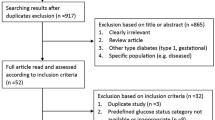
Abstract
Aims
Depression is a common co-morbidity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Untreated depression in these patients adversely affects self-care activities and other diabetes complications. The aim of this study is to estimate the prevalence of depression among patients with T2DM by conducting a meta-analysis of observational studies.
Methods
MEDLINE, Web of Science, Science Direct, and Google Scholar databases were searched for all observational studies that assessed depression in T2DM. Relevant articles were searched using the combination of Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms of “depression”, “depressive disorder”, and “diabetes mellitus” published between January 2007 and July 2018. Random effects model was used to estimate the weighted prevalence rates and 95% CI using “metaprop program in STATA 11”.
Results
In total, the 248 included studies (with 273 reported prevalence) identified 83,020,812 participants; of them, 23,245,827 (28%; 95% CI 27, 29) suffered from different severity levels of depressive disorders. The prevalence of depression was separately reported in 137,372 males and 134,332 females. Of them, 31,396 males (23%, 95% CI: 20, 26) and 45,673 females (34%, 95% CI: 31, 38) were depressed. Compared with global estimate, depression prevalence was lower in Europe (24%) and Africa (27%), but higher in Australia (29%) and Asia (32%). The prevalence in America was equal to the estimated prevalence in the world (28%). Depression was more common in subjects younger than 65 compared with elderlies (31% vs. 21%).
Conclusion
Our findings demonstrated that almost one in four adults with T2DM experienced depression. Given the high prevalence of depressive disorders in diabetic patients, screening these patients for co-morbid depression and its relevant risk factors is highly recommended.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federation ID (2017) IDF diabetes atlas. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation.. http://diabetesatlas.org/resources/2017-atlas.html. Accessed 17 July 2018
van Dieren S, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, Grobbee DE, Neal B (2010) The global burden of diabetes and its complications: an emerging pandemic. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 17(Suppl 1):S3–S8
Zimmet P (2003) The burden of type 2 diabetes: are we doing enough? Diabetes Metab 29(4 Pt 2):6s9–18
Eren I, Erdi O, Sahin M (2008) The effect of depression on quality of life of patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Depress Anxiety 25(2):98–106
Vos T, Allen C, Arora M et al (2016) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388(10053):1545–1602
Organization World Health (WHO) (2017) Depression and other common mental disorders: global health estimates. Available from: https://www.who.int/mental_health%2Fmanagement%2Fdepression%2Fprevalence_global_health_estimates%2Fen%2F. Accessed Feb 2019
American Psychiatric Association (2018) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). Available from: https://dsm.psychiatryonline.org/pb-assets/dsm/update/DSM5Update_October2018.pdf. Accessed Feb 2019
Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ (2001) The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 24(6):1069–1078
Ali S, Stone MA, Peters JL, Davies MJ, Khunti K (2006) The prevalence of co-morbid depression in adults with Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Med 23(11):1165–1173
Sweileh WM, Abu-Hadeed HM, Al-Jabi SW, Zyoud SH (2014) Prevalence of depression among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross sectional study in Palestine. BMC Public Health 14:163
Joshi S, Dhungana RR, Subba UK (2015) Illness perception and depressive symptoms among persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analytical cross-sectional study in clinical settings in Nepal. J Diabetes Res 2015:908374
Shehatah A, Rabie MA, Al-Shahry A (2010) Prevalence and correlates of depressive disorders in elderly with type 2 diabetes in primary health care settings. J Affect Disord 123(1–3):197–201
Habtewold TD, Islam MA, Radie YT, Tegegne BS (2016) Comorbidity of depression and diabetes: an application of biopsychosocial model. Int J Ment Health Syst 10:74
Oladeji BD, Gureje O (2013) The comorbidity between depression and diabetes. Curr Psychiatry Rep 15(9):390
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol 62(10):e1–e34
Harlow SD, Linet MS (1989) Agreement between questionnaire data and medical records. The evidence for accuracy of recall. Am J Epidemiol 129(2):233–248
Svenningsson I, Bjorkelund C, Marklund B, Gedda B (2012) Anxiety and depression in obese and normal-weight individuals with diabetes type 2: a gender perspective. Scand J Caring Sci 26(2):349–354
Roy T, Lloyd CE, Parvin M, Mohiuddin KG, Rahman M (2012) Prevalence of co-morbid depression in out-patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Bangladesh. BMC Psychiatry 12:123
Khamseh ME, Baradaran HR, Javanbakht A, Mirghorbani M, Yadollahi Z et al (2011) Comparison of the CES-D and PHQ-9 depression scales in people with type 2 diabetes in Tehran, Iran. BMC Psychiatry 11:61
Milette K, Hudson M, Baron M, Thombs BD, Canadian Scleroderma Research Group (2010) Comparison of the PHQ-9 and CES-D depression scales in systemic sclerosis: internal consistency reliability, convergent validity and clinical correlates. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49(4):789–796
Loosman WL, Siegert CE, Korzec A, Honig A (2010) Validity of the hospital anxiety and depression scale and the beck depression inventory for use in end-stage renal disease patients. Br J Clin Psychol 49(Pt 4):507–516
Cameron IM, Crawford JR, Lawton K, Reid IC (2008) Psychometric comparison of PHQ-9 and HADS for measuring depression severity in primary care. Br J Gen Pract 58(546):32–36
Nyaga VN, Arbyn M, Aerts M (2014) Metaprop: a Stata command to perform meta-analysis of binomial data. Arch Public Health 72(1):39
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Harris R, Bradburn M, Deeks J, Harbord R, Altman D, Sterne J (2008) Metan: fixed-and random-effects meta-analysis. Stata J 8(1):3
Sterne JA, Egger M, Smith GD (2001) Systematic reviews in health care: investigating and dealing with publication and other biases in meta-analysis. BMJ 323(7304):101–105
Wilson C, Twigg G (2003) Pharmacist-led depression screening and intervention in an underserved, rural, and multi-ethnic diabetic population. J Am Pharm Assoc 58(2):205–209
Tabesh M, Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Soderberg S, Koye DN et al (2018) The association between type 2 diabetes and disability: what is the contribution of diabetes risk factors and diabetes complications? J Diabetes 10(9):744–752
Sughra U, Imran M (2018) Co-morbid depression in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pak Med Assoc 68(1):109–111
Shinkov A, Borissova AM, Kovatcheva R, Vlahov J, Dakovska L, Atanassova I et al (2018) Increased prevalence of depression and anxiety among subjects with metabolic syndrome and known type 2 diabetes mellitus - a population-based study. Postgrad Med 130(2):251–257
Schinckus L, Dangoisse F, Van den Broucke S, Mikolajczak M (2018) When knowing is not enough: Emotional distress and depression reduce the positive effects of health literacy on diabetes self-management. Patient Educ Couns 101(2):324–330
Saman KA, Massad S, Ibaid AA, Anan H, Daher M, Salman R et al (2018) Factors associated with depression in patients with type 2 diabetes in the Gaza Strip: a cross sectional study. Lancet 391(Suppl 2):S19
Renn BN, Obetz V, Feliciano L. Comorbidity of depressive symptoms among primary care patients with diabetes in a federally qualified health center. J Health Psychol. 2018:1359105318755260
