Abstract
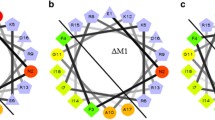
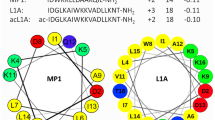
Melittin (MLT) is a lytic peptide with a broad spectrum of activity against both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. To understand the role of proline and the thiol group of cysteine in the cytolytic activity of MLT, native MLT and cysteine-containing analogs were prepared using solid phase peptide synthesis. The antimicrobial and cytolytic activities of the monomeric and dimeric MLT peptides against different cells and model membranes were investigated. The results indicated that the proline residue was necessary for antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity and its absence significantly reduced lysis of model membranes and hemolysis. Although lytic activity against model membranes decreased for the MLT dimer, hemolytic activity was increased. The native peptide and the MLT-P14C monomer were mainly unstructured in buffer while the dimer adopted a helical conformation. In the presence of neutral and negatively charged vesicles, the helical content of the three peptides was significantly increased. The lytic activity, therefore, is not correlated to the secondary structure of the peptides and, more particularly, on the propensity to adopt helical conformation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anaya-Lopez JL, Lopez-Meza JE, Ochoa-Zarzosa A (2013) Bacterial resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides. Crit Rev Microbiol 39(2):180–195
Anderson RL, Davis S (1982) An organic phosphorus assay which avoids the use of hazardous perchloric acid. Clin Chim Acta 121(1):111–116
Asthana N, Yadav SP, Ghosh JK (2004) Dissection of antibacterial and toxic activity of melittin: a leucine zipper motif plays a crucial role in determining its hemolytic activity but not antibacterial activity. J Biol Chem 279(53):55042–55050
Balla MS, Bowie JH, Separovic F (2004) Solid-state NMR study of antimicrobial peptides from Australian frogs in phospholipid membranes. Eur Biophys J 33(2):109–116
Beveridge TJ (1999) Structures of Gram-negative cell walls and their derived membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol 181:4725–4733
Burton MG, Huang QM, Hossain MA, Wade JD, Clayton AHA, Gee ML (2013) Long-time-scale interaction dynamics between a model antimicrobial peptide and giant unilamellar vesicles. Langmuir 29(47):14613–14621
Dempsey CE, Bazzo R, Harvey TS, Syperek I, Boheim G, Campbell ID (1991) Contribution of proline-14 to the structure and actions of melittin. FEBS Lett 281(1–2):240–244
Fernandez DI, Lee T-H, Sani M-A, Aguilar M-I, Separovic F (2013) Proline facilitates membrane insertion of the antimicrobial peptide maculatin 1.1 via surface indentation and subsequent lipid disordering. Biophys J 104(7):1495–1507
Ferre R, Melo MN, Correia AD, Feliu L, Bardaji E, Planas M, Castanho M (2009) Synergistic effects of the membrane actions of cecropin–melittin antimicrobial hybrid peptide BP100. Biophys J 96(5):1815–1827
Gajski G, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2013) Melittin: a lytic peptide with anticancer properties. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(2):697–705
Gali H, Sieckman GL, Hoffman TJ, Owen NK, Mazuru DG, Forte LR, Volkert WA (2002) Chemical synthesis of Escherichia Coli STh analogues by regioselective disulfide bond formation: biological evaluation of an 111In-DOTA-Phe19-STh analogue for specific targeting of human colon cancers. Bioconjug Chem 13(2):224–231
Gehman J, Luc F, Hall K, Lee T-H, Boland M, Pukala T, Bowie J, Aguilar M-I, Separovic F (2008) Effect of antimicrobial peptides from Australian tree frogs on anionic phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry 47(33):8557–8565
