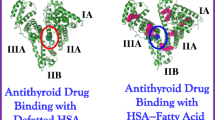
Abstract
Human serum albumin (HSA), the most abundant protein found in blood plasma, transports many drugs and ligands in the circulatory system. The drug binding ability of HSA strongly influences free drug concentrations in plasma, and is directly related to the effectiveness of clinical therapy. In current work, binding of HSA to angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are investigated using docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Docking results demonstrate that the main HSA–ARB binding site is subdomain IIIA of HSA. Simulation results reveal clearly how HSA binds with valsartan and telmisartan. Interestingly, electrostatic interactions appear to be more important than hydrophobic interactions in stabilizing binding of valsartan to HSA, and vice versa for HSA–telmisartan. The molecular distance between HSA Trp214 (donor) and the drug (acceptor) can be measured by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) in experimental studies. The average distances between Trp-214 and ARBs are estimated here based on our MD simulations, which could be valuable to future FRET studies. This work will be useful in the design of new ARB drugs with desired HSA binding affinity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Means GE, Bender ML (1975) Acetylation of human serum albumin by p-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochemistry 14:4989–4994
He XM, Carter DC (1992) Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 358:209–216
Carter DC, Ho JX (1994) Structure of serum albumin. Adv Protein Chem 45:153–203
Reidenberg MM, Erill S (1986) Drug–protein binding. Praeger, New York
Sudlow G, Birkett DJ, Wade DN (1975) The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol 11:824–832
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J (2005) Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 365:217–223
Mancia G, Rosei EA, Cifkova R, DeBacker G, Erdine S, Fagard R, Farsang C, Heagerty AM, Kawecka-Jaszcs K, Kiowski W, Kjeldsen S, Luscher T, McInnes G, Mallion JM, Brien EO, Poulter NR, Priori SG, Rahn KH, Rodicio JL, Ruilope LM, Safar M, Staessen JA, van Zwieten P, Waeber B, Williams B, Zanchetti A, Zannad F (2003) 2003 European Society of Hypertension-European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 21:1011–1053
Mancia G, Seravalle G, Grassi G (2003) Tolerability and treatment compliance with angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Am J Hypertens 16:1066–1073
Cheng QN, Law PK, de Gasparo M, Leung PSJ (2008) Combination of the dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor LAF237 [(S)-1-[(3-Hydroxy-1-adamantyl)ammo]acetyl-2-cyano-pyrrolidine] with the angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist valsartan [N-(1-Oxopentyl)-N-[[2′-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-[1, 1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-l-valine] enhances pancreatic islet morphology and function in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Pharmacol Exp Ther 327:683–691
Katayama K, Nomura S, Ishikawa H, Murata T, Koyabu S, Nakano T (2006) Comparison between valsartan and valsartan plus cilnidipine in type II diabetics with normo- and microalbuminuria. Kidney Int 70:151–156
Aslam S, Santha T, Leone A, Wilcox C (2006) Effects of amlodipine and valsartan on oxidative stress and plasma methylarginines in end-stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis. Kidney Int 70:2109–2115
Pfeffer MA, McMurray JJV, Velazquez EJ, Rouleau JL, Kober L, Maggioni AP, Solomon SD, Swedberg K, van de Werf F, White H, Leimberger JD, Henis M, Edwards S, Zelenkofske S, Sellers MA, Califf RM, Investigators VTN (2003) Valsartan, captopril, or both in myocardial infarction complicated by heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, or both. N Engl J Med 349:1893–1906
Latini R, Masson S, Arland I, Judd D, Maggioni AP, Chiang YT, Bevilacqua M, Salio M, Cardano P, Dunselman P, Holwerda NJ, Tognoni G, Cohn JN, Investigators VH (2002) Effects of valsartan on circulating brain natriuretic peptide and norepinephrine in symptomatic chronic heart failure. Circulation 106:2454–2458
