Abstract
Background
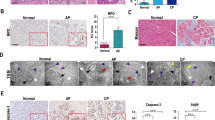
The EGFR ligand betacellulin (BTC) has been previously shown to protect mice against experimentally induced acute pancreatitis (AP). BTC binds both autonomous ERBB receptors EGFR and ERBB4. In this study, we evaluated the mechanism underlying the protection from AP-associated inflammation in detail.
Methods
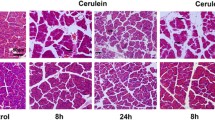
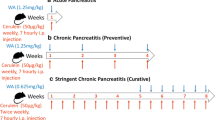
AP was induced with cerulein or l-arginine and investigated in a pancreas-specific ERBB4 knockout and in an EGFR knockdown mouse model (EgfrWa5/+). Pancreatitis was evaluated by scoring inflammation, necrosis, and edema, while microarrays were performed to analyze alterations in the transcriptome between mice with AP and animals which were protected against AP. The intracellular domain (ICD) of ERBB4 was analyzed in different cell compartments.
Results
While the pancreas of BTC transgenic mice in the background of EgfrWa5/+ is still protected against AP, the BTC-mediated protection is no longer present in the absence of ERBB4. We further demonstrate that BTC activates the ICD of ERBB4, and increases the expression of the extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins periostin and matrix gla protein as well as the ECM modulators matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 3, but only in the presence of ERBB4. Notably, the increased expression of these proteins is not accompanied by an increased ECM amount.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that BTC derivates, as a drug, or the ERBB4 receptor, as a druggable target protein, could play an important role in modulating the course of AP and even prevent AP in humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AP:
-
Acute pancreatitis
- BTC:
-
Betacellulin
- ECM:
-
Extra cellular matrix
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
EGF receptor
- H&E:
-
Haemotoxylin and eosin
- ICD:
-
Intracellular domain
- MDM2:
-
Mouse double minute 2 homolog
- MGP:
-
Matrix gla protein
- MMP:
-
Metalloproteinase
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PDAC:
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- POSTN:
-
Periostin
- SAPK:
-
Stress-activated protein kinase
- YAP1:
-
Yes-associated protein 1
References
Baron TH, Morgan DE. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(18):1412–7.
Frossard JL, Steer ML, Pastor CM. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 2008;371(9607):143–52.
Graber HU, Friess H, Kaufmann B, Willi D, Zimmermann A, Korc M, et al. ErbB-4 mRNA expression is decreased in non-metastatic pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 1999;84(1):24–7.
Mill CP, Gettinger KL, Riese DJ. Ligand stimulation of ErbB4 and a constitutively-active ErbB4 mutant result in different biological responses in human pancreatic tumor cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317(4):392–404.
Ardito CM, Gruner BM, Takeuchi KK, Lubeseder-Martellato C, Teichmann N, Mazur PK, et al. EGF receptor is required for KRAS-induced pancreatic tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2012;22(3):304–17.
Navas C, Hernández-Porras I, Schuhmacher Alberto J, Sibilia M, Guerra C, Barbacid M. EGF receptor signaling is essential for k-ras oncogene-driven pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;22(3):318–30.
Wagner M, Luhrs H, Kloppel G, Adler G, Schmid RM. Malignant transformation of duct-like cells originating from acini in transforming growth factor transgenic mice. Gastroenterology. 1998;115(5):1254–62.
Wagner M, Weber CK, Bressau F, Greten FR, Stagge V, Ebert M, et al. Transgenic overexpression of amphiregulin induces a mitogenic response selectively in pancreatic duct cells. Gastroenterology. 2002;122(7):1898–912.
Means AL, Ray KC, Singh AB, Washington MK, Whitehead RH, Harris RC Jr, et al. Overexpression of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in mouse pancreas results in fibrosis and epithelial metaplasia. Gastroenterology. 2003;124(4):1020–36.
Dahlhoff M, Algul H, Siveke JT, Lesina M, Wanke R, Wartmann T, et al. Betacellulin protects from pancreatitis by activating stress-activated protein kinase. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(4):1585–94.
Standop J, Standop S, Itami A, Nozawa F, Brand RE, Buchler MW, et al. ErbB2 oncogene expression supports the acute pancreatitis-chronic pancreatitis sequence. Virchows Arch. 2002;441(4):385–91 (Epub 2002/10/31).
Friess H, Yamanaka Y, Kobrin MS, Do DA, Buchler MW. Korc M (1995) Enhanced erbB-3 expression in human pancreatic cancer correlates with tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1(11):1413–20 (Epub 1995/11/01).
Gilbertson R, Hernan R, Pietsch T, Pinto L, Scotting P, Allibone R, et al. Novel ERBB4 juxtamembrane splice variants are frequently expressed in childhood medulloblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2001;31(3):288–94.
Veikkolainen V, Vaparanta K, Halkilahti K, Iljin K, Sundvall M, Elenius K. Function of ERBB4 is determined by alternative splicing. Cell Cycle. 2011;10(16):2647–57.
Zhang YW, Wang R, Liu Q, Zhang H, Liao FF, Xu H. Presenilin/gamma-secretase-dependent processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein regulates EGF receptor expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(25):10613–8.
Lee HJ, Jung KM, Huang YZ, Bennett LB, Lee JS, Mei L, et al. Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase-like intramembrane cleavage of ErbB4. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(8):6318–23.
Komuro A, Nagai M, Navin NE, Sudol M. WW domain-containing protein YAP associates with ErbB-4 and acts as a co-transcriptional activator for the carboxyl-terminal fragment of ErbB-4 that translocates to the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(35):33334–41.
Arasada RR, Carpenter G. Secretase-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Mdm2 by the ErbB-4 intracellular domain fragment. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(35):30783–7.
