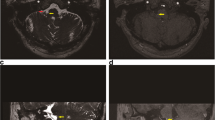
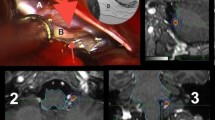
Abstract
Objective
To examine surgical findings and results of microvascular decompression (MVD) for glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GN).
Methods
Between 1990 and 2007, 31 consecutive patients affected by drug-resistant GN underwent MVD through a retromastoid keyhole in the supine position with the head rotated to the opposite side. A retrospective analysis was performed that paid particular attention to the relationship among surgical technique, pain control and side effects.
Results
A vascular compression of the glossopharyngeal nerve was found in all cases. Twenty-eight out of 31 patients (90.3%) were found to be pain free without medication at long-term follow-up (1–17 years, mean 7.5 years). Three patients (9.7%) were found to require medication to control pain paroxysms that were less frequent and less severe than those observed preoperatively. Two patients required repeated surgery for a drug-resistant recurrence of pain for a total of 33 MVDs. We observed no mortality and did not find any long-term surgical morbidity. Cranial nerve impairment, when observed, always resolved in the following months.
Conclusions
MVD is a safe and effective treatment for GN in patients of all ages.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams CB (1989) Microvascular compression: an alternative view and hypothesis. J Neurosurg 57:1–12
Barbash GI, Keren G, Korczyn AD, Sharpless NS, Chayen M, Copperman Y, Laniado S (1986) Mechanisms of syncope in glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 63:231–235. doi:10.1016/0013-4694(86)90089-1
Bernard EJ, Nashold BS, Caputi F, Moossy JJ (1987) Nucleus caudalis DREZ lesions for facial pain. Br J Neurosurg 1:81–92. doi:10.3109/02688698709034343
Brock S, Scaioli V, Ferroli P, Broggi G (2004) Neurovascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia: role of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring in the learning period. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 82:199–206. doi:10.1159/000082446
Crue BL, Carregal JA, Felsoory A (1972) Percutaneous stereotactic radiofrequency: Trigeminal tractotomy with neurophysiological recordings. Confin Neurol 34:389–397. doi:10.1159/000103087
Dandy WE (1927) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia (tic douloureux): Its diagnosis and treatment. Arch Surg 15:198–214
Dandy WE (1934) Concerning the cause of trigeminal neuralgia. Am J Surg 24:447–455. doi:10.1016/S0002-9610(34)90403-7
Ferroli P, Franzini A, Pluderi M, Broggi G (1999) Vagoglossopharyngeal neuralgia caused by a neuroma of vagal rootlets. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141(8):897–898. doi:10.1007/s007010050395
Garcia-Callejo FJ, Velert-Vila MM, Talamantes-Escriba F, Blay-Galaud L (1999) Clinical response of gabapentin for glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Rev Neurol 28(4):380–384
Giorgi C, Broggi G (1984) Surgical treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia and pain from cancer of the nasopharynx. J Neurosurg 61:952–955
Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society (2004) The International Classification of Headache Disorders. Cephalgia 24(Suppl 1):1–150
Hitchcock E (1970) Stereotactic trigeminal tractotomy. Ann Clin Res 2:131–135
Isamat F, Ferran E, Acebes JJ (1981) Selective percutaneous thermocoagulation rhizotomy in essential glossopharyngeal nevralgia. J Neurosurg 55:575–580
Jannetta PJ (2007) Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 107(1):216–219. doi:10.3171/JNS-07/07/0216
Jannetta PJ (1977) Observation on the aetiology of trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm, acoustic nerve dysfunction and glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Definitive microsurgical treatment and result in 117 patients. Neurochirurgia (Stutt) 20:145–154
Kanpolat Y, Savas A, Batay F, Sinav A (1998) Computer Tomography-guided Trigeminal Tractotomy-Nucleotomy in the managment of vagoglossopharyngeal and geniculate neuralgias. Neurosurgery 43:484–489. doi:10.1097/00006123-199809000-00045
Kondo A (1998) Follow-up results of using microvascular decompression for treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 88:221–225
Kunc Z (1965) Treatment of essential neuralgia of the 9th nerve by selective tractotomy. J Neurosurg 23:494–500