Israili ZH (2000) Clinical pharmacokinetics of angiotensin II (AT1) receptor blockers in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 14:S73–S86
Ruilope L (1997) Human pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic profile of irbesartan: a new potent angiotensin II receptor antagonist. J Hypertens 15:S15–S20
Gardner SF, Franks AM (2003) Olmesartan medoxomil: the seventh angiotensin receptor antagonist. Ann Pharmacother 37:99–105
Kratochwil NA, Huber W, Muller F, Kansy M, Gerber PR (2002) Predicting plasma protein binding of drugs: a new approach. Biochem Pharmacol 64:1355–1374
Mao HY, Hajduk PJ, Craig R, Bell R, Borre T, Fesik SW (2001) Rational design of diflunisal analogues with reduced affinity for human serum albumin. J Am Chem Soc 123:10429–10435
Schmidt B, Schieffer B (2003) Angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonists. Clinical implications of active metabolites. J Med Chem 46:2261–2003
Colussi DM, Parisot C, Rossolino ML, Brunner LA, Lefevre GYJ (1997) Protein binding in plasma of valsartan, a new angiotensin II receptor antagonist. J Clin Pharmacol 37:214–221
Christ DD (1995) Human plasma protein binding of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist losartan potassium (DuP 753/MK 954) and its pharmacologically active metabolite EXP3174. J Clin Pharmacol 35:515–520
Maillard MP, Rossat J, Brunner HR, Burnier M (2000) Tasosartan, enoltasosartan, and angiotensin II receptor blockade: the confounding role of protein binding. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:649–654
Votano JR, Parham M, Hall LM, Hall LH, Kier LB, Oloff S, Tropsha A (2006) QSAR modeling of human serum protein binding with several modeling techniques utilizing structure—information representation. J Med Chem 49:7169–7181
Ermondi G, Lorenti M, Caron G (2004) Contribution of ionization and lipophilicity to drug binding to albumin: a preliminary step toward biodistribution prediction. J Med Chem 47:3949–3961
Aureli L, Cruciani G, Cesta MC, Anacardio R, de Simone L, Moriconi A (2005) Predicting human serum albumin affinity of interleukin-8 (CXCL8) inhibitors by 3D-QSPR approach. J Med Chem 48:2469–2479
Diaz N, Suarez D, Sordo TL, Merz KM (2001) Molecular dynamics study of the IIA binding site in human serum albumin: influence of the protonation state of Lys195 and Lys199. J Med Chem 44:250–260
Fujiwara SI, Amisaki T (2006) Molecular dynamics study of conformational changes in human serum albumin by binding of fatty acids. Proteins 64:730–739
Fujiwara SI, Amisaki T (2008) Identification of high affinity fatty acid binding sites on human serum albumin by MM-PBSA method. Biophys J 94:95–103
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662
Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Shrivastava S, Hassanali M, Stothard P, Chang Z, Woolsey J (2006) DrugBank: a comprehensive resource for in silico drug discovery and exploration. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D668–D672
Petitpas I, Bhattacharya AA, Twine S, East M, Curry S (2001) Crystal structure analysis of warfarin binding to human serum albumin. J Biol Chem 276:22804–22809
Bhattacharya AA, Curry S, Franks NP (2000) Binding of the general anesthetics propofol and halothane to human serum albumin. J Biol Chem 275:38731–38738
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Huey R, Olson AJ (1996) Distributed automated docking of flexible ligands to proteins parallel applications of AutoDock 2.4. J Comput Aid Mol Des 10:293–304
Berendsen HJC, van der Spoel D, van Drunen R (1995) GROMACS: a message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput Phys Commun 91:43–56
Lindahl E, Hess B, van der Spoel D (2001) GROMACS 3.0: a package for molecular simulation and trajectory analysis. J Mol Model 7:306–317
Ott KH, Meyer B (1996) Parametrization of GROMOS force field for oligosaccharides and assessment of efficiency of molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 17:1068–1084
