Abstract
Background
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and Helicobacter pylori infection are major causes of gastric mucosal lesions. In Japan, histamine-2 receptor antagonists are frequently prescribed, but the literature regarding their efficacy is limited. In this study, we compare the effects of famotidine and rebamipide on NSAID-associated gastric mucosal lesions using upper gastrointestinal endoscopy.
Methods
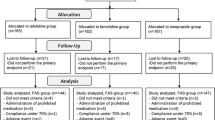
This study examined 112 patients taking NSAIDs for either gastric hemorrhage or erosion. Before treat-ment, the patients were assessed by endoscopy. Using blind randomization, patients were divided into two groups: group F (famotidine, 20 mg/day) and group R (rebamipide, 300 mg/day). Efficacy was examined 4 weeks later using endoscopy.
Results
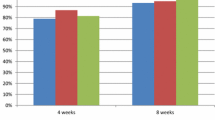
After treatment, the Lanza score decreased significantly in group F (P < 0.001) but not in group R (P = 0.478). The change in the Lanza score in group F was significantly greater (P = 0.002) than that in group R.
Conclusions
Famotidine was superior to rebamipide in treating NSAID-associated mucosal lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Research Team for the Development of Guidelines for Evidence-Based Gastric Ulcer Diagnosis, Guideline for Clinical Practice of Gastric Ulcer Based on EBM (in Japanese with English abstract). Jiho 2003;7–14
JQ Huang S Sridhar RH Hunt (2002) ArticleTitleRole of Helicobacter pylori infection and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in peptic-ulcer disease: a meta-analysis Lancet 359 14–22 Occurrence Handle11809181 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07273-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsV2msQ%3D%3D
M Asaka K Satoh K Sugano T Sugiyama S Takahashi T Shimoyama et al. (2001) ArticleTitleGuidelines in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection In Japan Helicobacter 6 177–86 Occurrence Handle11683920 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1523-5378.2001.00027.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnjsFalsA%3D%3D
H Miwa N Sakaki K Sugano H Sekine K Higucni T Sugiyama et al. (2004) ArticleTitleRecurrent peptic ulcers in patients following successful Helicobacter pylori eradication: a multicenter study of 4940 patients Helicobacter 9 9–26 Occurrence Handle15156899 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1083-4389.2004.00194.x
A Robert (1976) ArticleTitleAntisecretory anti-ulcer, cytoprotective and diarrheogenic properties of prostaglandins Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res 2 507–20 Occurrence Handle983858 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28XhsVGjtbY%3D
M Ligumsky EM Golanska DG Hansen GL Kauffman (1983) ArticleTitleAspirin can inhibit gastric mucosal cyclo-oxygenase without causing lesions in rat Gastroenterology 84 756–61 Occurrence Handle6402412 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXhtFCksbw%3D
M Frezza N Gorji M Melato (2001) ArticleTitleThe histopathology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug induced gastroduodenal damage: correlation with Helicobacter pylori, ulcers, and hemorrhagic events J Clin Pathol 54 521–5 Occurrence Handle11429423 Occurrence Handle10.1136/jcp.54.7.521 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mznt1Kqtw%3D%3D
T Funatsu K Chono T Hirata Y Keto A Kimoto M Sasamata (2004) ArticleTitleThe possible role of gastric acid against non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-induced gastric microcirculatory disturbance in rats Jpn Pharmacol Ther 32 429–34 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXntlOku7g%3D
AS Taha N Hudson CJ Hawkey AJ Swannell PE Trye J Cottrell et al. (1996) ArticleTitleFamotidine for the prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers caused by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs N Engl J Med 334 1435–9 Occurrence Handle8618582 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199605303342204 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XktF2kurk%3D
N Hudson AS Taha RI Russell P Trye J Cottrell SG Mann et al. (1997) ArticleTitleFamotidine for healing and maintenance in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated gastroduodenal ulceration Gastroenterology 112 1817–22 Occurrence Handle9178671 Occurrence Handle10.1053/gast.1997.v112.pm9178671 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjvFagtbg%3D
Y Keto T Funatsu T Hirata T Toyama K Sudoh M Sasamata (2003) ArticleTitleInhibitory effects of famotidine on NSAIDs and bisphosphonate-induced mucosal lesions in rats Jpn Pharmacol Ther 31 485–93 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmtFamtr4%3D
JB Raskin RH White JE Jackson AL Weaver EA Tindall RB Leis et al. (1991) ArticleTitleMisoprostol dosage in the prevention of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastric and duodenal ulcers: a comparison of three regimens Ann Intern Med 115 195–200
NM Agrawal HE Van Kerckhove LJ Erhardt GS Geis (1995) ArticleTitleMisoprostol coadministered with diclofenac for prevention of gastroduodenal ulcers. A one-year study Dig Dis Sci 40 1125–31 Occurrence Handle7729275 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02064210 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M3ks1Gluw%3D%3D
TS Bocanegra AL Weaver EA Tindall DH Sikes JA Ball CB Wallemark et al. (1998) ArticleTitleDiclofenac/misoprostol compared with diclofenac in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee or hip: a randomized, placebo controlled trial. Arthrotec Osteoarthritis Study Group J Rheumatol 25 1602–11 Occurrence Handle9712107 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlsF2gtrs%3D