Laha RK, Jannetta PJ (1977) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 47:316–320
Lazorthes Y, Verdie JC (1974) Radiofrequency Coagulation of the Petrus Ganglion in Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia. Neurosurg 4(6):512–516
Lillie H, Craig WM (1936) Anomalous vascular lesion in the cerebellopontine angle. Arch Otolaryngol 23:642–645
Møller AR, Jannetta PJ (1984) Monitoring auditory nerve potentials during operations in the cerebellopontine angle. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 92(4):434–439
Olds MJ, Woods CI, Winfield JA (1995) Microvascular decompression in glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Am J Otol 16:326–330
Patel A, Kassam A, Horowitz M, Chang YF (2002) Microvascular decompression in the management of glossopharyngeal neuralgia: Analysis of 217 cases. Neurosurgery 50:705–711. doi:10.1097/00006123-200204000-00004
Polo G, Fischer C, Sindou MP, Marneffe V (2004) Brainstem auditory evoked potential monitoring during microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm: intraoperative brainstem auditory evoked potential changes and warning values to prevent hearing loss—prospective study in a consecutive series of 84 patients. Neurosurgery 54(1):97–104
Resnick DK, Jannetta PJ, Bissonnette D, Jho HD, Lanzino G (1995) Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 36:64–69. doi:10.1097/00006123-199501000-00008
Rushton JG, Stevens JC, Miller RH (1981) Glossopharyngeal (vagoglossopharyngeal) neuralgia: A study of 217 cases. Arch Neurol 38:201–205
Sampson JH, Grossi M, Asaoka K, Fukushima T (2004) Microvascular decompression for the glossopharyngeal neuralgia: long term effectiveness and complication avoidance. Neurosurgery 54:884–890. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000114142.98655.CC
Sato S, Yamada M, Koizumi H, Onozawa Y, Shimokawa N, Kawashima E, Fujii K (2009) Neurophysiological mechanisms of conduction impairment of the auditory nerve during cerebellopontine angle surgery. Clin Neurophysiol 120(2):329–335 Epub 2008 Dec 23
Sicard R, Robineau J (1920) Communications et presentations: Part I—Algie vélopharyngée essentielle: Traitement chirugical. Rev Neurol (Paris) 36:256–257
Sindou M, Mertens P (1993) Microsurgical vascular decompression in trigeminal and glossopharyngeal neuralgias: A 20 year experience. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 58:168–170
Stieber VW, Bourland JD, Ellis TL (2005) Glossopharyngeal neuralgia treated with gamma knife surgery: treatment outcome and failure analysis. Case report. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):155–157
Taha JM, Tew JM Jr (1995) Long-term results of treatment of idiopathic neuralgias of the glossopharyngeal and vagal nerves. Neurosurgery 36:926–931. doi:10.1097/00006123-199505000-00006
Tew JM Jr, Tobler WD, Van Loveren H (1982) Percutaneous rhizotomy in the treatment of intractable facial pain. In: Schmidek HH, Sweet WH (eds) Operative neurosurgical techniques, vol 2. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 1083–1106
Titlic M, Jukic I, Tonkic A, Grani P, Jukic J, 1 (2006) Use of lamotrigine in glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a case report. Headache 46:167–169. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00316_2.x http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=16412166&dopt=Abstract
Wakiya K, Fukushima T, Miyazaki S (1989) Results of microvascular decompression in 16 cases of glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 29(12):1113–1118. doi:10.2176/nmc.29.1113 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=2484190&dopt=Abstract
Wallin BG, Westerberg CE, Sundlof G (1984) Syncope induced by glossopharyngeal neuralgia: Sympathetic outflow to muscle. Neurology 34:522–524 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=6538307&dopt=Abstract
White JC, Sweet WH (1969) Pain and the neurosurgeon: a 40-year experience. Charles C Thomas, Springfield, III, pp 265–302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferroli, P., Fioravanti, A., Schiariti, M. et al. Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia: a long-term retrospectic review of the Milan-Bologna experience in 31 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir 151, 1245–1250 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0330-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0330-5