Schuettelkopf AW, van Aalten DMF (2004) PRODRG: a tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein–ligand complexes. Acta Crystal D60:1355–1363
Berendsen HJC, Grigera JR, Straatsma TP (1987) The missing term in effective pair potentials. J Phys Chem 91:6269–6271
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJC, Fraaije JGEM (1997) LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18:1463–1472
Essman U, Perela L, Berkowitz ML, Darden HL, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577–8593
Kholmurodov K, Smith W, Yasuoka K, Darden T, Ebisuzaki T (2000) A smooth-particle mesh Ewald method for DL_POLY molecular dynamics simulation package on the Fujitsu VPP700. J Comput Chem 21:1187–1191
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, DiNola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690
Wallace AC, Laskowski RA, Thornton JM (1995) LIGPOLT: a program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng 8:127–134
Bhattacharya AA, Grune T, Curry S (2000) Crystallographic analysis reveals common modes of binding of medium and long-chain fatty acids to human serum albumin. J Mol Biol 303:721–732
Watanabe H, Tanase S, Nakajou K, Maruyama T, Kragh-Hansen U, Otagiri M (2000) Role of Arg-410 and Tyr-411 in human serum albumin for ligand binding and esterase-like activity. Biochem J 349:813–819
Li B, Schopfer LM, Hinrichs SH, Masson P, Lockridge O (2007) Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry assay for organophosphorus toxicants bound to human albumin at Tyr411. Anal Biochem 361:263–272
Monti S, Manet I, Manoli F, Capobianco ML, Marconi G (2008) Gaining an insight into the photoreactivity of a drug in a protein environment: a case study on nalidixic acid and serum albumin. J Phys Chem B 112:5742–5754
Ahmed N, Dobler D, Dean M, Thornalley PJ (2005) Peptide mapping identifies hotspot site of modification in human serum albumin by methylglyoxal involved in ligand binding and esterase activity. J Biol Chem 280:5724–5732
Ko S, Lee W, Lee S, Park H (2008) Nanosecond molecular dynamics simulations of Cdc25B and its complex with a 1, 4-naphthoquinone inhibitor: implications for rational inhibitor design. J Mol Graph Model 27:13–19
Tuccinardi T, Calderone V, Rapposelli S, Martinelli A (2006) Proposal of a new binding orientation for nNon-Peptide AT1 antagonists: homology modeling, docking and three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis. J Med Chem 49:4305–4316
Potamitis C, Zervou M, Katsiaras V, Zoumpoulakis P, Durdagi S, Papadopoulos MG, Hayes JM, Grdadolnik SG, Kyrikou I, Argyropoulos D, Vatougia G, Mavromoustakos T (2009) Antihypertensive drug valsartan in solution and at the AT1 receptor: conformational analysis, dynamic NMR spectroscopy, in Silico docking, and molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Inf Model 49:726–739
Abou-Zied OK, Al-Shihi OIK (2008) Characterization of subdomain IIA binding site of human serum albumin in its native, unfolded, and refolded states. J Am Chem Soc 130:10793–10801
Patel S, Datta A (2007) Steady state and time-resolved fluorescence investigation of the specific binding of two chlorin derivatives with human serum albumin. J Phys Chem B 111:10557–10562
Zhang G, Keita B, Brochon JC, Oliveira P, Nadjo L, Craescu CT, Miron S (2007) Molecular interaction and energy transfer between human serum albumin and polyoxometalates. J Phys Chem B 111:1809–1814
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China (No. 20706029, 20876073), Jiangsu Science and Technology Department of China (BK2008372), and Nanjing University of Technology of China. We want to express our thanks to the reviewers for their valuable suggestions for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material
(DOC 751 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhu, X., Yang, C. et al. Characterization of the binding of angiotensin II receptor blockers to human serum albumin using docking and molecular dynamics simulation. J Mol Model 16, 789–798 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-009-0612-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-009-0612-0