RP Walt (1992) ArticleTitleMisoprostol for the treatment of peptic ulcer and antiinflammatory-drug-induced gastroduodenal ulceration N Engl J Med 327 1575–80 Occurrence Handle1435885 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s%2FmtlSluw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199211263272207
K Katsuragi A Noda T Tachikawa A Azuma F Mukai K Murakami et al. (1998) ArticleTitleHighly sensitive urine-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter 3 289–95 Occurrence Handle9844071 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1523-5378.1998.08045.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2Fmt1Smug%3D%3D
M Kato M Asaka M Saito H Sekine S Ohara T Toyota et al. (2000) ArticleTitleClinical usefulness of urine-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to Helicobacter pylori: a collaborative study in nine medical institutions in Japan Helicobacter 5 109–19 Occurrence Handle10849061 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1523-5378.2000.00017.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXksFSlsrc%3D
FL Lanza GL Royer RS Nelson TT Chen CE Seckman MF Rack (1981) ArticleTitleA comparative endoscopic evaluation of the damaging effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents on the gastric and duodenal mucosa Am J Gastroenterol 75 17–21 Occurrence Handle7234826 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL3M3gsVentg%3D%3D
Y Naito T Yoshikawa S Iinuma N Yagi K Matsuyama Y Boku et al. (1998) ArticleTitleRebamipide protects against indomethacin-induced mucosal lesion in healthy volunteers in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study Dig Dis Sci 43 83–9
CJ Hawkey JA Karrasch L Szczepanski DG Walker A Barkun AJ Swannell et al. (1998) ArticleTitleOmeprazole compared with misoprostol for ulcers associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Omeprazole versus Misoprostol for NSAID-induced Ulcer Management (OMNIUM) Study Group N Engl J Med 338 727–34 Occurrence Handle9494149 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199803123381105 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitFars7w%3D
CS Wu SH Wang PC Chen VCC Wu (1998) ArticleTitleDose famotidine have similar efficacy to misoprostol in the treatment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastropathy? Int J Clin Pract 52 472–4 Occurrence Handle10622088 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnslCjurc%3D
K Miyake N Ueki K Suzuki Y Shinji M Kusunoki T Hiratsuka et al. (2005) ArticleTitlePreventive therapy for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced ulcers in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the current situation and a prospective controlled-study of the preventive effects of lansoprazole or famotidine Aliment Pharmacol Ther 21 IssueIDSuppl 2 67–72 Occurrence Handle15943850 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02477.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXlvFShtbk%3D
K Kitagami K Oku N Umemoto Y Mizokami K Shiozama S Yamana et al. (1993) ArticleTitleClinical study of rebamipide for NSAIDs induced gastritis J Adult Dis 23 1477–88
T Matsuhisa T Hayama H Nakamura S Yoshino N Yamada (1998) ArticleTitleClinical usefulness of rebamipide against symptoms, gastric lesions and histological gastritis caused by long-term administration of NSAIDs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Gastroenterology (Tokyo) 27 118–30
Y Kinoshita C Kawanami K Kishi H Nakata Y Seino T Chiba (1997) ArticleTitleHelicobacter pylori independent chronological change in gastric acid secretion in the Japanese Gut 41 452–8 Occurrence Handle9391241 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2Flt1Kgsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1136/gut.41.4.452
EM El-Omar ID Penman JES Ardill RS Chittajallu C Howie KEL Mccoll (1995) ArticleTitleHelicobacter pylori infection and abnormalities of acid secretion in patients with duodenal ulcer disease Gastroenterology 109 681–91 Occurrence Handle7657096 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-5085(95)90374-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXos1Grtbk%3D
M Feldman CT Richardson SK Lam IM Samloff (1988) ArticleTitleComparison of gastric acid secretion rates and serum pepsinogen I and II concentrations in occidental and oriental duodenal ulcer patients Gastroenterology 95 630–5 Occurrence Handle3396811 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c3osVWrtQ%3D%3D
H Kawaguchi K Haruma K Komoto M Yoshihara K Sumii G Kajiyama (1996) ArticleTitleHelicobacter pylori infection is the major risk factor for atrophic gastritis Am J Gastroenterol 91 959–62 Occurrence Handle8633588 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK283ht1Ohuw%3D%3D
K Haruma T Kamada H Kawaguchi S Okamoto M Yoshihara K Sumii et al. (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of age and Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric acid secretion J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15 277–83 Occurrence Handle10764028 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1440-1746.2000.02131.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3isFSqug%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamao, Ji., Kikuchi, E., Matsumoto, M. et al. Assessing the efficacy of famotidine and rebamipide in the treatment of gastric mucosal lesions in patients receiving long-term NSAID therapy (FORCE—famotidine or rebamipide in comparison by endoscopy). J Gastroenterol 41, 1178–1185 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-006-1952-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-006-1952-5