Abstract
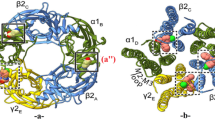
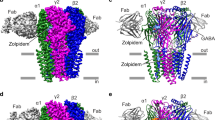
Gamma-aminobutyric type A receptor (GABAAR) is a member of the Cys-loop family of pentameric ligand gated ion channels (pLGICs). It has been identified as a key target for many clinical drugs. In the present study, we construct the structure of human 2α12β2γ2 GABAAR using a homology modeling method. The structures of ten benzodiazepine type drugs and two non-benzodiazepine type drugs were then docked into the potential benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAAR. By analyzing the docking results, the critical residues His102 (α1), Phe77 (γ2) and Phe100 (α1) were identified in the binding site. To gain insight into the binding affinity, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed for all the receptor–ligand complexes. We also examined single mutant GABAAR (His102A) in complexes with the three drugs (flurazepam, eszopiclone and zolpidem) to elucidate receptor–ligand interactions. For each receptor–ligand complex (with flurazepam, eszopiclone and zolpidem), we calculated the average distance between the Cα of the mutant residue His102A (α1) to the center of mass of the ligands. The results reveal that the distance between the Cα of the mutant residue His102A (α1) to the center of flurazepam is larger than that between His102 (α1) to flurazepam in the WT type complex. Molecular mechanic-generalized Born surface area (MM-GBSA)-based binding free energy calculations were performed. The binding free energy was decomposed into ligand-residue pairs to create a ligand-residue interaction spectrum. The predicted binding free energies correlated well (R 2 = 0.87) with the experimental binding free energies. Overall, the major interaction comes from a few groups around His102 (α1), Phe77 (γ2) and Phe100 (α1). These groups of interaction consist of at least of 12 residues in total with a binding energy of more than 1 kcal mol−1. The simulation study disclosed herein provides a meaningful insight into GABAAR–ligand interactions and helps to arrive at a binding mode hypothesis with implications for drug design.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Absalom NL, Schofield PR, Lewis TM (2009) Pore structure of the Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channels. Neurochem Res 34(10):1805–1815
Pritchett DB, Sontheimer H, Shivers BD, Ymer S, Kettenmann H, Schofield PR, Seeburg PH (1989) Importance of a novel GABAA receptor subunit for benzodiazepine pharmacology. Nature 338(6216):582–585
Sieghart W, Sperk G (2002) Subunit composition, distribution and function of GABA(A) receptor subtypes. