Abstract
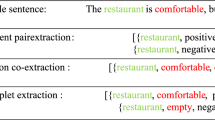
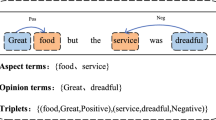
Aspect-oriented Fine-grained Opinion Extraction (AFOE) aims to extract the aspect terms, corresponding opinion terms and sentiment polarity in a target sentence. Most previous methods treat AFOE as word-level or span-level task, which ignore the complementarity of these two tasks. To integrate the merits of word-level and span-level information, we construct an end-to-end Span-based Multi-Table Labeling (SpanMTL) framework. SpanMTL combines word-based and span-based table labeling to tackle AFOE task. Specifically, in the proposed model, we use two separate BiLSTMs to encode the information of aspect and opinion terms into a word-based 2D representation table. Based on the table, we construct span-based table with CNN by associating the word-pair representations. At last, we integrate the table label distributions of word- and span-based table labeling to generate a multi-table labeling. The proposed method improves the performances of Opinion Pair Extraction (OPE) and Opinion Triplet Extraction (OTE) tasks by introducing span information, especially on the datasets with lots of spans. We have conducted various experiments on AFOE datasets to validate our method. The experimental results show that our method outperforms other baselines when the sentences having lots of span information.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article: Wu, Z., Ying, C., Zhao, F., Fan, Z., Dai, X., Xia, R. used grid tagging scheme for aspect-oriented fine-grained opinion extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.04640 (2020).
References
Bakshi RK, Kaur N, Kaur R, Kaur G (2016) Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. In: 2016 3rd International conference on computing for sustainable global development (INDIACom), pp. 452–455. IEEE
Bojanowski P, Grave E, Joulin A, Mikolov T (2017) Enriching word vectors with subword information. Trans Assoc Comput Linguist 5:135–146
Boumhidi A, Benlahbib A, Nfaoui EH (2022) Cross-platform reputation generation system based on aspect-based sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 10:2515–2531. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3139956
Cai H, Tu Y, Zhou X, Yu J, Xia R (2020) Aspect-category based sentiment analysis with hierarchical graph convolutional network. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on computational linguistics
Cambria E (2016) Affective computing and sentiment analysis. IEEE Intell Syst 31(2):102–107. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIS.2016.31
Cambria E, Liu Q, Decherchi S, Xing F, Kwok K (2022) Senticnet 7: a commonsense-based neurosymbolic ai framework for explainable sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of LREC 2022
Chen S, Wang Y, Liu J, Wang Y (2021) Bidirectional machine reading comprehension for aspect sentiment triplet extraction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 35(14):12666–12674
Cho K, van Merriënboer B, Gulcehre C, Bahdanau D, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bengio Y (2014) Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder–decoder for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), pp. 1724–1734. Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/D14-1179. https://aclanthology.org/D14-1179
Dai H, Song Y (2019) Neural aspect and opinion term extraction with mined rules as weak supervision. In: Proceedings of the 57th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp. 5268–5277. Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P19-1520. https://aclanthology.org/P19-1520
Dong L, Wei F, Tan C, Tang D, Zhou M, Xu K (2014) Adaptive recursive neural network for target-dependent twitter sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 52nd annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (volume 2: Short Papers), pp. 49–54
Fan Z, Wu Z, Dai X, Huang S, Chen J (2019) Target-oriented opinion words extraction with target-fused neural sequence labeling. In: Proceedings of the 2019 conference of the north american chapter of the association for computational linguistics: human language technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pp. 2509–2518
Feldman R (2013) Techniques and applications for sentiment analysis. Commun ACM 56(4):82–89
Feng A, Zhang X, Song X (2022) Unrestricted attention may not be all you need-masked attention mechanism focuses better on relevant parts in aspect-based sentiment analysis. IEEE Access 10:8518–8528. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3142178
Graves A, Fernández S, Schmidhuber J (2007) Multi-dimensional recurrent neural networks. In: International conference on artificial neural networks, pp. 549–558. Springer
He R, Lee WS, Ng HT, Dahlmeier D (2017) An unsupervised neural attention model for aspect extraction. In: Proceedings of the 55th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 388–397
He R, Lee WS, Ng HT, Dahlmeier D (2019) An interactive multi-task learning network for end-to-end aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 57th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp. 504–515. Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy . https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P19-1048. https://aclanthology.org/P19-1048
Huang L, Wang P, Li S, Liu T, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Yin D, Wang H (2021) First target and opinion then polarity: enhancing target-opinion correlation for aspect sentiment triplet extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.08549
Hu M, Liu B (2004) Mining and summarizing customer reviews. In: Proceedings of the Tenth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp. 168–177
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980
Kocoń J, Baran J, Gruza M, Janz A, Kajstura M, Kazienko P, Korczyński W, Miłkowski P, Piasecki M, Szołomicka J (2022) Neuro-symbolic models for sentiment analysis. In: International conference on computational science, pp. 667–681. Springer
Li Z, Li L, Zhou A, Lu H (2021) Jtsg: a joint term-sentiment generator for aspect-based sentiment analysis. Neurocomputing 459:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.06.045
Liang B, Su H, Gui L, Cambria E, Xu R (2022) Aspect-based sentiment analysis via affective knowledge enhanced graph convolutional networks. Knowl Based Syst 235:107643
Li X, Bing L, Li P, Lam W (2019) A unified model for opinion target extraction and target sentiment prediction. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 6714–6721
Liu P, Joty S, Meng H (2015) Fine-grained opinion mining with recurrent neural networks and word embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 2015 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp. 1433–1443
Liu G, Wu J, Zhou Z-H (2012) Key instance detection in multi-instance learning. In: Asian conference on machine learning, pp. 253–268. PMLR
Li Y, Wang F, Zhang W, Zhong S-h, Yin C, He Y (2021) A more fine-grained aspect-sentiment-opinion triplet extraction task. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.15255
Li Z, Wei Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Li X (2019) Exploiting coarse-to-fine task transfer for aspect-level sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 4253–4260
Mao Y, Shen Y, Yu C, Cai L (2021) A joint training dual-mrc framework for aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 35(15):13543–13551
Peng H, Xu L, Bing L, Huang F, Lu W, Si L (2020) Knowing what, how and why: a near complete solution for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 8600–8607
Pennington J, Socher R, Manning CD (2014) Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), pp. 1532–1543
Pontiki M, Galanis D, Papageorgiou H, Androutsopoulos I, Manandhar S, Al-Smadi M, Al-Ayyoub M, Zhao Y, Qin B, De Clercq O et al (2016) Semeval-2016 task 5: Aspect based sentiment analysis. In: International workshop on semantic evaluation, pp. 19–30
Pontiki M, Galanis D, Papageorgiou H, Manandhar S, Androutsopoulos I (2015) Semeval-2015 task 12: Aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 9th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval 2015), pp. 486–495
Pontiki M, Galanis D, Pavlopoulos J, Papageorgiou H, Androutsopoulos I, Manandhar S (2014) SemEval-2014 task 4: Aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 8th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval 2014), pp. 27–35. Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/S14-2004. https://aclanthology.org/S14-2004
Soni PK, Rambola R (2022) A survey on implicit aspect detection for sentiment analysis: terminology, issues, and scope. IEEE Access 10:63932–63957. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3183205
Tang D, Qin B, Liu T (2016) Aspect level sentiment classification with deep memory network. In: Proceedings of the 2016 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp. 214–224. Association for Computational Linguistics, Austin, Texas. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D16-1021. https://aclanthology.org/D16-1021
Tay Y, Tuan LA, Hui SC (2018) Learning to attend via word-aspect associative fusion for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 32
Wang W, Pan SJ, Dahlmeier D, Xiao X (2016) Recursive neural conditional random fields for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2016 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp. 616–626. Association for Computational Linguistics, Austin, Texas . https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D16-1059. https://aclanthology.org/D16-1059
Wang W, Pan SJ, Dahlmeier D, Xiao X (2017) Coupled multi-layer attentions for co-extraction of aspect and opinion terms. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 31
Wu Z, Ying C, Zhao F, Fan Z, Xia R (2020) Grid tagging scheme for aspect-oriented fine-grained opinion extraction. In: Findings of the association for computational linguistics: EMNLP 2020
Xu L, Li H, Lu W, Bing L (2020) Position-aware tagging for aspect sentiment triplet extraction. In: Proceedings of the 2020 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), pp. 2339–2349. Association for Computational Linguistics, Online. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.183. https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-main.183
Xu H, Liu B, Shu L, Yu PS (2018) Double embeddings and CNN-based sequence labeling for aspect extraction. In: Proceedings of the 56th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), pp. 592–598. Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P18-2094. https://aclanthology.org/P18-2094
Zhang C, Li Q, Song D, Wang B (2020) A multi-task learning framework for opinion triplet extraction. In: Findings of the association for computational linguistics: EMNLP 2020, pp. 819–828. Association for Computational Linguistics, Online. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.findings-emnlp.72. https://aclanthology.org/2020.findings-emnlp.72
Zhang Y, Qi P, Manning CD (2018) Graph convolution over pruned dependency trees improves relation extraction. In: Proceedings of the 2018 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp. 2205–2215. Association for Computational Linguistics, Brussels, Belgium. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D18-1244. https://aclanthology.org/D18-1244
Zhao M, Yang J, Zhang J, Wang S (2022) Aggregated graph convolutional networks for aspect-based sentiment classification. Inf Sci 600:73–93
Zhao H, Huang L, Zhang R, Lu Q, Xue H (2020) Spanmlt: a span-based multi-task learning framework for pair-wise aspect and opinion terms extraction. In: Proceedings of the 58th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp. 3239–3248
Zhuang L, Jing F, Zhu X-Y (2006) Movie review mining and summarization. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, pp. 43–50
Funding
This work was partially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.U1933114, No.62172418), Open Project Foundation of Information Security Evaluation Center of Civil Aviation, China (No.ISECCA-202005), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Civil Aviation University of China (No.3122022091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Y., Zhu, Y., Fan, W. et al. SpanMTL: a span-based multi-table labeling for aspect-oriented fine-grained opinion extraction. Soft Comput 27, 4627–4637 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07721-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07721-5