Rawlings AM, Sharrett AR, Golden SH, Windham BG, Selvin E (2018) Prevalence and correlates of depressive symptoms in older adults across the glycaemic spectrum: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Diabetes Med 35(5):583–587
Purewal R, Fisher PL (2018) The contribution of illness perceptions and metacognitive beliefs to anxiety and depression in adults with diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 136:16–22
Mocan AS, Iancu SS, Baban AS (2018) Association of cognitive-emotional regulation strategies to depressive symptoms in type 2 diabetes patients. Rom J Intern Med 56(1):34–40
Meneilly GS, Berard LD, Cheng AYY, Lin PJ, MacCallum L, Tsuyuki RT et al (2018) Insights into the current management of older adults with type 2 diabetes in the Ontario primary care setting. Can J Diabetes 42(1):23–30
Ma Y, Li X, Zhao D, Wu R, Sun H, Chen S et al (2018) Association between cognitive vulnerability to depression—dysfunctional attitudes and glycaemic control among in-patients with type 2 diabetes in a hospital in Beijing: a multivariate regression analysis. Psychol Health Med 23(2):189–197
Lloyd CE, Nouwen A, Sartorius N, Ahmed HU, Alvarez A, Bahendeka S et al (2018) Prevalence and correlates of depressive disorders in people with Type 2 diabetes: results from the International Prevalence and Treatment of Diabetes and Depression (INTERPRET-DD) study, a collaborative study carried out in 14 countries. Diabetes Med 35(6):760–769
Kotsani M, Chatziadamidou T, Economides D, Benetos A (2018) Higher prevalence and earlier appearance of geriatric phenotypes in old adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 135:206–217
Gois C, Duarte TA, Paulino S, Raposo JF, do Carmo I, Barbosa A (2018) Depressive symptoms are associated with poor glycemic control among women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Res Notes 11(1):38
Furukawa S, Sakai T, Niiya T, Miyaoka H, Miyake T, Yamamoto S et al (2018) Nocturia and prevalence of depressive symptoms in Japanese adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the DOGO study. Can J Diabetes 42(1):51–55
Eker S (2018) Prevalence of depression symptoms in diabetes mellitus. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 6(2):340–343
Choi WH, Seo YM, Ha Y (2018) Evaluation of factors related to glycaemic control among South Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Nurs Pract 24(1):e12616
Braizat O, Feinn R, Abbott G, Wagner J (2018) Relationship style and glycaemic control in women with type 2 diabetes: the mediating role of psychological distress. Stress Health 34(3):462–467
Younis BB, Arshad R, Yousuf H, Salman F, Masood J, Khurshid S (2017) Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on quality of life in people with diabetespresenting to a specialist diabetes clinic. Turk J Med Sci 47(1):123–126
Wong EM, Afshar R, Qian H, Zhang M, Elliott TG, Tang TS (2017) Diabetes distress, depression and glycemic control in a canadian-based specialty care setting. Can J Diabetes 41(4):362–365
Webb M, Davies M, Ashra N, Bodicoat D, Brady E, Webb D et al (2017) The association between depressive symptoms and insulin resistance, inflammation and adiposity in men and women. PloS One 12(11):e0187448
Wang Y, Yang H, Meng P, Han Y (2017) Association between low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and depression in a large sample of Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Affect Disord 224:56–60
Taylor S, McDermott R, Thompson F, Usher K (2017) Depression and diabetes in the remote Torres Strait Islands. Health Promot J Aust 28(1):59–66
Tan ML, Tan CS, Griva K, Lee YS, Lee J, Tai ES et al (2017) Factors associated with diabetes-related distress over time among patients with T2DM in a tertiary hospital in Singapore. BMC Endocr Disord 17(1):36
Sidhu R, Tang TS (2017) Diabetes distress and depression in south Asian Canadians with type 2 diabetes. Can J Diabetes 41(1):69–72
Shin N, Hill-Briggs F, Langan S, Payne JL, Lyketsos C, Golden SH (2017) The association of minor and major depression with health problem-solving and diabetes self-care activities in a clinic-based population of adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Compl 31(5):880–885
Patel PJ, Hayward KL, Rudra R, Horsfall LU, Hossain F, Williams S et al (2017) Multimorbidity and polypharmacy in diabetic patients with NAFLD: Implications for disease severity and management. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(26):e6761
Naicker K, Overland S, Johnson JA, Manuel D, Skogen JC, Sivertsen B et al (2017) Symptoms of anxiety and depression in type 2 diabetes: Associations with clinical diabetes measures and self-management outcomes in the Norwegian HUNT study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 84:116–123
Moreira BS, Sampaio RF, Diz JB, Bastone AC, Ferriolli E, Neri AL et al (2017) Factors associated with fear of falling in community-dwelling older adults with and without diabetes mellitus: findings from the Frailty in Brazilian Older People Study (FIBRA-BR). Exp Gerontol 89:103–111
Lee CM, Chang CF, Pan MY, Hsu TH, Chen MY (2017) Depression and its associated factors among rural diabetic residents. J Nurs Res 25(1):31–40
Kav S, Yilmaz AA, Bulut Y, Dogan N (2017) Self-efficacy, depression and self-care activities of people with type 2 diabetes in Turkey. Collegian 24(1):27–35
Golden SH, Shah N, Naqibuddin M, Payne JL, Hill-Briggs F, Wand GS et al (2017) The prevalence and specificity of depression diagnosis in a clinic-based population of adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Psychosomatics 58(1):28–37
Gahlan D, Rajput R, Gehlawat P, Gupta R (2018) Prevalence and determinants of diabetes distress in patients of diabetes mellitus in a tertiary care centre. Diabetes Metab Syndr 12(3):333–336
Cardenas V, Mausbach BT, Sommerfeld D, Jimenez D, von Kanel R, Ho JS et al (2017) Depression is associated with increased risk for metabolic syndrome in latinos with type 2 diabetes. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 25(6):646–653
AlBekairy A, AbuRuz S, Alsabani B, Alshehri A, Aldebasi T, Alkatheri A et al (2017) Exploring factors associated with depression and anxiety among hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Princ Pract 26(6):547–553
Albasheer OB, Mahfouz MS, Solan Y, Khan DA, Muqri MA, Almutairi HA et al (2018) Depression and related risk factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Jazan area, KSA: a cross-sectional study. Diabetes Metab Syndr 12(2):117–121
Zhang P, Lou P, Chang G, Chen P, Zhang L, Li T et al (2016) Combined effects of sleep quality and depression on quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Fam Pract 17:40
Whitworth SR, Bruce DG, Starkstein SE, Davis WA, Davis TM, Bucks RS (2016) Lifetime depression and anxiety increase prevalent psychological symptoms and worsen glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study Phase II. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 122:190–197
Wang Y, Lopez JM, Bolge SC, Zhu VJ, Stang PE (2016) Depression among people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 2005–20126. BMC Psychiatry 16:88
Urrutia-Aliano D, Segura ER (2016) [Depressive symptoms and type 2 diabetes mellitus in outpatients of an Armed Forces hospital in Lima, Peru, 2012: a cross-sectional study]. Medwave 16(3):e6435
Sun N, Lou P, Shang Y, Zhang P, Wang J, Chang G et al (2016) Prevalence and determinants of depressive and anxiety symptoms in adults with type 2 diabetes in China: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 6(8):e012540
Sopjani I, Vehapi S, Gorani D, Imeri M, Vitoja S, Tahiri S (2016) The relation between depressive symptoms and self-care in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 in Kosovo. Med Arch 70(6):425–428
