Abstract
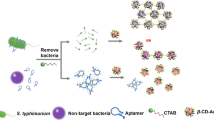
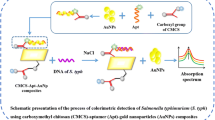
A novel aptamer-AuNP-conjugated carboxymethyl chitosan–functionalized graphene oxide (CMC/GO@Apt-Au NP) probe was for the first time developed for the determination of Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium). Owing to the conformational change of the aptamers in the presence of S. typhimurium, the Au NPs, which were pre-adsorbed on the aptamers through van der Waals forces, were released into the solution phase and induced the color change of the solution. As a result, S. typhimurium ranging from 102 to 107 CFU/mL was successfully identified using the designed assay with a limit of detection (LOD) of 10 CFU/mL. This low detection level allowed the sensitive recognition of S. typhimurium in milk samples within 40 min without sample pretreatment, a conclusion that agreed well with the traditional plate counting method. The developed method not only provides a rapid way for the determination of S. typhimurium with simplicity and sensitivity but also shows potential universality in the quantification of other pathogenic microorganisms.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Bryan CA, Ricke SC, Marcy JA (2022) Public health impact of Salmonella spp on raw poultry: current concepts and future prospects in the United States. Food Control 132:108539
Wang Z, Xu Q, Liu S, Liu Y, Gao Y, Wang M, Zhang L, Chang H, Wei Q, Sui Z (2022) Rapid and multiplexed quantification of Salmonella, Escherichia coli O157:H7, and Shigella flexneri in ground beef using flow cytometry. Talanta 238:123005
Sannigrahi S, Arumugasamy SK, Mathiyarasu J, Suthindhiran K (2020) Magnetosome-anti-Salmonella antibody complex based biosensor for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Mater Sci Eng C 114:111071
Pang T, Bhutta ZA, Finlay BB, Altwegg M (1995) Typhoid fever and other salmonellosis: a continuing challenge. Trends Microbiol 3:253–255
Shen Y, Xu L, Li Y (2021) Biosensors for rapid detection of Salmonella in food: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 20:149–197
Lin L, Zheng Q, Lin J, Yuk HG, Guo L (2020) Immuno- and nucleic acid-based current technique for Salmonella detection in food. Eur Food Res Technol 246:373–395
Bayraç C, Eyidoğan F, AvniÖktem H (2017) DNA aptamer-based colorimetric detection platform for Salmonella Enteritidis Biosens. Bioelectron 98:22–28
Wu Y, Wu M, Liu C, Tian Y, Fang S, Yang H, Li B, Liu Q (2021) Colloidal gold immunochromatographic test strips for broad-spectrum detection of Salmonella. Food Control 126:108052
Zheng L, Cai G, Qi W, Wang S, Wang M, Lin J (2020) Optical biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on porous gold@platinum nanocatalysts and a 3D fluidic chip. ACS Sens 5:65–72
Joshi DJ, Koduru JR, Malek NI, Hussain CM, Kailasa SK (2021) Surface modifications and analytical applications of graphene oxide: a review, TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 144:116448
Gao L, Lian C, Zhou Y, Yan L, Li Q, Zhang C, Chen L, Chen K (2014) Graphene oxide-DNA based sensors. Biosens Bioelectron 60:22–29
Zhao XH, Kong RM, Zhang XB, Meng HM, Liu WN, Tan W, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2011) Graphene-DNAzyme based biosensor for amplified fluorescence “turn-on” detection of Pb2+ with a high selectivity. Anal Chem 83:5062–5066
Zhu Y, Cai Y, Xu L, Zheng L, Wang L, Qi B, Xu C (2015) Building An aptamer/graphene oxide FRET biosensor for one-step detection of bisphenol A. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:7492–7496
Zhang Z, Xiang X, Hu Y, Deng Y, Li L, Zhao W, Wu T (2021) A sensitive biomolecules detection device with catalytic hairpin assembly and cationic conjugated polymer-assisted dual signal amplification strategy. Talanta 223:121716
Qin J, Cui X, Wu P, Jiang Z, Chen Y, Yang R, Hu Q, Sun Y, Zhao S (2017) Fluorescent sensor assay for β-lactamase in milk based on a combination of aptamer and graphene oxide. Food Control 73:726–733
Weng X, Neethirajan S (2016) A microfluidic biosensor using graphene oxide and aptamer-functionalized quantum dots for peanut allergen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 85:649–656
Chinnappan R, AlAmer S, Eissa S, Rahamn AA, Abu Salah KM, Zourob M (2017) Fluorometric graphene oxide-based detection of Salmonella enteritis using a truncated DNA aptamer. Microchim. Acta 185:61
Ma DL, He HZ, Leung KH, Zhong HJ, Chan DSH, Leung CH (2013) Label-free luminescent oligonucleotide-based probes. Chem Soc Rev 42:3427–3440
Wei H, Li B, Li J, Wang E, Dong S (2007) Simple and sensitive aptamer-based colorimetric sensing of protein using unmodified gold nanoparticle probes. Chem Commun 36:3735–3737
