Summary
Background
The aim of this study was to compare short-term and mid-term outcomes in low-risk octogenarian population treated with transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation (tf-TAVI) or minimally invasive aortic valve replacement (mini-AVR) for severe aortic stenosis.
Methods
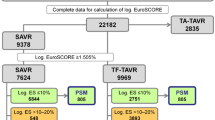
In this single-center, retrospective cohort study we gathered data on low-risk (Society of Thoracic Surgeons [STS] score < 4%) octogenarians before and after tf-TAVI and mini-AVR performed between January 2013 and May 2019; follow-up was completed in May 2022. Short-term outcomes were hospital length of stay, in-hospital all-cause mortality and other major postoperative outcomes. Mid-term clinical outcomes were 1‑year and 3‑year all-cause mortality. Propensity score-based matching was performed.
Results
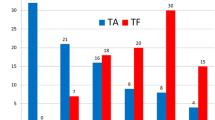
In total 106 patients were matched, resulting in 53 pairs. In-hospital complications were similar between the matched groups of patients with the exception of mild and moderate paravalvular leak (mini-AVR vs. tf-TAVI: mild PVL: 3.8% vs. 45.3%, p < 0.001; moderate PVL: 0% vs. 3.8%, p = 0.4952) and of postprocedural acute kidney injury that was more frequent in mini-AVR group (mini-AVR vs. tf-TAVI: 22.6% vs. 5.7%; p = 0.023). Hospital length of stay (p = 0.239) and in-hospital mortality (p = 0.495) did not differ between groups. The 1-year and 3‑year all-cause mortality Kaplan-Meier estimates were similar between mini-AVR and tf-TAVI.
Conclusion
In the present study on low-risk octogenarians, transfemoral TAVI and minimally invasive AVR showed comparable short-term and mid-term results. Both procedures are deemed safe and effective. Larger RCTs will be required to determine which low-risk patients will benefit most from TAVI.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cahill TJ, Chen M, Hayashida K, Latib A, Modine T, Piazza N, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation: current status and future perspectives. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(28):2625–34.
Thyregod HGH, Steinbrüchel DA, Ihlemann N, Nissen H, Kjeldsen BJ, Petursson P, et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis 1‑year results from the all-comers NOTION randomized clinical trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(20):2184–94.
Serruys PW, Modolo R, Reardon M, Miyazaki Y, Windecker S, Popma J, et al. One-year outcomes of patients with severe aortic stenosis and an STS PROM of less than three percent in the SURTAVI trial. EuroIntervention. 2018;14(8):877–83.
Mack MJ, Leon MB, Thourani VH, Makkar R, Kodali SK, Russo M, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a balloon-expandable valve in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(18):1695–705.
Popma JJ, Deeb GM, Yakubov SJ, Mumtaz M, Gada H, O’Hair D, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a self-expanding valve in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(18):1706–15.
Cosgrove DM, Sabik JF, Navia JL. Minimally invasive valve operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998;65(6):1535–9.
Bacco LD, Miceli A, Glauber M. Minimally invasive aortic valve surgery. J Thorac Dis. 2021;13(3):1945–59.
Brown ML, McKellar SH, Sundt TM, Schaff HV. Ministernotomy versus conventional sternotomy for aortic valve replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;137(3):670–679.e5.
Glauber M, Miceli A, Gilmanov D, Ferrarini M, Bevilacqua S, Farneti PA, et al. Right anterior minithoracotomy versus conventional aortic valve replacement: a propensity score matched study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;145(5):1222–6.
Salmasi MY, Hamilton H, Rahman I, Chien L, Rival P, Benedetto U, et al. Mini-sternotomy vs right anterior thoracotomy for aortic valve replacement. J Card Surg. 2020;35(7):1570–82.
Al-Maisary S, Farag M, Gussinklo WHT, Kremer J, Pleger ST, Leuschner F, et al. Are sutureless and rapid-deployment aortic valves a serious alternative to TA-TAVI? A matched-pairs analysis. J Clin Med. 2021;10(14):3072.
