Abstract
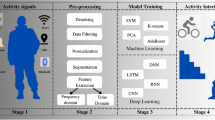
This study investigates how we can provide a database map model for full-body gestures by utilizing the hierarchical nested set model and its features to cover all aspects of existing gestures and motions. A mapping model allows us to execute any appropriate gesture pattern for each motion state via a hierarchically nested set tracking feature that executes at a varied speed or time. The nested set model allows us to distinguish each node location with its right and left values, which aids us in controlling the power to motors at a certain time and speed while taking data quantity into account by eliminating the time and interaction data for speed and motor management. The main issue in this study is that instead of reprocessing data for each movement change, machine learning methods are used to create a map model from classified data. This paper discusses the connection between sensors and databases for exchanging data models in the form of a map that may be used to interact between different positions of the robot's parts based on sensor data. For example, suppose a robot falls down and the sensors such as the gyroscope, accelerometers, touch sensor, camera (image processing), or voice recognition are set as an input command to understand the current position. Then, using artificial modeling in our database, we can control the robot to return to the standard position, such as standing up on its legs. We used motion flex sensor gloves to record all gestures at varied motion speeds and execution durations, and then we ran three different classification algorithms on the recorded data to achieve the best data categorization. Finally, based on a nested set model for the whole body, we provided a database map with those classified data gathered from the sensor, and as a consequence, we made a comparison with parent and child categorization to highlight the complexity and data collection differences between these two techniques.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Głomb, P., Romaszewski, M., Opozda, S., Sochan, A.: Choosing and modeling the Hand Gesture Database for a natural user interface. In: Gesture Workshop (2011)
Supancic, J.S., Rogez, G., Yang, Y., Shotton J., Ramanan, D.: Depth-based hand pose estimation: data, methods, and challenges. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2015, pp. 1868–1876. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.217
Tan, D.J., et al.: Fits like a glove: rapid and reliable hand shape personalization. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016, pp. 5610-5619, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.605
Chen, X., Wang, G., Guo, H., Zhang, C., Wang, H., Zhang, L.: Mfa-net: Motion feature augmented network for dynamic hand gesture recognition from skeletal data. Sensors 19(2), 239 (2019)
Syed Mubarak Ali, S.A.A., Ahmad, N.S., Goh, P.: Flex sensor compensator via Hammerstein–Wiener modeling approach for improved dynamic goniometry and constrained control of a bionic hand. Sensors 19(18), 3896 (2019)
Müller, M., Röder, T., Clausen, M., Eberhardt, B., Krüger, B., Weber, A. Mocap database HDM05. Institut für Informatik II, Universität Bonn 2(7) (2007)
Guo, H., Wang, G., Chen, X., Zhang, C.: Towards good practices for deep 3D hand pose estimation. ArXiv:abs/1707.07248 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Xu, C., Cheng, L.: Learning to search on manifolds for 3D pose estimation of articulated objects. ArXiv:abs/1612.00596 (2016)
Ma, C., Wang, A., Chen, G., Xu, C.: Hand joints-based gesture recognition for noisy dataset using nested interval unscented Kalman filter with LSTM network. Vis. Comput. 34, 1053–1063 (2018)
Wang, C., Liu, Z., Chan, S.: Superpixel-based hand gesture recognition with Kinect depth camera. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 17(1), 29–39 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2014.2374357
Núñez, J.C., Cabido, R., Pantrigo, J.J., Montemayor, A.S., Vélez, J.F.: Convolutional neural networks and long short-term memory for skeleton-based human activity and hand gesture recognition. Pattern Recognit. 76, 80–94 (2018)
Zhu, G., Zhang, L., Shen, P., Song, J.: Multimodal gesture recognition using 3-D convolution and convolutional LSTM. IEEE Access 5, 4517–4524 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2684186
Ghosh et al.: On automatizing recognition of multiple human activities using ultrasonic sensor grid. In: 2017 9th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), 2017, pp. 488–491. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMSNETS.2017.7945440
Ghosh, A., Chakraborty, A., Chakraborty, D., et al.: UltraSense: A non-intrusive approach for human activity identification using heterogeneous ultrasonic sensor grid for smart home environment. J. Ambient Intell. Human. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01260-y
Lefebvre, G., Berlemont, S., Mamalet, F., Garcia, C.: Blstm-rnn based 3D gesture classification. In: Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning, pp. 381–388. Springer, New York, 2013.
