Abstract
Purpose
Research investigating swallowing problems (dysphagia) and complications within the oral cavity in non-head and neck cancer patients is limited. The purpose of this study was to determine the prevalence of patient-reported dysphagia and oral complications in all cancer patients and to examine the relationships between cancer types, oral complications and dysphagia.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted at a specialist cancer centre in Australia. Data on patient-reported dysphagia and oral complications were collected using the Vanderbilt Head and Neck Symptom Survey (version 2.0) which was completed by participants in one of three settings: inpatients, ambulatory patients receiving chemotherapy, or ambulatory patients receiving radiotherapy.
Results
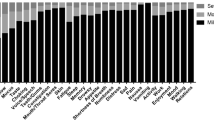
Data were collected on 239 patients, receiving treatment for 14 cancer types. The proportion of patients who reported dysphagic symptoms were as follows: any dysphagia (54%); dysphagia for liquids (20%); and dysphagia for solids (46%). Significantly more head and neck patients and significantly fewer breast patients reported dysphagia, but there were no differences between other tumour types. Oral symptoms across all cancer types were reported at the following rates: taste changes (62%); xerostomia (56%); voice changes (37%); smell changes (35%); thick mucous (33%); difficulty with teeth/dentures (25%); mouth/throat pain (20%); and trismus (19%).
Conclusions
This is the first time comprehensive data on dysphagia and oral complications across all cancer patients have been collected. We have identified that dysphagic symptoms and oral complications—which have implications for quality of life and function—are common in all cancer patients, not just those with head and neck cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong HM (2014) Oral complications and management strategies for patients undergoing cancer therapy. Sci World J 2014:1–14
Epstein JB, Thariat J, Bensadoun RJ, Barasch A, Murphy BA, Kolnick L, Popplewell L, Maghami E (2012) Oral complications of cancer and cancer therapy: from cancer treatment to survivorship. CA Cancer J Clin 62(6):400–422
Feng F, Kim H, Lynden T, Haxer M, Feng M, Worden F, Chepeha D, Eisbruch A (2007) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy of head and neck cancer aiming to reduce dysphagia: early dose-effect relationships for the swallowing structures. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68(5):1289–1298
Rosenthal D, Lewin J, Eisbruch A (2006) Prevention and treatment of dysphagia and aspiration after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(17):2636–2643
Murphy BA, Gilbert J (2009) Dysphagia in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiation: assessment, sequelae, and rehabilitation. In: Seminars in radiation oncology, vol 1. Elsevier, pp 35–42
Patterson JM, McColl E, Carding PN, Hildreth AJ, Kelly C, Wilson JA (2014) Swallowing in the first year after chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer: clinician-and patient-reported outcomes. Head Neck 36(3):352–358
van der Laan HP, Bijl HP, Steenbakkers RJ, van der Schaaf A, Chouvalova O, Vemer-van den Hoek JG, Gawryszuk A, van der Laan BF, Oosting SF, Roodenburg JL (2015) Acute symptoms during the course of head and neck radiotherapy or chemoradiation are strong predictors of late dysphagia. Radiother Oncol 115(1):56–62
Moroney LB, Helios J, Ward EC, Crombie J, Wockner LF, Burns CL, Spurgin A-L, Blake C, Kenny L, Hughes BG (2017) Patterns of dysphagia and acute toxicities in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing helical IMRT±concurrent chemotherapy. Oral Oncol 64:1–8
Barnhart MK, Robinson RA, Simms VA, Ward EC, Cartmill B, Chandler SJ, Smee RI (2018) Treatment toxicities and their impact on oral intake following non-surgical management for head and neck cancer: a 3-year longitudinal study. Support Care Cancer 26(7):2341–2351