Ghosh AK, Rukmini R, Chattopadhyay A (1997) Modulation of tryptophan environment in membrane-bound melittin by negatively charged phospholipids: implications in membrane organization and function. Biochemistry 36(47):14291–14305
Hall K, Lee TH, Aguilar MI (2011) The role of electrostatic interactions in the membrane binding of melittin. J Mol Recognit 24(1):108–118
Heerklotz H, Seelig J (2007) Leakage and lysis of lipid membranes induced by the lipopeptide surfactin. Eur Biophy J 36(4–5):305–314
Henriksen JR, Etzerodt T, Gjetting T, Andresen TL (2014) Side chain hydrophobicity modulates therapeutic activity and membrane selectivity of antimicrobial peptide mastoparan-X. PLoS One 9(3):e91007
Hincha DK, Crowe JH (1996) The lytic activity of the bee venom peptide melittin is strongly reduced by the presence of negatively charged phospholipids or chloroplast galactolipids in the membranes of phosphatidylcholine large unilamellar vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1284(2):162–170
Hyun-Ji C, Jeong-Han K, Kwan-Kyu P, Jung-Yoon C, Yoon-Yub P, Yong-Suk M, Il-Kyung C, Hyeun-Wook C, Cheorl-Ho K, Yung Hyun C, Wun-Jae K, Sung-Kwon M, Young-Chae C (2013) Comparative proteome analysis of tumor necrosis factor α-stimulated human vascular smooth muscle cells in response to melittin. Proteome Sci 11:20
Izadpanah A, Gallo RL (2005) Antimicrobial peptides. J Am Acad Dermatol 52(3 Pt 1):381–390
Jackson KE, Spielmann T, Hanssen E, Adisa A, Separovic F, Dixon MW, Trenholme KR, Hawthorne PL, Gardiner DL, Gilberger T, Tilley L (2007) Selective permeabilization of the host cell membrane of Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells with streptolysin O and equinatoxin II. Biochem J 403(1):167–175
John E, Jähnig F (1993) A synthetic analogue of melittin aggregates in large oligomers. Biophys J 63(6):1536
Johnson JW, Fisher JF, Mobashery S (2013) Bacterial cell-wall recycling. Ann NY Acad Sci 1277:54–75
Juba M, Porter D, Dean S, Gillmor S, Bishop B (2013) Characterization and performance of short cationic antimicrobial peptide isomers. Pept Sci 100(4):387–401
Khatun UL, Mukhopadhyay C (2013) Interaction of bee venom toxin melittin with ganglioside GM1 bicelle. Biophys Chem 180–181:66–75
Klocek G, Seelig J (2008) Melittin interaction with sulfated cell surface sugars. Biochemistry 47(9):2841–2849
Lad MD, Birembaut F, Clifton LA, Frazier RA, Webster JR, Green RJ (2007) Antimicrobial peptide–lipid binding interactions and binding selectivity. Biophys J 92(10):3575–3586
Lam YH, Wassall SR, Morton CJ, Smith R, Separovic F (2001) Solid-state NMR structure determination of melittin in a lipid environment. Biophys J 81:2752–2761
Lam YH, Morton J, Separovic F (2002) Solid-state NMR conformational studies of a melittin-inhibitor complex. Eur Biophys J 31(5):383
Lee TH, Heng C, Swann MJ, Gehman JD, Separovic F, Aguilar MI (2010) Real-time quantitative analysis of lipid disordering by aurein 1.2 during membrane adsorption, destabilisation and lysis. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1798(10):1977–1986
Lee J, Lee D, Choi H, Kim HH, Kim H, Hwang JS, Lee DG, Kim JI (2014) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of cysteine-free coprisin nonapeptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443(2):483–488
Lorenzon EN, Cespedes GF, Vicente EF, Nogueira LG, Bauab TM, Castro MS, Cilli EM (2012) Effects of dimerization on the structure and biological activity of antimicrobial peptide Ctx-Ha. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56(6):3004–3010
Maróti G, Kereszt A, Kondorosi E, Mergaert P (2011) Natural roles of antimicrobial peptides in microbes, plants and animals. Res Microbiol 162(4):363–374