Sehlo MG, Alzahrani OH, Alzahrani HA (2016) Illness invalidation from spouse and family is associated with depression in diabetic patients with first superficial diabetic foot ulcers. Int J Psychiatry Med 51(1):16–30
Mut-Vitcu G, Timar B, Timar R, Oancea C, Citu IC (2016) Depression influences the quality of diabetes-related self-management activities in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Clin Interv Aging 11:471–479
Mutambudzi M, Chen NW, Markides KS, Al Snih S (2016) Effects of functional disability and depressive symptoms on mortality in older mexican-american adults with diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc 64(11):e154–e159
Mushtaque A, Gulati R, Hossain MM, Azmi SA (2016) Prevalence of depression in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross sectional study in a tertiary care centre. Diabetes Metab Syndr 10(4):238–241
Li Z, Guo X, Jiang H, Sun G, Sun Y, Abraham MR (2016) Diagnosed but not undiagnosed diabetes is associated with depression in rural areas. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(11):1136
Khullar S, Dhillon H, Kaur G, Sharma R, Mehta K, Aggarwal R et al (2016) The prevalence and predictors of depression in type 2 diabetic population of Punjab. Community Ment Health J 52(4):479–483
Jones LC, Clay OJ, Ovalle F, Cherrington A, Crowe M (2016) Correlates of depressive symptoms in older adults with diabetes. J Diabetes Res 2016:8702730
Johnson ST, Al Sayah F, Mathe N, Johnson JA (2016) The relationship of diabetes-related distress and depressive symptoms with physical activity and dietary behaviors in adults with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. J Diabetes Compl 30(5):967–970
Hashim NA, Ariaratnam S, Salleh MR, Said MA, Sulaiman AH (2016) Depression and associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. East Asian Arch Psychiatry 26(2):77–82
Habtewold TD, Alemu SM, Haile YG (2016) Sociodemographic, clinical, and psychosocial factors associated with depression among type 2 diabetic outpatients in Black Lion General Specialized Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 16:103
Cols-Sagarra C, Lopez-Simarro F, Alonso-Fernandez M, Mancera-Romero J, Perez-Unanua MP et al (2016) Prevalence of depression in patients with type 2 diabetes attended in primary care in Spain. Prim Care Diabetes 10(5):369–375
Chew BH, Vos R, Mohd-Sidik S, Rutten GE (2016) Diabetes-related distress, depression and distress-depression among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Malaysia. PloS One 11(3):e0152095
Birhanu AM, Alemu FM, Ashenafie TD, Balcha SA, Dachew BA (2016) Depression in diabetic patients attending University of Gondar Hospital Diabetic Clinic, Northwest Ethiopia. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 9:155–162
Arshad AR, Alvi KY (2016) Frequency of depression in type 2 diabetes mellitus and an analysis of predictive factors. J Pak Med Assoc 66(4):425–429
Zhang Y, Ting RZ, Yang W, Jia W, Li W, Ji L et al (2015) Depression in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: associations with hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and poor treatment adherence. J Diabetes 7(6):800–808
Zhang W, Xu H, Zhao S, Yin S, Wang X, Guo J et al (2015) Prevalence and influencing factors of co-morbid depression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a General Hospital based study. Diabetol Metab Syndr 7:60
Wang L, Song R, Chen Z, Wang J, Ling F (2015) Prevalence of depressive symptoms and factors associated with it in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study in China. BMC Public Health 15:188
Thour A, Das S, Sehrawat T, Gupta Y (2015) Depression among patients with diabetes mellitus in North India evaluated using patient health questionnaire-9. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 19(2):252–255
Tan KC, Chan GC, Eric H, Maria AI, Norliza MJ, Oun BH et al (2015) Depression, anxiety and stress among patients with diabetes in primary care: a cross-sectional study. Malays Fam Physician 10(2):9–21
Taheri Tanjani P, Moradinazar M, Esmail Mottlagh M, Najafi F (2015) The prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) type II among Iranian elderly population and its association with other age-related diseases, 2012. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 60(3):373–379
Rodriguez Calvin JL, Zapatero Gaviria A, Martin Rios MD (2015) Prevalence of depression in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Rev Clin Esp 215(3):156–164
Parildar H, Cigerli O, Demirag NG (2015) Depression, coping strategies, glycemic control and patient compliance in type 2 diabetic patients in an endocrine outpatient clinic. Pak J Med Sci 31(1):19–24
Okumiya K, Fujisawa M, Sakamoto R, Wada T, Chen WL, Imai H et al (2015) Effect of early diagnosis and lifestyle modification on depressive symptoms in community-dwelling elderly adults with glucose intolerance: 5-year longitudinal study. J Am Geriatr Soc 63(2):393–395
Nefs G, Donga E, van Someren E, Bot M, Speight J, Pouwer F (2015) Subjective sleep impairment in adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes: Results from Diabetes MILES—The Netherlands. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 109(3):466–475
Mishra SR, Sharma A, Bhandari PM, Bhochhibhoya S, Thapa K (2015) Depression and health-related quality of life among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study in Nepal. PloS One 10(11):e0141385
Mir K, Mir K, Malik I, Shehzadi A (2015) The prevalence of co-morbid depression in diabetic population. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 27(1):99–101
Mayberry LS, Egede LE, Wagner JA, Osborn CY (2015) Stress, depression and medication nonadherence in diabetes: test of the exacerbating and buffering effects of family support. J Behav Med 38(2):363–371
March D, Williams J, Wells S, Eimicke JP, Teresi JA, Almonte C et al (2015) Discrimination and depression among urban hispanics with poorly controlled diabetes. Ethn Dis 25(2):130–137
Knaster ES, Fretts AM, Phillips LE (2015) The association of depression with diabetes management among urban American Indians/Alaska Natives in the United States, 2011. Ethn Dis 25(1):83–89
Islam SM, Rawal LB, Niessen LW (2015) Prevalence of depression and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Asian J Psychiatr 17:36–41
Hapunda G, Abubakar A, Pouwer F, van de Vijver F (2015) Diabetes mellitus and comorbid depression in Zambia. Diabetes Med 32(6):814–818
Gemeay EM, Moawed SA, Mansour EA, Ebrahiem NE, Moussa IM, Nadrah WO (2015) The association between diabetes and depression. Saudi Med J 36(10):1210–1215
Foran E, Hannigan A, Glynn L (2015) Prevalence of depression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Irish primary care and the impact of depression on the control of diabetes. Ir J Med Sci 184(2):319–322
El Mahalli AA (2015) Prevalence and predictors of depression among type 2 diabetes mellitus outpatients in eastern province, Saudi Arabia. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 9(2):119–126
Derakhshanpour F, Vakili MA, Farsinia M, Mirkarimi K (2015) Depression and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes. Iran Red Crescent Med J 17(5):e27676
Czech SJ, Orsillo SM, Pirraglia PA, English TM, Connell AJ (2015) Association between specific depression symptoms and glycemic control among patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes and provisional depression. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.14m01754
Crispin-Trebejo B, Robles-Cuadros MC, Bernabe-Ortiz A (2015) Association between depression and glycemic control among type 2 diabetes patients in Lima, Peru. Asia Pac Psychiatry 7(4):419–426