De Ruysscher D, Dehing C, Bremer R, Bentzen S, Koppe F, Pijls-Johannesma M, Harzée L, Minken A, Wanders R, Hochstenbag M (2007) Maximal neutropenia during chemotherapy and radiotherapy is significantly associated with the development of acute radiation-induced dysphagia in lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol 18(5):909–916
Dehing-Oberije C, De Ruysscher D, Petit S, Van Meerbeeck J, Vandecasteele K, De Neve W, Dingemans AMC, El Naqa I, Deasy J, Bradley J (2010) Development, external validation and clinical usefulness of a practical prediction model for radiation-induced dysphagia in lung cancer patients. Radiother Oncol 97(3):455–461
Brady GC, Roe JW, O’Brien M, Boaz A, Shaw C (2018) An investigation of the prevalence of swallowing difficulties and impact on quality of life in patients with advanced lung cancer. Support Care Cancer 26(2):515–519
Mercadante S, Aielli F, Adile C, Ferrera P, Valle A, Fusco F, Caruselli A, Cartoni C, Massimo P, Masedu F (2015) Prevalence of oral mucositis, dry mouth, and dysphagia in advanced cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 23(11):3249–3255
Raber-Durlacher JE, Brennan MT, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, Gibson RJ, Eilers JG, Waltimo T, Bots CP, Michelet M, Sollecito TP, Rouleau TS (2012) Swallowing dysfunction in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 20(3):433–443
Kenny C, Gilheaney Ó, Walsh D, Regan J (2018) Oropharyngeal dysphagia evaluation tools in adults with solid malignancies outside the head and neck and upper GI tract: a systematic review. Dysphagia 33(3):303–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-018-9892-9
Vera-Llonch M, Oster G, Hagiwara M, Sonis S (2006) Oral mucositis in patients undergoing radiation treatment for head and neck carcinoma: risk factors and clinical consequences. Cancer 106(2):329–336
Dirix P, Nuyts S, Van den Bogaert W (2006) Radiation-induced xerostomia in patients with head and neck cancer: a literature review. Cancer 107(11):2525–2534
Pinna R, Campus G, Cumbo E, Mura I, Milia E (2015) Xerostomia induced by radiotherapy: an overview of the physiopathology, clinical evidence, and management of the oral damage. Ther Clin Risk Manag 11:171
Lee R, Slevin N, Musgrove B, Swindell R, Molassiotis A (2012) Prediction of post-treatment trismus in head and neck cancer patients. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50(4):328–332
Bensadoun R-J, Riesenbeck D, Lockhart PB, Elting LS, Spijkervet FK, Brennan MT (2010) A systematic review of trismus induced by cancer therapies in head and neck cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 18(8):1033–1038
Epstein JB, Emerton S, Kolbinson DA, Le ND, Phillips N, Stevenson-Moore P, Osoba D (1999) Quality of life and oral function following radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Head Neck 21(1):1–11
Langius A, Lind M (1995) Well-being and coping in oral and pharyngeal cancer patients. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 31(4):242–249
Bjordal K, Freng A, Thorvik J, Kaasa S (1995) Patient self-reported and clinician-rated quality of life in head and neck cancer patients: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 31(4):235–241
Hovan AJ, Williams PM, Stevenson-Moore P, Wahlin YB, KEO O, Elting LS, Spijkervet FKL, Brennan MT, Dysgeusia Section OCSG, Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer /International Society of Oral Oncology (2010) A systematic review of dysgeusia induced by cancer therapies. Support Care Cancer 18(8):1081–1087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-010-0902-1
Bernhardson B-M, Tishelman C, Rutqvist LE (2008) Self-reported taste and smell changes during cancer chemotherapy. Support Care Cancer 16(3):275–283
Lalla RV, Sonis ST, Peterson DE (2008) Management of oral mucositis in patients who have cancer. Dent Clin N Am 52(1):61–77
Jensen SB, Mouridsen HT, Reibel J, Brünner N, Nauntofte B (2008) Adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients induces temporary salivary gland hypofunction. Oral Oncol 44(2):162–173