Maruyama K, Nagasawa H, Suzuki A (1999) 2,2′-Bispyridyl disulfide rapidly induces intramolecular disulfide bonds in peptides. Peptides 20(7):881–884
Ningsih Z, Hossain MA, Wade JD, Clayton AH, Gee ML (2012) Slow insertion kinetics during interaction of a model antimicrobial peptide with unilamellar phospholipid vesicles. Langmuir 28(4):2217–2224
Popham DL (2013) Visualizing the production and arrangement of peptidoglycan in Gram-positive cells. Mol Microbiol 88(4):645–649
Raghuraman H, Chattopadhyay A (2004) Interaction of melittin with membrane cholesterol: a fluorescence approach. Biophys J 87(4):2419–2432
Raghuraman H, Chattopadhyay A (2007) Orientation and dynamics of melittin in membranes of varying composition utilizing NBD fluorescence. Biophys J 92(4):1271–1283
Rapson AC, Hossain MA, Wade JD, Nice EC, Smith TA, Clayton AH, Gee ML (2011) Structural dynamics of a lytic peptide interacting with a supported lipid bilayer. Biophys J 100(5):1353–1361
Reddy KV, Yedery RD, Aranha C (2004) Antimicrobial peptides: premises and promises. Int J Antimicrob Agents 24(6):536–547
Rivett DE, Kirkpatrick A, Hewish DR, Reilly W, Werkmeister JA (1996) Dimerization of truncated melittin analogues results in cytolytic peptides. Biochem J 316(Pt 2):525–529
Sani MA, Whitwell TC, Gehman JD, Robins-Browne RM, Pantarat N, Attard TJ, Reynolds EC, O’Brien-Simpson NM, Separovic F (2013) Maculatin 1.1 disrupts Staphylococcus aureus lipid membranes via a pore mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(8):3593–3600
Scholtz JM, Qian H, York EJ, Stewart JM, Baldwin RL (1991) Parameters of helix–coil transition theory for alanine-based peptides of varying chain lengths in water. Biopolymers 31(13):1463–1470
Schubert D, Pappert G, Boss K (1985) Does dimeric melittin occur in aqueous solutions? Biophys J 48(2):327–329
Sessa G, Freer JH, Colacicc G, Weissman G (1969) Interaction of a lytic polypeptide, melittin, with lipid membrane systems. J Biol Chem 244(13):3575–3582
Takei J, Reményi A, Clarke AR, Dempsey CE (1998) Self-association of disulfide-dimerized melittin analogues. Biochemistry 37(16):5699–5708
Terwilliger TC, Eisenberg D (1982) The structure of melittin. II. Interpretation of the structure. J Biol Chem 257(11):6016–6022
Tomoyoshi T, Fumimasa N, Yasunori Y, Yohko T-T, Michio H, Kingo T (2013) Multiple membrane interactions and versatile vesicle deformations elicited by melittin. Toxins 5(4):637–664
Tosteson MT, Levy JJ, Caporale LH, Rosenblatt M, Tosteson DC (1987) Solid-phase synthesis of melittin: purification and functional characterization. Biochemistry 26(21):6627–6631
Wade JD, Lin F, Hossain MA, Dawson R (2012) Chemical synthesis and biological evaluation of an antimicrobial peptide gonococcal growth inhibitor. Amino Acids 43(6):2279–2283
Ward JB (1981) Teichoic and teichuronic acids: biosynthesis, assembly, and location. Microbiol Rev 45(2):211–243
Zhao Z, Rolli H, Schneider CH (1995) Immunogenicity of dinitrocarboxyphenylated melittin: the influence of C-terminal chain shortening, N-terminal substitution and prolin insertion at positions 5 and 10. J Pept Sci 1(2):140–148
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge partial support of the studies undertaken in the authors’ laboratory by the Australian Research Council (DP150103522) to MAH and JDW. Research at the FNI was supported by the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program. EJ thanks the University of Melbourne for an MIRS.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamasbi, E., Batinovic, S., Sharples, R.A. et al. Melittin peptides exhibit different activity on different cells and model membranes. Amino Acids 46, 2759–2766 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1833-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1833-9