Camara A, Balde NM, Enoru S, Bangoura JS, Sobngwi E, Bonnet F (2015) Prevalence of anxiety and depression among diabetic African patients in Guinea: association with HbA1c levels. Diabetes Metab 41(1):62–68
Zheng Y, Sun Q, Chen K, Yan W, Pan C, Lu J et al (2014) Waist-to-hip ratio, dyslipidemia, glycemic levels, blood pressure and depressive symptoms among diabetic and non-diabetic Chinese women: a cross-sectional study. PloS One 9(10):e109765
Vanderlip ER, Katon W, Russo J, Lessler D, Ciechanowski P (2014) Depression among patients with diabetes attending a safety-net primary care clinic: relationship with disease control. Psychosomatics 55(6):548–554
Pearson S, Nash T, Ireland V (2014) Depression symptoms in people with diabetes attending outpatient podiatry clinics for the treatment of foot ulcers. J Foot Ankle Res 7(1):47
Palta P, Golden SH, Teresi JA, Palmas W, Trief P, Weinstock RS et al (2014) Depression is not associated with diabetes control in minority elderly. J Diabetes Compl 28(6):798–804
Omagari K, Sakaki M, Tsujimoto Y, Shiogama Y, Iwanaga A, Ishimoto M et al (2014) Coffee consumption is inversely associated with depressive status in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Biochem Nutr 55(2):135–142
Musselman DL, Ziemer DC, McNutt MD, Seay JS, Royster EB, Larsen B et al (2014) Depression, deficits in functional capacity, and impaired glycemic control in urban African Americans with type 2 diabetes. J Psychiatr Res 52:21–27
Mikaliukstiene A, Zagminas K, Juozulynas A, Narkauskaite L, Salyga J, Jankauskiene K et al (2014) Prevalence and determinants of anxiety and depression symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes in Lithuania. Med Sci Monit 20:182–190
Martinez Hernandez F, Tovilla Zarate CA, Lopez Narvaez L, Juarez Rojop IE, Jimenez Santos MA, Gonzalez Gutierrez CP et al (2014) [Prevalence and gravity of depression and anxiety in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes: a study in the population of Tabasco, Mexico]. Gac Med Mex 150(Suppl 1):101–106
Limongi F, Noale M, Crepaldi G, Maggi S (2014) Prevalence of diabetes and depressive symptomatology and their effect on mortality risk in elderly Italians: the Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Diabetes Metab 40(5):373–378
Lara Munoz Mdel C, Jacobs EA, Escamilla MA, Mendenhall E (2014) Depression among diabetic women in urban centers in Mexico and the United States of America: a comparative study. Rev Panam Salud Publica 36(4):225–231
Khan MA, Sultan SM, Nazli R, Akhtar T, Khan MA, Sher N et al (2014) Depression among patients with type-II diabetes mellitus. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 24(10):770–771
Jafari N, Farajzadegan Z, Loghmani A, Majlesi M, Jafari N (2014) Spiritual well-being and quality of life of Iranian adults with type 2 diabetes. Evid Based Compl Alternat Med 2014:619028
Hayashino Y, Mashitani T, Tsujii S, Ishii H (2014) Elevated levels of hs-CRP are associated with high prevalence of depression in japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: the Diabetes Distress and Care Registry at Tenri (DDCRT 6). Diabetes Care 37(9):2459–2465
Gorska-Ciebiada M, Saryusz-Wolska M, Ciebiada M, Loba J (2014) Mild cognitive impairment and depressive symptoms in elderly patients with diabetes: prevalence, risk factors, and comorbidity. J Diabetes Res 2014:179648
Ganasegeran K, Renganathan P, Manaf RA, Al-Dubai SA (2014) Factors associated with anxiety and depression among type 2 diabetes outpatients in Malaysia: a descriptive cross-sectional single-centre study. BMJ Open 4(4):e004794
Dismuke CE, Hernandez-Tejada MA, Egede LE (2014) Relationship of serious psychological distress to quality of life in adults with diabetes. Int J Psychiatry Med 48(2):135–146
Carper MM, Traeger L, Gonzalez JS, Wexler DJ, Psaros C, Safren SA (2014) The differential associations of depression and diabetes distress with quality of life domains in type 2 diabetes. J Behav Med 37(3):501–510
Bensbaa S, Agerd L, Boujraf S, Araab C, Aalouane R, Rammouz I et al (2014) Clinical assessment of depression and type 2 diabetes in Morocco: Economical and social components. J Neurosci Rural Pract 5(3):250–253
Azad N, Gondal M, Abbas N, Shahid A (2014) Frequency of depression and anxiety in patients attending a diabetes clinic. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 26(3):323–327
Alonso-Moran E, Satylganova A, Orueta JF, Nuno-Solinis R (2014) Prevalence of depression in adults with type 2 diabetes in the Basque Country: relationship with glycaemic control and health care costs. BMC Public Health 14:769
Zhang J, Xu CP, Wu HX, Xue XJ, Xu ZJ, Li Y et al (2013) Comparative study of the influence of diabetes distress and depression on treatment adherence in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional survey in the People’s Republic of China. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 9:1289–1294
Yu MK, Katon W, Young BA (2013) Diabetes self-care, major depression, and chronic kidney disease in an outpatient diabetic population. Nephron Clin Pract 124(1–2):106–112
Wu SF, Young LS, Yeh FC, Jian YM, Cheng KC, Lee MC (2013) Correlations among social support, depression, and anxiety in patients with type-2 diabetes. J Nurs Res 21(2):129–138
Twist K, Stahl D, Amiel SA, Thomas S, Winkley K, Ismail K (2013) Comparison of depressive symptoms in type 2 diabetes using a two-stage survey design. Psychosom Med 75(8):791–797
Tanenbaum ML, Ritholz MD, Binko DH, Baek RN, Shreck MS, Gonzalez JS (2013) Probing for depression and finding diabetes: a mixed-methods analysis of depression interviews with adults treated for type 2 diabetes. J Affect Disord 150(2):533–539
Schierhout G, Nagel T, Si D, Connors C, Brown A, Bailie R (2013) Do competing demands of physical illness in type 2 diabetes influence depression screening, documentation and management in primary care: a cross-sectional analytic study in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander primary health care settings. Int J Ment Health Syst 7(1):16
Palizgir M, Bakhtiari M, Esteghamati A (2013) Association of depression and anxiety with diabetes mellitus type 2 concerning some sociological factors. Iran Red Crescent Med J 15(8):644–648
Niraula K, Kohrt BA, Flora MS, Thapa N, Mumu SJ, Pathak R et al (2013) Prevalence of depression and associated risk factors among persons with type-2 diabetes mellitus without a prior psychiatric history: a cross-sectional study in clinical settings in urban Nepal. BMC Psychiatry 13:309
Myers AK, Grannemann BD, Lingvay I, Trivedi MH (2013) Brief report: depression and history of suicide attempts in adults with new-onset Type 2 Diabetes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38(11):2810–2814
Madhu M, Abish A, Anu K, Jophin RI, Kiran AM, Vijayakumar K (2013) Predictors of depression among patients with diabetes mellitus in Southern India. Asian J Psychiatr 6(4):313–317
Kaur G, Tee GH, Ariaratnam S, Krishnapillai AS, China K (2013) Depression, anxiety and stress symptoms among diabetics in Malaysia: a cross sectional study in an urban primary care setting. BMC Fam Pract 14:69
Joseph N, Unnikrishnan B, Raghavendra Babu YP, Kotian MS, Nelliyanil M (2013) Proportion of depression and its determinants among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in various tertiary care hospitals in Mangalore city of South India. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 17(4):681–688
Hawamdeh S, Almakhzoomy I, Hayajneh Y (2013) Screening and correlates of depression and HbA1 C in United Arab Emirates (UAE) women with diabetes. Perspect Psychiatr Care 49(4):262–268
Hajos TR, Pouwer F, Skovlund SE, Den Oudsten BL, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn PH, Tack CJ et al (2013) Psychometric and screening properties of the WHO-5 well-being index in adult outpatients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Med 30(2):e63–e69
