner, Sebastian, Epstein, and Alport-like syndromes. Am J Hum Genet 69:1033–1045
Castelletti F, Donadelli R, Banterla F, Hildebrandt F, Zipfel PF, Bresin E, Otto E, Skerka C, Renieri A, Todeschini M, Caprioli J, Caruso RM, Artuso R, Remuzzi G, Noris M (2008) Mutations in FN1 cause glomerulopathy with fibronectin deposits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:2538–2543
Plaisier E, Gribouval O, Alamowitch S, Mougenot B, Prost C, Verpont MC, Marro B, Desmettre T, Cohen SY, Roullet E, Dracon M, Fardeau M, Van Agtmael T, Kerjaschki D, Antignac C, Ronco P (2007) COL4A1 mutations and hereditary angiopathy, nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps. N Engl J Med 357:2687–2695
Scolari F, Amoroso A, Savoldi S, Mazzola G, Prati E, Valzorio B, Viola BF, Nicola B, Movilli E, Sandrini M, Campanini M, Maiorca R (1999) Familial clustering of IgA nephropathy: further evidence in an Italian population. Am J Kidney Dis 33:857–865
Milillo A, La Carpia F, Costanzi S, D'Urbano V, Martini M, Lanuti P, Vischini G, Larocca LM, Marchisio M, Miscia S, Amoroso A, Gurrieri F, Sangiorgi E (2015) A SPRY2 mutation leading to MAPK/ERK pathway inhibition is associated with an autosomal dominant form of IgA nephropathy. Eur J Hum Genet 23:1673–1678
Heidet L, Bongers EM, Sich M, Zhang SY, Loirat C, Meyrier A, Broyer M, Landthaler G, Faller B, Sado Y, Knoers NV, Gubler MC (2003) In vivo expression of putative LMX1B targets in nail-patella syndrome kidneys. Am J Pathol 163:145–155
Morello R, Zhou G, Dreyer SD, Harvey SJ, Ninomiya Y, Thorner PS, Miner JH, Cole W, Winterpacht A, Zabel B, Oberg KC, Lee B (2001) Regulation of glomerular basement membrane collagen expression by LMX1B contributes to renal disease in nail patella syndrome. Nat Genet 27:205–208
Savige J, Dalgleish R, Cotton RG, den Dunnen JT, Macrae F, Povey S (2015) The Human Variome Project: ensuring the quality of DNA variant databases in inherited renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 30:1893–1901
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The following guidelines were developed by an international group of expert adult and paediatric physicians, geneticists and researchers who work on Alport syndrome, and met for discussion at the Second Alport syndrome meeting in Gottingen, Germany in 2015 and at Glagow, UK in 2017. The guidelines have been further refined until a consensus was reached after a year of email discussions. These guidelines are complementary to the ‘Expert guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Alport syndrome and thin basement membrane nephropathy’ (JASN 2013).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savige, J., Ariani, F., Mari, F. et al. Expert consensus guidelines for the genetic diagnosis of Alport syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 34, 1175–1189 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-3985-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-3985-4