Jensen SB, Pedersen AML, Vissink A, Andersen E, Brown CG, Davies AN, Dutilh J, Fulton JS, Jankovic L, Lopes NN (2010) A systematic review of salivary gland hypofunction and xerostomia induced by cancer therapies: prevalence, severity and impact on quality of life. Support Care Cancer 18(8):1039–1060
Bressan V, Stevanin S, Bianchi M, Aleo G, Bagnasco A, Sasso L (2016) The effects of swallowing disorders, dysgeusia, oral mucositis and xerostomia on nutritional status, oral intake and weight loss in head and neck cancer patients: a systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev 45:105–119
Cooperstein E, Gilbert J, Epstein JB, Dietrich MS, Bond SM, Ridner SH, Wells N, Cmelak A, Murphy BA (2012) Vanderbilt Head and Neck Symptom Survey version 2.0: report of the development and initial testing of a subscale for assessment of oral health. Head Neck 34(6):797–804
Vainshtein JM, Samuels S, Tao Y, Lyden T, Haxer M, Spector M, Schipper M, Eisbruch A (2016) Impact of xerostomia on dysphagia after chemotherapy–intensity-modulated radiotherapy for oropharyngeal cancer: prospective longitudinal study. Head Neck 38(S1):E1605–E1612
Agresti A (2002) Categorical data analysis, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Baden LR, Swaminathan S, Angarone M, Blouin G, Camins BC, Casper C, Cooper B, Dubberke ER, Engemann AM, Freifeld AG (2016) Prevention and treatment of cancer-related infections, version 2.2016, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 14(7):882–913
Xu B, Boero IJ, Hwang L, Le QT, Moiseenko V, Sanghvi PR, Cohen EE, Mell LK, Murphy JD (2015) Aspiration pneumonia after concurrent chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Cancer 121(8):1303–1311
Van Cutsem E, Arends J (2005) The causes and consequences of cancer-associated malnutrition. Eur J Oncol Nurs 9:S51–S63
Osoba D (2007) Health-related quality of life and predicting survival in cancer: not a simple matter. Support Care Cancer 15:353–355
Bottomley A (2002) The cancer patient and quality of life. Oncologist 7(2):120–125
Elad S, Zadik Y, Yarom N (2017) Oral complications of nonsurgical cancer therapies. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin N Am 25(2):133–147
Camidge D (2001) The causes of dysphagia in carcinoma of the lung. J R Soc Med 94(11):567–572
Sreedharan A, Harris K, Crellin A, Forman D, Everett SM (2009) Interventions for dysphagia in oesophageal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4
Logemann J, Larsen K (2012) Oropharyngeal dysphagia: pathophysiology and diagnosis for the anniversary issue of Diseases of the Esophagus. Dis Esophagus 25(4):299–304
National Cancer Institute (2009) Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) Version 4.0. National Institutes of Health, Available at: http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm. Accessed 3 Dec 2018
World Health Organization (1979) WHO handbook for reporting results of cancer treatment. World Health Organization, Geneva
Trotti A, Bellm LA, Epstein JB, Frame D, Fuchs HJ, Gwede CK, Komaroff E, Nalysnyk L, Zilberberg MD (2003) Mucositis incidence, severity and associated outcomes in patients with head and neck cancer receiving radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy: a systematic literature review. Radiother Oncol 66(3):253–262
Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Lazarus CL, Mittal B, Gaziano J, Stachowiak L, MacCracken E, Newman LA (2003) Xerostomia: 12-month changes in saliva production and its relationship to perception and performance of swallow function, oral intake, and diet after chemoradiation. Head Neck 25(6):432–437
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Jess Sao and Rishni Perera for assistance with data collection and Allison Drosdowsky for assistant with data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval was obtained (HREC No: LNR/17/PMCC/35).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frowen, J., Hughes, R. & Skeat, J. The prevalence of patient-reported dysphagia and oral complications in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 28, 1141–1150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-019-04921-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-019-04921-y