Furuya M, Hayashino Y, Tsujii S, Ishii H, Fukuhara S (2013) Comparative validity of the WHO-5 Well-Being Index and two-question instrument for screening depressive symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 50(2):117–121
Frederick FT, Maharajh HD (2013) Prevalence of depression in type 2 diabetic patients in Trinidad and Tobago. West Indian Med J 62(7):628–631
Das R, Singh O, Thakurta RG, Khandakar MR, Ali SN, Mallick AK et al (2013) Prevalence of depression in patients with type II diabetes mellitus and its impact on quality of life. Indian J Psychol Med 35(3):284–289
Clyde M, Smith KJ, Gariepy G, Schmitz N (2013) The association between smoking and depression in a Canadian community-based sample with type 2 diabetes. Can J Diabetes 37(3):150–155
Chung JO, Cho DH, Chung DJ, Chung MY (2013) Assessment of factors associated with the quality of life in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. Intern Med 52(2):179–185
Choi SE, Reed PL (2013) Contributors to depressive symptoms among Korean immigrants with type 2 diabetes. Nurs Res 62(2):115–121
Baradaran HR, Mirghorbani SM, Javanbakht A, Yadollahi Z, Khamseh ME (2013) Diabetes distress and its association with depression in patients with type 2 diabetes in iran. Int J Prev Med 4(5):580–584
Tsujii S, Hayashino Y, Ishii H (2012) Diabetes distress, but not depressive symptoms, is associated with glycaemic control among Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: Diabetes Distress and Care Registry at Tenri (DDCRT 1). Diabetes Med 29(11):1451–1455
Trento M, Raballo M, Trevisan M, Sicuro J, Passera P, Cirio L et al (2012) A cross-sectional survey of depression, anxiety, and cognitive function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 49(3):199–203
Tovilla-Zarate C, Juarez-Rojop I, Peralta Jimenez Y, Jimenez MA, Vazquez S, Bermudez-Ocana D et al (2012) Prevalence of anxiety and depression among outpatients with type 2 diabetes in the Mexican population. PloS One 7(5):e36887
Shah BM, Gupchup GV, Borrego ME, Raisch DW, Knapp KK (2012) Depressive symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: do stress and coping matter? Stress Health 28(2):111–122
Rahman M, Rahman MA, Flora MS, Karim R, Zaman MR (2012) Depression and its association with socio-demographic characteristics among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients of Bangladesh. Mymensingh Med J 21(3):490–496
Park H, Kim MT (2012) Impact of social role strain, depression, social support and age on diabetes self-efficacy in Korean women with type 2 diabetes. J Cardiovasc Nurs 27(1):76–83
Osme SF, Ferreira L, Jorge MT, de Souza Andreo J, Jorge M, de Melo Costa Pinto R et al (2012) Difference between the prevalence of symptoms of depression and anxiety in non-diabetic smokers and in patients with type 2 diabetes with and without nicotine dependence. Diabetol Metab Syndr 4(1):39
Osborn CY, Egede LE (2012) The relationship between depressive symptoms and medication nonadherence in type 2 diabetes: the role of social support. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 34(3):249–253
Mendenhall E, Jacobs EA (2012) Interpersonal abuse and depression among mexican immigrant women with type 2 diabetes. Cult Med Psychiatry 36(1):136–153
Maia AC, Braga Ade A, Brouwers A, Nardi AE, Oliveira e Silva AC (2012) Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in patients with diabetes types 1 and 2. Compr Psychiatry 53(8):1169–1173
Lynch CP, Hernandez-Tejada MA, Strom JL, Egede LE (2012) Association between spirituality and depression in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ 38(3):427–435
Lofman S, Hakko H, Mainio A, Timonen M, Rasanen P (2012) Characteristics of suicide among diabetes patients: a population based study of suicide victims in Northern Finland. J Psychosom Res 73(4):268–271
Labad J, Price JF, Strachan MW, Fowkes FG, Deary IJ, Seckl JR et al (2012) Leptin levels and depressive symptoms in people with type 2 diabetes: the edinburgh type 2 diabetes study. Psychosom Med 74(1):39–45
Katon W, Lyles CR, Parker MM, Karter AJ, Huang ES, Whitmer RA (2012) Association of depression with increased risk of dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Diabetes and Aging Study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69(4):410–417
Hosoya T, Matsushima M, Nukariya K, Utsunomiya K (2012) The relationship between the severity of depressive symptoms and diabetes-related emotional distress in patients with type 2 diabetes. Intern Med 51(3):263–269
Guruprasad KG, Niranjan MR, Ashwin S (2012) A study of association of depressive symptoms among the type 2 diabetic outpatients presenting to a tertiary care hospital. Indian J Psychol Med 34(1):30–33
Green AJ, Fox KM, Grandy S (2012) Self-reported hypoglycemia and impact on quality of life and depression among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 96(3):313–318
Feinkohl I, Sattar N, Welsh P, Reynolds RM, Deary IJ, Strachan MW et al (2012) Association of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide with cognitive function and depression in elderly people with type 2 diabetes. PloS One 7(9):e44569
Bassett J, Adelman A, Gabbay R, Anel-Tiangco RM (2012) Relationship between depression and treatment satisfaction among patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Metab 3(7):1–8
Wu SF, Huang YC, Liang SY, Wang TJ, Lee MC, Tung HH (2011) Relationships among depression, anxiety, self-care behaviour and diabetes education difficulties in patients with type-2 diabetes: a cross-sectional questionnaire survey. Int J Nurs Stud 48(11):1376–1383
van Steenbergen-Weijenburg KM, van Puffelen AL, Horn EK, Nuyen J, van Dam PS et al (2011) More co-morbid depression in patients with Type 2 diabetes with multiple complications. An observational study at a specialized outpatient clinic. Diabetes Med 28(1):86–89
Sorkin DH, Ngo-Metzger Q, Billimek J, August KJ, Greenfield S, Kaplan SH (2011) Underdiagnosed and undertreated depression among racially/ethnically diverse patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 34(3):598–600
So ES, Chin YR, Lee IS (2011) Relationship between health-related behavioral and psychological factors and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases comorbidity among korean adults with diabetes. Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci) 5(4):204–209
Rodriguez-Pascual C, Rodriguez-Justo S, Garcia-Villar E, Narro-Vidal M, Torrente-Carballido M, Paredes-Galan E (2011) Quality of life, characteristics and metabolic control in diabetic geriatric patients. Maturitas 69(4):343–347
Poongothai S, Anjana RM, Pradeepa R, Ganesan A, Unnikrishnan R, Rema M et al (2011) Association of depression with complications of type 2 diabetes—the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-102). J Assoc Physicians India 59:644–648
Papelbaum M, Moreira RO, Coutinho W, Kupfer R, Zagury L, Freitas S et al (2011) Depression, glycemic control and type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr 3(1):26
Miller ST (2011) Diabetes and psychological profile of younger rural African American women with type 2 diabetes. J Health Care Poor Underserved 22(4):1239–1252
Mantyselka P, Korniloff K, Saaristo T, Koponen H, Eriksson J, Puolijoki H et al (2011) Association of depressive symptoms with impaired glucose regulation, screen-detected, and previously known type 2 diabetes: findings from the Finnish D2D Survey. Diabetes Care 34(1):71–76
Joshi A, Joshi A, Maseeh A, Jha PK, Bhatt M, Vyasa B (2011) A study of prevalence of depression in diabetes mellitus: analysis from urban India. Indian J Med Sci 65(11):497–501
Balhara YP, Sagar R (2011) Correlates of anxiety and depression among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 15(Suppl 1):S50–S54