Schneider MR, Dahlhoff M, Herbach N, Renner-Mueller I, Dalke C, Puk O, et al. Betacellulin overexpression in transgenic mice causes disproportionate growth, pulmonary hemorrhage syndrome, and complex eye pathology. Endocrinology. 2005;146(12):5237–46.
Lee D, Cross SH, Strunk KE, Morgan JE, Bailey CL, Jackson IJ, et al. Wa5 is a novel ENU-induced antimorphic allele of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mamm Genome. 2004;15(7):525–36.
Long W, Wagner KU, Lloyd KC, Binart N, Shillingford JM, Hennighausen L, et al. Impaired differentiation and lactational failure of Erbb4-deficient mammary glands identify ERBB4 as an obligate mediator of STAT5. Development. 2003;130(21):5257–68.
Nakhai H, Sel S, Favor J, Mendoza-Torres L, Paulsen F, Duncker GI, et al. Ptf1a is essential for the differentiation of GABAergic and glycinergic amacrine cells and horizontal cells in the mouse retina. Development. 2007;134(6):1151–60 (Epub 2007/02/16).
Schmidt J, Lewandrowski K, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Mandavilli U, Compton CC, Warshaw AL, et al. Histopathologic correlates of serum amylase activity in acute experimental pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1992;37(9):1426–33.
Vrolyk V, Schneberger D, Le K, Wobeser BK, Singh B. Mouse model to study pulmonary intravascular macrophage recruitment and lung inflammation in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Cell Tissue Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03023-9(Epub ahead of print)
Dahlhoff M, Schafer M, Muzumdar S, Rose C, Schneider MR. ERBB3 is required for tumor promotion in a mouse model of skin carcinogenesis. Mol Oncol. 2015;9(9):1825–33.
Hoesl C, Rohrl JM, Schneider MR, Dahlhoff M. The receptor tyrosine kinase ERBB4 is expressed in skin keratinocytes and influences epidermal proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018;1862(4):958–66 (Epub 2018/02/08).
Muraoka-Cook RS, Caskey LS, Sandahl MA, Hunter DM, Husted C, Strunk KE, et al. Heregulin-dependent delay in mitotic progression requires HER4 and BRCA1. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(17):6412–24.
Haskins JW, Nguyen DX, Stern DF. Neuregulin 1-activated ERBB4 interacts with YAP to induce Hippo pathway target genes and promote cell migration. Sci Signal. 2014;7(355):116 (Epub 2014/12/11).
Kudo A, Kii I. Periostin function in communication with extracellular matrices. J Cell Commun Signal. 2018;12(1):301–8 (Epub 2017/11/01).
Luo G, Ducy P, McKee MD, Pinero GJ, Loyer E, Behringer RR, et al. Spontaneous calcification of arteries and cartilage in mice lacking matrix GLA protein. Nature. 1997;386(6620):78–81 (Epub 1997/03/06).
Lekstan A, Lampe P, Lewin-Kowalik J, Olakowski M, Jablonska B, Labuzek K, et al. Concentrations and activities of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and their inhibitors (TIMPS) in chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;63(6):589–99 (Epub 2013/02/08).
Bramhall SR, Stamp GW, Dunn J, Lemoine NR, Neoptolemos JP. Expression of collagenase (MMP2), stromelysin (MMP3) and tissue inhibitor of the metalloproteinases (TIMP1) in pancreatic and ampullary disease. Br J Cancer. 1996;73(8):972–8 (Epub 1996/04/01).
Lopez JI, Mouw JK, Weaver VM. Biomechanical regulation of cell orientation and fate. Oncogene. 2008;27(55):6981–93 (Epub 2008/11/26).
Chan LK, Gerstenlauer M, Konukiewitz B, Steiger K, Weichert W, Wirth T, et al. Epithelial NEMO/IKKgamma limits fibrosis and promotes regeneration during pancreatitis. Gut. 2017;66(11):1995–2007 (Epub 2016/07/29).
Gu H, Fortunato F, Bergmann F, Buchler MW, Whitcomb DC, Werner J. Alcohol exacerbates LPS-induced fibrosis in subclinical acute pancreatitis. Am J Pathol. 2013;183(5):1508–17 (Epub 2013/10/05).
Hausmann S, Regel I, Steiger K, Wagner N, Thorwirth M, Schlitter AM, et al. Loss of periostin results in impaired regeneration and pancreatic atrophy after cerulein-induced pancreatitis. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(1):24–31 (Epub 2015/12/04).
Kusnierz-Cabala B, Gurda-Duda A, Solnica B, Fedak D, Dumnicka P, Panek J, et al. Serum matrix Gla protein concentrations in patients with mild and severe acute pancreatitis. Clin Lab. 2011;57(11–12):999–1006 (Epub 2012/01/14).
Feng Y, Liao Y, Huang W, Lai X, Luo J, Du C, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells-derived matrix Gla protein contribute to the alleviation of experimental colitis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(6):691 (Epub 2018/06/09).
Viegas CSB, Costa RM, Santos L, Videira PA, Silva Z, Araujo N, et al. Gla-rich protein function as an anti-inflammatory agent in monocytes/macrophages: implications for calcification-related chronic inflammatory diseases. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(5):e0177829 (Epub 2017/05/26).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Ingrid Renner-Müller and Petra Renner for excellent animal care, Stefanie Riesemann for assistance with Western blot analysis, Josef Millauer for mouse genotyping and Maximilian Marschall for immunohistochemistry. This work was supported by the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hedegger, K., Stumpf, F., Blum, H. et al. The protective effect of betacellulin against acute pancreatitis is ERBB4 dependent. J Gastroenterol 55, 317–329 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01613-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01613-6