Miceli A, Gilmanov D, Murzi M, Marchi F, Ferrarini M, Cerillo AG, et al. Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement with a sutureless valve through a right anterior mini-thoracotomy versus transcatheter aortic valve implantation in high-risk patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;49(3):960–5.
Paparella D, Santarpino G, Malvindi PG, Moscarelli M, Marchese A, Guida P, et al. Minimally invasive surgical versus transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a multicenter study. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2019;23:100362.
Witberg G, Landes U, Lador A, Yahav D, Kornowski R. Meta-analysis of transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients at low surgical risk. EuroIntervention. 2019;15(12):e1047–56.
Kappetein AP, Head SJ, Généreux P, Piazza N, van Mieghem NM, Blackstone EH, et al. Updated standardized endpoint definitions for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: the valve academic research consortium‑2 consensus document. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(19):2403–18.
Bekeredjian R, Szabo G, Balaban Ü, Bleiziffer S, Bauer T, Ensminger S, et al. Patients at low surgical risk as defined by the society of thoracic surgeons score undergoing isolated interventional or surgical aortic valve implantation: in-hospital data and 1‑year results from the German aortic valve registry (GARY). Eur Heart J. 2018;40(17):1323–30.
Schaefer A, Schofer N, Goßling A, Seiffert M, Schirmer J, Deuschl F, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement in low-risk patients: a propensity score-matched analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;56(6):1131–9.
Brízido C, Madeira M, Brito J, Madeira S, Teles RC, Raposo L, et al. Surgical versus transcatheter aortic valve replacement in low-risk patients: a long-term propensity score-matched analysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021;98(7):E1033–43.
Doyle MP, Woldendorp K, Ng M, Vallely MP, Wilson MK, Yan TD, et al. Minimally-invasive versus transcatheter aortic valve implantation: systematic review with meta-analysis of propensity-matched studies. J Thorac Dis. 2021;13(3):1671–83.
Laakso T, Laine M, Moriyama N, Dahlbacka S, Airaksinen J, Virtanen M, et al. Impact of paravalvular regurgitation on the mid-term outcome after transcatheter and surgical aortic valve replacement. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020;58(6):1145–52.
Makkar RR, Thourani VH, Mack MJ, Kodali SK, Kapadia S, Webb JG, et al. Five-year outcomes of transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(9):799–809.
Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack MJ, Makkar RR, Svensson LG, Kodali SK, et al. Transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(17):1609–20.
Reardon MJ, Mieghem NMV, Popma JJ, Kleiman NS, Søndergaard L, Mumtaz M, et al. Surgical or transcatheter aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(14):1321–31.
Takagi H, Umemoto T, ALICE (All-Literature Investigation of Cardiovascular Evidence) Group. Impact of paravalvular aortic regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation on survival. Int J Cardiol. 2016;221:46–51.
Ando T, Briasoulis A, Telila T, Afonso L, Grines CL, Takagi H. Does mild paravalvular regurgitation post transcatheter aortic valve implantation affect survival? A meta-analysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;91(1):135–47.
Gomes B, Geis NA, Chorianopoulos E, Meder B, Leuschner F, Katus HA, et al. Improvements of procedural results with a new-generation self-expanding transfemoral aortic valve prosthesis in comparison to the old-generation device. J Interv Cardiol. 2017;30(1):72–8.
Yoshijima N, Yanagisawa R, Hase H, Tanaka M, Tsuruta H, Shimizu H, et al. Update on the clinical impact of mild aortic regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: insights from the Japanese multicenter OCEAN-TAVI registry. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020;95(1):35–44.