Al-Amer RM, Sobeh MM, Zayed AA, Al-Domi HA (2011) Depression among adults with diabetes in Jordan: risk factors and relationship to blood sugar control. J Diabetes Compl 25(4):247–252
Yu R, L YH, Hong L (2010) Depression in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 30(2):102–104
Yekta Z, Pourali R, Yavarian R (2010) Behavioural and clinical factors associated with depression among individuals with diabetes. East Mediterr Health J 16(3):286–291
Tsirogianni E, Kouniakis F, Baltatzi M, Lavrentiadis G, Alevizos M (2010) [Biological factors associated with depression in patients with type IotaIota diabetes mellitus]. Psychiatriki 21(2):115–125
Sapozhnikova IE, Tarlovskaia EI, Sobolev AA, Rodygina EV (2010) [Frequency and specific features of depressive disorders in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus]. Klin Med (Mosk) 88(3):43–46
Raval A, Dhanaraj E, Bhansali A, Grover S, Tiwari P (2010) Prevalence and determinants of depression in type 2 diabetes patients in a tertiary care centre. Indian J Med Res 132:195–200
Pouwer F, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn PH, Tack CJ, Bazelmans E, Beekman AJ, Heine RJ et al (2010) Prevalence of comorbid depression is high in out-patients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Results from three out-patient clinics in the Netherlands. Diabet Med 27(2):217–224
Poongothai S, Anjana RM, Pradeepa R, Ganesan A, Umapathy N, Mohan V (2010) Prevalence of depression in relation to glucose intolerance in urban south Indians—the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-76). Diabetes Technol Ther 12(12):989–994
Khuwaja AK, Lalani S, Dhanani R, Azam IS, Rafique G, White F (2010) Anxiety and depression among outpatients with type 2 diabetes: a multi-centre study of prevalence and associated factors. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2:72
Cherrington A, Wallston KA, Rothman RL (2010) Exploring the relationship between diabetes self-efficacy, depressive symptoms, and glycemic control among men and women with type 2 diabetes. J Behav Med 33(1):81–89
Bair MJ, Brizendine EJ, Ackermann RT, Shen C, Kroenke K, Marrero DG (2010) Prevalence of pain and association with quality of life, depression and glycaemic control in patients with diabetes. Diabet Med 27(5):578–584
Yang J, Li S, Zheng Y (2009) Predictors of depression in Chinese community-dwelling people with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Nurs 18(9):1295–1304
Subramaniam M, Sum CF, Pek E, Stahl D, Verma S, Liow PH et al (2009) Comorbid depression and increased health care utilisation in individuals with diabetes. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 31(3):220–224
Lee HJ, Chapa D, Kao CW, Jones D, Kapustin J, Smith J et al (2009) Depression, quality of life, and glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. J Am Acad Nurse Pract 21(4):214–224
Kokoszka A, Pouwer F, Jodko A, Radzio R, Mucko P, Bienkowska J et al (2009) Serious diabetes-specific emotional problems in patients with type 2 diabetes who have different levels of comorbid depression: a Polish study from the European Depression in Diabetes (EDID) Research Consortium. Eur Psychiatry 24(7):425–430
Koopmans B, Pouwer F, de Bie RA, van Rooij ES, Leusink GL, Pop VJ (2009) Depressive symptoms are associated with physical inactivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. The DIAZOB Primary Care Diabetes study. Fam Pract 26(3):171–173
Graco M, Berlowitz DJ, Fourlanos S, Sundram S (2009) Depression is greater in non-English speaking hospital outpatients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 83(2):e51–e53
Aujla N, Abrams KR, Davies MJ, Taub N, Skinner TC, Khunti K (2009) The prevalence of depression in white-European and South-Asian people with impaired glucose regulation and screen-detected type 2 diabetes mellitus. PloS One 4(11):e7755
Collins-McNeil JC, Holston EC, Edwards CL, Benbow D, Ford Y (2009) Physical activity, depressive symptoms, and social support among African-American women with type 2 diabetes. Can J Nurs Res 41(3):24–43
Collins MM, Corcoran P, Perry IJ (2009) Anxiety and depression symptoms in patients with diabetes. Diabet Med 26(2):153–161
Ali S, Davies MJ, Taub NA, Stone MA, Khunti K (2009) Prevalence of diagnosed depression in South Asian and white European people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in a UK secondary care population. Postgrad Med J 85(1003):238–243
Zhang CX, Chen YM, Chen WQ (2008) Association of psychosocial factors with anxiety and depressive symptoms in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 79(3):523–530
Sotiropoulos A, Papazafiropoulou A, Apostolou O, Kokolaki A, Gikas A, Pappas S (2008) Prevalence of depressive symptoms among non insulin treated Greek type 2 diabetic subjects. BMC Res Notes 1:101
Rhee MK, Musselman D, Ziemer DC, Vaccarino V, Kolm P, Weintraub WS et al (2008) Unrecognized glucose intolerance is not associated with depression. Screening for Impaired Glucose Tolerance study 3 (SIGT 3). Diabet Med 25(11):1361–1365
Almawi W, Tamim H, Al-Sayed N, Arekat MR, Al-Khateeb GM, Baqer A et al (2008) Association of comorbid depression, anxiety, and stress disorders with Type 2 diabetes in Bahrain, a country with a very high prevalence of Type 2 diabetes. J Endocrinol Invest 31(11):1020–1024
Mier N, Bocanegra-Alonso A, Zhan D, Zuniga MA, Acosta RI (2008) Health-related quality of life in a binational population with diabetes at the Texas-Mexico border. Rev Panam Salud Publ 23(3):154–163
Mier N, Bocanegra-Alonso A, Zhan D, Wang S, Stoltz SM, Acosta-Gonzalez RI et al (2008) Clinical depressive symptoms and diabetes in a binational border population. J Am Board Fam Med 21(3):223–233
Adriaanse MC, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, Snoek FJ, Beekman AJ, Stehouwer CD et al (2008) Symptoms of depression in people with impaired glucose metabolism or Type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Hoorn Study. Diabetes Med 25(7):843–849
Wessels AM, Pouwer F, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn PH, Snel M, Kostense PJ, Scheltens P et al (2007) No evidence for increased self-reported cognitive failure in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Diabet Med 24(7):735–740
Sundaram M, Kavookjian J, Patrick JH, Miller LA, Madhavan SS, Scott VG (2007) Quality of life, health status and clinical outcomes in Type 2 diabetes patients. Qual Life Res 16(2):165–177
Sacco WP, Wells KJ, Friedman A, Matthew R, Perez S, Vaughan CA (2007) Adherence, body mass index, and depression in adults with type 2 diabetes: the mediational role of diabetes symptoms and self-efficacy. Health Psychol 26(6):693–700
Kogan SM, Brody GH, Crawley C, Logan P, Murry VM (2007) Correlates of elevated depressive symptoms among rural African American adults with type 2 diabetes. Ethn Dis 17(1):106–112
Knol MJ, Heerdink ER, Egberts AC, Geerlings MI, Gorter KJ, Numans ME et al (2007) Depressive symptoms in subjects with diagnosed and undiagnosed type 2 diabetes. Psychosom Med 69(4):300–305
Gonzalez JS, Safren SA, Cagliero E, Wexler DJ, Delahanty L, Wittenberg E et al (2007) Depression, self-care, and medication adherence in type 2 diabetes: relationships across the full range of symptom severity. Diabetes Care 30(9):2222–2227
Fisher L, Skaff MM, Mullan JT, Arean P, Mohr D, Masharani U et al (2007) Clinical depression versus distress among patients with type 2 diabetes: not just a question of semantics. Diabetes Care 30(3):542–548
Chazova TE, Voznesenskaia TG, Golitsyna T (2007) [Anxiety-depressive disorders in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with acute coronary syndrome]. Kardiologiia 47(6):10–14
Arima H, Miwa M, Kawahara K (2007) The prevalence of co-morbid depression among employees with type 2 diabetes in a Japanese corporation: a descriptive study using an integrated health database. J Med Dent Sci 54(1):39–48