Gupta, H.P., Chudgar, H.S., Mukherjee, S., Dutta, T., Sharma, K.: A continuous hand gestures recognition technique for human–machine interaction using accelerometer and gyroscope sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 16(16), 6425–6432 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2016.2581023
Du, Y., Wang, W., Wang, L.: Hierarchical recurrent neural network for skeleton based action recognition. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2015, pp. 1110–1118. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298714.
Zhang, X., Chen, X., Li, Y., Lantz, V., Wang, K., Yang, J.: A framework for hand gesture recognition based on accelerometer and EMG sensors. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 41(6), 1064–1076 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCA.2011.2116004
Ma, C., Zhang, S., Wang, A., Qi, Y., Chen, G.: Skeleton-based dynamic hand gesture recognition using an enhanced network with one-shot learning. Appl. Sci. 10(11), 3680 (2020)
Chuang, W.C., Hwang, W.J., Tai, T.M., Huang, D.R., Jhang, Y.J.: Continuous finger gesture recognition based on flex sensors. Sensors 19(18), 3986 (2019)
Xu, R., Zhou, S., Li, W.J.: MEMS accelerometer based nonspecific-user hand gesture recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 12(5), 1166–1173 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2011.2166953
Gupta, H.P., Chudgar, H.S., Mukherjee, S., Dutta, T., Sharma, K.: A continuous hand gestures recognition technique for human-machine interaction using accelerometer and gyroscope sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 16(16), 6425–6432 (2016)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (2016)
Tai, T.M., Jhang, Y.J., Liao, Z.W., Teng, K.C., Hwang, W.J.: Sensor-based continuous hand gesture recognition by long short-term memory. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2(3), 1–4 (2018)
Chu, Y.C., Jhang, Y.J., Tai, T.M., Hwang, W.J.: Recognition of hand gesture sequences by accelerometers and gyroscopes. Appl. Sci. 10(18), 6507 (2020)
Jhang, Y.J., Chu, Y.C., Tai, T.M., Hwang, W.J., Cheng, P.W. and Lee, C.K.: Sensor based dynamic hand gesture recognition by PairNet. In: 2019 International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData), IEEE. p. 994–1001. (2019)
http://mikehillyer.com/articles/managing-hierarchical-data-in-mysql/
Damdoo, R., Kalyani, K., Sanghavi, J.: Adaptive hand gesture recognition system using machine learning approach. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 13, 106–110 (2020)
Al-Hammadi, M., et al.: Deep learning-based approach for sign language gesture recognition with efficient hand gesture representation. IEEE Access 8, 192527–192542 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3032140
Alhussein, M., Muhammad, G.: ‘Voice pathology detection using deep learning on mobile healthcare framework.’ IEEE Access 6, 41034–41041 (2018)
Muhammad, G., Alhamid, M.F., Long, X.: Computing and processing on the edge: smart pathology detection for connected healthcare. IEEE Network 33(6), 44–49 (2019)
Hou, R., Chen, C., Shah, M.: An end-to-end 3D convolutional neural network for action detection and segmentation in videos. 2017. arXiv:1712.01111 [Online]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1712.01111
Varol, G., Laptev, I., Schmid, C.: Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(6), 1510–1517 (2017)
Sasaki, K. et al.: An automated structural approach to support theatrical performances by introducing gesture recognition to a cuing system. CRIWG/CollabTech (2019)
Reale, M.J., Canavan, S., Yin, L., Hu, K., Hung, T.: A multi-gesture interaction system using a 3-D iris disk model for gaze estimation and an active appearance model for 3-D hand pointing. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 13(3), 474–486 (2011)
Zhu, C., Yang, J., Shao, Z., Liu, C.: Vision based hand gesture recognition using 3D shape context. IEEE/CAA J Autom. Sinica. 8, 1600–1613 (2019)