Li H, Rothberg L (2004) Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:14036–14039
Sun J, Lu Y, He L, Pang J, Yang F, Liu Y (2020) Colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticles: design principles and recent advances, TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 122:115754
Liu Z, Liu H, Wang L, Su X (2016) A label-free fluorescence biosensor for highly sensitive detection of lectin based on carboxymethyl chitosan-quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 932:88–97
Zimet P, Mombrú ÁW, Mombrú D, Castro A, Villanueva JP, Pardo H, Rufo C (2019) Physico-chemical and antilisterial properties of nisin-incorporated chitosan/carboxymethyl chitosan films. Carbohydr Polym 219:334–343
Shariatinia Z (2018) Carboxymethyl chitosan: properties and biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1406–1419
Tian L, Qi J, Ma X, Wang X, Yao C, Song W, Wang Y (2018) A facile DNA strand displacement reaction sensing strategy of electrochemical biosensor based on N-carboxymethyl chitosan/molybdenum carbide nanocomposite for microRNA-21 detection. Biosens Bioelectron 122:43–50
Zhang M, Yang M, Woo MW, Li Y, Han W, Dang X (2021) High-mechanical strength carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogel film for antibacterial wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym 256:117590
Yi J, Wu P, Li G, Xiao W, Li L, He Y, He Y, Ding P, Chen C (2019) A composite prepared from carboxymethyl chitosan and aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric determination of Salmonella typhimurium. Microchim Acta 186:711
Al-Gaashani R, Najjar A, Zakaria Y, Mansour S, Atieh M (2019) XPS and structural studies of high quality graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide prepared by different chemical oxidation methods. Ceram Int 45:14439–14448
Yuan D, Cadien K, Liu Q, Zeng H (2019) Adsorption characteristics and mechanisms of O-carboxymethyl chitosan on chalcopyrite and molybdenite. J Colloid Interface Sci 552:659–670
Huang Z, Li Z, Zheng L, Zhou L, Chai Z, Wang X, Shi W (2017) Interaction mechanism of uranium (VI) with three-dimensional graphene oxide-chitosan composite: insights from batch experiments, IR, XPS, and EXAFS spectroscopy. Chem Eng J 328:1066–1074
Du S, Wang Y, Liu Z, Xu Z, Zhang H (2019) A portable immune-thermometer assay based on the photothermal effect of graphene oxides for the rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Biosens Bioelectron 144:111670
Srisa-Art M, Boehle KE, Geiss BJ, Henry CS (2018) Highly sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using a colorimetric paper-based analytical device coupled with immunomagnetic separation. Anal Chem 90:1035–1043
Hu J, Jiang YZ, Tang M, Wu LL, Xie HY, Zhang ZL, Pang DW (2019) Colorimetric-fluorescent-magnetic nanosphere-based multimodal assay platform for Salmonella detection. Anal Chem 91:1178–1184
Wang X, Niazi S, Yukun H, Sun W, Wu S, Duan N, Hun X, Wang Z (2017) Homogeneous time-resolved FRET assay for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium using aptamer-modified NaYF4:Ce/Tb nanoparticles and a fluorescent DNA label. Microchim Acta 184:4021–4027
Wang S, Zheng L, Cai G, Liu N, Liao M, Li Y, Zhang X, Lin J (2019) A microfluidic biosensor for online and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using fluorescence labeling and smartphone video processing. Biosens Bioelectron 140:111333
Guo R, Wang S, Huang F, Chen Q, Li Y, Liao M, Lin J (2019) Rapid detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using magnetic nanoparticle immunoseparation, nanocluster signal amplification and smartphone image analysis. Sens Actuators, B 284:134–139
Hu J, Tang F, Wang L, Tang M, Jiang YZ, Liu C (2021) Nanozyme sensor based-on platinum-decorated polymer nanosphere for rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium with the naked eye. Sens Actuators, B 346:130560
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 82073607), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ30637), the start-up funds from Central South University (grant number 202045008), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (grant number 2022ZZTS0893).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, P., Huang, R., Chen, C. et al. Aptamer-AuNP-conjugated carboxymethyl chitosan–functionalized graphene oxide for colorimetric identification of Salmonella typhimurium. Microchim Acta 189, 408 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05494-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05494-0