Iwase M, Fujii H, Nakamura U, Ohkuma T, Ide H, Jodai-Kitamura T et al (2018) Incidence of diabetic foot ulcer in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Fukuoka diabetes registry. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 137:183–189
Chima CC, Salemi JL, Wang M, Mejia de Grubb MC, Gonzalez SJ, Zoorob RJ (2017) Multimorbidity is associated with increased rates of depression in patients hospitalized with diabetes mellitus in the United States. J Diabetes Compl 31(11):1571–1579
Zurita-Cruz JN, Manuel-Apolinar L, Arellano-Flores ML, Gutierrez-Gonzalez A, Najera-Ahumada AG, Cisneros-Gonzalez N (2018) Health and quality of life outcomes impairment of quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes 16(1):94
Wang D, Shi L, Li L, Guo X, Li Y, Xu Y et al (2018) Subthreshold depression among diabetes patients in Beijing: cross-sectional associations among sociodemographic, clinical, and behavior factors. J Affect Disord 237:80–86
Ronel J, Dinkel A, Wolf E, Marten-Mittag B, Mueck B, Mayr C et al (2018) Anxiety, depression, and health-related quality of life in aging people living with HIV compared to diabetes patients and patients with minor health conditions: a longitudinal study. Psychol Health Med 10:1–8
Rathmann W, Scheerer M, Rohwedder K, Busch S, Kostev K (2018) Changes in patient characteristics, glucose lowering treatment, glycemic control and complications in type 2 diabetes in general practices (Disease Analyzer, Germany: 2008–2016). Postgrad Med 130(2):244–250
Nanayakkara N, Pease A, Ranasinha S, Wischer N, Andrikopoulos S, Speight J et al (2018) Depression and diabetes distress in adults with type 2 diabetes: results from the Australian National Diabetes Audit (ANDA) 2016. Sci Rep 8(1):7846
Fung ACH, Tse G, Cheng HL, Lau ESH, Luk A, Ozaki R et al (2018) Depressive symptoms, co-morbidities, and glycemic control in Hong Kong Chinese Elderly Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:261
Tu HP, Hsieh HM, Liu TL, Jiang HJ, Wang PW, Huang CJ (2017) Prevalence of depressive disorder in persons with type 2 diabetes: a National Population-Based Cohort Study 2000–2010. Psychosomatics 58(2):151–163
Saetung S, Nimitphong H, Siwasaranond N, Manodpitipong A, Crowley SJ, Hood MM et al (2017) Eveningness is associated with greater depressive symptoms in type 2 diabetes patients: a study in two different ethnic cohorts. Behav Sleep Med 16:1–11
Smith KJ, Pedneault M, Schmitz N (2016) Investigation of anxiety and depression symptom co-morbidity in a community sample with type 2 diabetes: Associations with indicators of self-care. Can J Public Health 106(8):e496–e501
Rajput R, Gehlawat P, Gehlan D, Gupta R, Rajput M (2016) Prevalence and predictors of depression and anxiety in patients of diabetes mellitus in a tertiary care center. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 20(6):746–751
Nicolau J, Simo R, Sanchis P, Ayala L, Fortuny R, Rivera R et al (2016) Prevalence and clinical correlators of undiagnosed significant depressive symptoms among individuals with type 2 diabetes in a mediterranean population. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 124(10):630–636
Bruce DG, Davis WA, Dragovic M, Davis TM, Starkstein SE (2016) Comorbid anxiety and depression and their impact on cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: the fremantle diabetes study phase II. Depress Anxiety 33(10):960–966
Barnacle M, Strand MA, Werremeyer A, Maack B, Petry N (2016) Depression screening in diabetes care to improve outcomes: are we meeting the challenge? Diabetes Educ 42(5):646–651
Park CY, Kim SY, Gil JW, Park MH, Park JH, Kim Y (2015) Depression among Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ansan-community-based epidemiological study. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 6(4):224–232
Browne JL, Nefs G, Pouwer F, Speight J (2015) Depression, anxiety and self-care behaviours of young adults with Type 2 diabetes: results from the International Diabetes Management and Impact for Long-term Empowerment and Success (MILES) Study. Diabetes Med 32(1):133–140
Wami WM, Buntinx F, Bartholomeeusen S, Goderis G, Mathieu C, Aerts M (2013) Influence of chronic comorbidity and medication on the efficacy of treatment in patients with diabetes in general practice. Br J Gen Pract 63(609):e267–e273
Koekkoek PS, Rutten GE, Ruis C, Reijmer YD, van den Berg E, Gorter KJ et al (2013) Mild depressive symptoms do not influence cognitive functioning in patients with type 2 diabetes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38(3):376–386
Lewko J, Zarzycki W, Krajewska-Kulak E (2012) Relationship between the occurrence of symptoms of anxiety and depression, quality of life, and level of acceptance of illness in patients with type 2 diabetes. Saudi Med J 33(8):887–894
Sieu N, Katon W, Lin EH, Russo J, Ludman E, Ciechanowski P (2011) Depression and incident diabetic retinopathy: a prospective cohort study. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 33(5):429–435
Heckbert SR, Rutter CM, Oliver M, Williams LH, Ciechanowski P, Lin EH et al (2010) Depression in relation to long-term control of glycemia, blood pressure, and lipids in patients with diabetes. J Gen Intern Med 25(6):524–529
Dirmaier J, Watzke B, Koch U, Schulz H, Lehnert H, Pieper L et al (2010) Diabetes in primary care: prospective associations between depression, nonadherence and glycemic control. Psychother Psychosom 79(3):172–178
Chiu CJ, Wray LA, Beverly EA, Dominic OG (2010) The role of health behaviors in mediating the relationship between depressive symptoms and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: a structural equation modeling approach. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 45(1):67–76
Holt RI, Phillips DI, Jameson KA, Cooper C, Dennison EM, Peveler RC (2009) The relationship between depression and diabetes mellitus: findings from the Hertfordshire Cohort Study. Diabet Med 26(6):641–648
Icks A, Kruse J, Dragano N, Broecker-Preuss M, Slomiany U, Mann K et al (2008) Are symptoms of depression more common in diabetes? Results from the Heinz Nixdorf Recall study. Diabet Med 25(11):1330–1336
Pawaskar MD, Anderson RT, Balkrishnan R (2007) Self-reported predictors of depressive symptomatology in an elderly population with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study. Health Qual Life Outcomes 5:50
Ismail K, Winkley K, Stahl D, Chalder T, Edmonds M (2007) A cohort study of people with diabetes and their first foot ulcer: the role of depression on mortality. Diabetes Care 30(6):1473–1479
Chowdhury SH, Karim MN, Selim S, Ahmed F, Azad AK, Maksud SA et al (2017) Risk of depression among Bangladeshi type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab Syndr 11(Suppl 2):S1009–S10s12
Samaan Z, Garasia S, Gerstein HC, Engert JC, Mohan V, Diaz R et al (2015) Lack of association between type 2 diabetes and major depression: epidemiologic and genetic evidence in a multiethnic population. Transl Psychiatry 5:e618
Islam SM, Ferrari U, Seissler J, Niessen L, Lechner A (2015) Association between depression and diabetes amongst adults in Bangladesh: a hospital based case-control study. J Glob Health 5(2):020406
Ferreira MC, Piaia C, Cadore AC, Antoniolli MA, Gamborgi GP, Oliveira PP (1992) Clinical variables associated with depression in patients with type 2 diabetes. Rev Assoc Med Bras 61(4):336–340 2015
Singh H, Raju MS, Dubey V, Kurrey R, Bansal S, Malik M (2014) A study of sociodemographic clinical and glycemic control factors associated with co-morbid depression in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ind Psychiatry J 23(2):134–142