Chen, G., Xu, Z., Li, Z., Tang, H., Qu, S., Ren, K., Knoll, A.: A novel illumination-robust hand gesture recognition system with event-based neuromorphic vision sensor. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 18(2), 508–520 (2021)
Zhang, W., Wang, J., Lan, F.: Dynamic hand gesture recognition based on short-term sampling neural networks. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 8(1), 110–120 (2020)
Jia, G., Lam, H.K., Ma, S., Yang, Z., Xu, Y., Xiao, B.: Classification of electromyographic hand gesture signals using modified fuzzy C-means clustering and two-step machine learning approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 28(6), 1428–1435 (2020)
Wong, W.K., Juwono, F.H., Khoo, B.T.T.: Multi-features capacitive hand gesture recognition sensor: a machine learning approach. IEEE Sens. J. 21(6), 8441–8450 (2021)
Ehrnsperger, M.G., Brenner, T., Hoese, H.L., Siart, U., Eibert, T.F.: Real-time gesture detection based on machine learning classification of continuous wave radar signals. IEEE Sens. J. 21(6), 8310–8322 (2020)
Gowthul Alam, M.M., Baulkani, S.: Reformulated query-based document retrieval using optimised kernel fuzzy clustering algorithm. Int. J. Bus. Intell. Data Min. 12(3), 299 (2017)
Sundararaj, V.: An efficient threshold prediction scheme for wavelet based ECG signal noise reduction using variable step size firefly algorithm. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 9(3), 117–126 (2016)
Gowthul Alam, M.M., Baulkani, S.: Geometric structure information based multi-objective function to increase fuzzy clustering performance with artificial and real-life data. Soft Comput. 23(4), 1079–1098 (2019)
Sundararaj, V.: Optimised denoising scheme via opposition-based self-adaptive learning PSO algorithm for wavelet-based ECG signal noise reduction. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 31(4), 325 (2019)
Aswini, J., Yamini, B., Jatothu, R., Nayaki, K.S. and Nalini, M., 2021. An efficient cloud‐based healthcare services paradigm for chronic kidney disease prediction application using boosted support vector machine. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, p.e6722.
Hassan, B.A., Rashid, T.A.: Datasets on statistical analysis and performance evaluation of backtracking search optimisation algorithm compared with its counterpart algorithms. Data Brief 28, 105046 (2020)
Hassan BA (2020) CSCF: a chaotic sine cosine firefly algorithm for practical application problems. Neural Comput Appl 1–20
Rejeesh, M.R.: Interest point based face recognition using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system. Multimed. Tools Appl. 78(16), 22691–22710 (2019)
Sundararaj, V., Muthukumar, S., Kumar, R.S.: An optimal cluster formation based energy efficient dynamic scheduling hybrid MAC protocol for heavy traffic load in wireless sensor networks. Comput. Secur. 77, 277–288 (2018)
Sundararaj, V., Anoop, V., Dixit, P., Arjaria, A., Chourasia, U., Bhambri, P., Rejeesh, M.R., Sundararaj, R.: CCGPA-MPPT: Cauchy preferential crossover-based global pollination algorithm for MPPT in photovoltaic system. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 28(11), 1128–1145 (2020)
Vinu, S.: Optimal task assignment in mobile cloud computing by queue based ant-bee algorithm. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 104(1), 173–197 (2019)
Manikandan, N., Gobalakrishnan, N., Pradeep, K.: Bee optimization based random double adaptive whale optimization model for task scheduling in cloud computing environment. Comput. Commun. 187, 35–44 (2022)
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Kong.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hekmat, A., Zuping, Z. & Al-deen, H.S. Map modeling for full body gesture using flex sensor and machine learning algorithms. Multimedia Systems 28, 2319–2334 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-022-00946-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-022-00946-2