Kodali SK, Williams MR, Smith CR, Svensson LG, Webb JG, Makkar RR, Fontana GP, Dewey TM, Thourani VH, Pichard AD, Fischbein M, Szeto WY, Lim S, Greason KL, Teirstein PS, Malaisrie SC, Douglas PS, Hahn RT, Whisenant B, Zajarias A, Wang D, Akin JJ, Anderson WN, Leon MB, PARTNER Trial Investigators. Two-year outcomes after transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(18):1686–95.
Hagar A, Li Y, Wei X, Peng Y, Xu Y, Ou Y, et al. Incidence, predictors, and outcome of paravalvular leak after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J Interv Cardiol. 2020;2020:8249497.
Bhushan S, Huang X, Li Y, He S, Mao L, Hong W, et al. Paravalvular leak after trancatheter aortic valve implantation its incidence, diagnosis, clinical implications, prevention, management and future perspectives: a review article. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2021;47(10):100957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2021.100957.
Siddiqui WJ, Alvarez C, Aslam M, Bakar A, Khan MH, Aslam A, et al. Meta-analysis comparing outcomes and need for renal replacement therapy of transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement. Am J Cardiol. 2018;122(3):468–76.
Hirji SA, Funamoto M, Lee J, Val FRD, Kolkailah AA, McGurk S, et al. Minimally invasive versus full sternotomy aortic valve replacement in low-risk patients: which will stand against transcatheter aortic valve replacement? Surgery. 2018;164(2):282–7.
Wilson TW, Horns JJ, Sharma V, Goodwin ML, Kagawa H, Pereira SJ, et al. Minimally invasive versus full sternotomy SAVR in the era of TAVR: an institutional review. J Clin Med. 2022;11(3):547.
Sinning JM, Ghanem A, Steinhäuser H, Adenauer V, Hammerstingl C, Nickenig G, et al. Renal function as predictor of mortality in patients after percutaneous transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Jacc Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3(11):1141–9.
Zaleska-Kociecka M, Dabrowski M, Stepinska J. Acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement in the elderly: outcomes and risk management. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:195–201.
Moriyama N, Laakso T, Raivio P, Dahlbacka S, Kinnunen EM, Juvonen T, et al. Acute kidney injury following aortic valve replacement in patients without chronic kidney disease. Can J Cardiol. 2021;37(1):37–46.
Kolte D, Vlahakes GJ, Palacios IF, Sakhuja R, Passeri JJ, Inglessis I, et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in low-risk patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(12):1532–40.
Rosato S, Santini F, Barbanti M, Biancari F, D’Errigo P, Onorati F, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation compared with surgical aortic valve replacement in low-risk patients. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;9(5):e3326.
Santarpino G, Lorusso R, Moscarelli M, Mikus E, Wisniewski K, Dell’Aquila AM, et al. Sutureless versus transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a multicenter analysis of “real-world” data. J Cardiol. 2022;79(1):121–6.
Sammour Y, Krishnaswamy A, Kumar A, Puri R, Tarakji KG, Bazarbashi N, et al. Incidence, predictors, and implications of permanent pacemaker requirement after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Jacc Cardiovasc Interv. 2021;14(2):115–34.
Jørgensen TH, Thyregod HGH, Ihlemann N, Nissen H, Petursson P, Kjeldsen BJ, et al. Eight-year outcomes for patients with aortic valve stenosis at low surgical risk randomized to transcatheter vs. surgical aortic valve replacement. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(30):2912–9.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design of the study: TK, NL and MB. Data collection: TK, ST and AK. Analysis and interpretation: TK and MJ. Drafting or critical review of the article: TK, NL, and MB. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
T. Kolar, M. Bunc, M. Jelenc, S. Terseglav, A. Kotnik, and N. Lakič declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval to conduct the study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Republic of Slovenia (Protocol number—0120-318/2019/5).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Data Availability
The dataset used and analyzed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolar, T., Bunc, M., Jelenc, M. et al. Minimally invasive surgical aortic valve replacement versus transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation in low-risk octogenarians. Wien Klin Wochenschr 135, 703–711 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-022-02094-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-022-02094-z