Siddiqui S, Jha S, Waghdhare S, Agarwal NB, Singh K (2014) Prevalence of depression in patients with type 2 diabetes attending an outpatient clinic in India. Postgrad Med J 90(1068):552–556
Kalantari S, Jafarinezhad A, Zohrevand B (2014) Association of depression with type 2 diabetes and relevant factors. Adv Biomed Res 3:244
Ali N, Jyotsna VP, Kumar N, Mani K (2013) Prevalence of depression among type 2 diabetes compared to healthy non diabetic controls. J Assoc Physicians India 61(9):619–621
Zahra S, Hossein S, Ali KV (2012) Relationship between opium abuse and severity of depression in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab J 36(2):157–162
Ceretta LB, Reus GZ, Abelaira HM, Jornada LK, Schwalm MT, Hoepers NJ et al (2012) Increased prevalence of mood disorders and suicidal ideation in type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol 49(Suppl 1):S227–S234
Bener A, Ghuloum S, Al-Hamaq AO, Dafeeah EE (2012) Association between psychological distress and gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 3(6):123–129
Bajaj S, Agarwal SK, Varma A, Singh VK (2012) Association of depression and its relation with complications in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 16(5):759–763
Castro-Ake GA, Tovar-Espinosa JA, Mendoza-Cruz U (2009) [Association between depression and glycemic control disorder in patients with diabetes mellitus 2]. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc 47(4):377–382
Khamseh ME, Baradaran HR, Rajabali H (2007) Depression and diabetes in Iranian patients: a comparative study. Int J Psychiatry Med 37(1):81–86
Weikert B, Buttery AK, Heidemann C, Rieckmann N, Paprott R, Maske UE et al. Glycaemic status and depressive symptoms among adults in Germany: results from the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1). Diabetes Med. 2018
Lopez-de-Andres A, Jimenez-Trujillo MI, Hernandez-Barrera V, de Miguel-Yanes JM, Mendez-Bailon M, Perez-Farinos N et al (2015) Trends in the prevalence of depression in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes in Spain: analysis of hospital discharge data from 2001 to 2011. PloS One 10(2):e0117346
Agbir TM, Audu MD, Adebowale TO, Goar SG (2010) Depression among medical outpatients with diabetes: a cross-sectional study at Jos University Teaching Hospital, Jos, Nigeria. Ann Afr Med 9(1):5–10
Kalsekar ID, Madhavan SS, Amonkar MM, Makela EH, Scott VG, Douglas SM et al (2006) Depression in patients with type 2 diabetes: impact on adherence to oral hypoglycemic agents. Ann Pharmacother 40(4):605–611
Hermanns N, Kulzer B, Krichbaum M, Kubiak T, Haak T (2006) How to screen for depression and emotional problems in patients with diabetes: comparison of screening characteristics of depression questionnaires, measurement of diabetes-specific emotional problems and standard clinical assessment. Diabetologia 49(3):469–477
Collins-McNeil J (2006) Psychosocial characteristics and cardiovascular risk in African Americans with diabetes. Arch Psychiatr Nurs 20(5):226–233
Chyun DA, Melkus GD, Katten DM, Price WJ, Davey JA, Grey N et al (2006) The association of psychological factors, physical activity, neuropathy, and quality of life in type 2 diabetes. Biol Res Nurs 7(4):279–288
Brown LC, Majumdar SR, Newman SC, Johnson JA (2006) Type 2 diabetes does not increase risk of depression. CMAJ 175(1):42–46
Pibernik-Okanovic M, Peros K, Szabo S, Begic D, Metelko Z (2005) Depression in Croatian Type 2 diabetic patients: prevalence and risk factors. A Croatian survey from the European Depression in Diabetes (EDID) Research Consortium. Diabetic Med 22(7):942–945
Noh JH, Park JK, Lee HJ, Kwon SK, Lee SH, Park JH et al (2005) Depressive symptoms of type 2 diabetics treated with insulin compared to diabetics taking oral anti-diabetic drugs: a Korean study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 69(3):243–248
Katon WJ, Rutter C, Simon G, Lin EH, Ludman E, Ciechanowski P et al (2005) The association of comorbid depression with mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 28(11):2668–2672
Hill-Briggs F, Gary TL, Bone LR, Hill MN, Levine DM, Brancati FL (2005) Medication adherence and diabetes control in urban African Americans with type 2 diabetes. Health Psychol 24(4):349–357
Engum A, Mykletun A, Midthjell K, Holen A, Dahl AA (2005) Depression and diabetes: a large population-based study of sociodemographic, lifestyle, and clinical factors associated with depression in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 28(8):1904–1909
Bruce DG, Davis WA, Starkstein SE, Davis TM (2005) A prospective study of depression and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetologia 48(12):2532–2539
Ismail K, Winkley K, Rabe-Hesketh S (2004) Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of psychological interventions to improve glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet 363(9421):1589–1597
Haghighatdoost F, Azadbakht L (2013) Dietary treatment options for depression among diabetic patient, focusing on macronutrients. J Diabetes Res 2013:421832
Alzoubi A, Abunaser R, Khassawneh A, Alfaqih M, Khasawneh A, Abdo N (2018) The bidirectional relationship between diabetes and depression: a literature review. Korean J Fam Med 39(3):137–146
Kan C, Silva N, Golden SH, Rajala U, Timonen M, Stahl D et al (2013) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between depression and insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 36(2):480–489
Azimova K, Rude J, Mallawaarachchi I, Dwivedi A, Sarosiek J, Mukherjee D (2015) Glucose levels and depression in Hispanic patients admitted to the cardiovascular intensive care unit: a cross-sectional study. Angiology 66(1):57–64
Sun JC, Xu M, Lu JL, Bi YF, Mu YM, Zhao JJ et al (2015) Associations of depression with impaired glucose regulation, newly diagnosed diabetes and previously diagnosed diabetes in Chinese adults. Diabet Med 32(7):935–943
Nouwen A, Nefs G, Caramlau I, Connock M, Winkley K, Lloyd CE et al (2011) Prevalence of depression in individuals with impaired glucose metabolism or undiagnosed diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the European Depression in Diabetes (EDID) Research Consortium. Diabetes Care 34(3):752–762
Chen S, Zhang Q, Dai G, Hu J, Zhu C, Su L et al (2016) Association of depression with pre-diabetes, undiagnosed diabetes, and previously diagnosed diabetes: a meta-analysis. Endocrine 53(1):35–46
Musselman DL, Betan E, Larsen H, Phillips LS (2003) Relationship of depression to diabetes types 1 and 2: epidemiology, biology, and treatment. Biol Psychiatry 54(3):317–329
Paile-Hyvarinen M, Raikkonen K, Forsen T, Kajantie E, Yliharsila H, Salonen MK et al (2007) Depression and its association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and birth weight. Ann Med 39(8):634–640
Collaboration C (2018) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane Collaboration. Available from: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook. Accessed Feb 2019
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Endocrine and metabolism research center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran (no: 397089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Statement of human and animal rights
This study is a meta-analysis of other studies where all procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Informed consent
For this type of study consent form is not required.
Additional information
Managed by Antonio Secchi.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khaledi, M., Haghighatdoost, F., Feizi, A. et al. The prevalence of comorbid depression in patients with type 2 diabetes: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis on huge number of observational studies. Acta Diabetol 56, 631–650 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-019-01295-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-019-01295-9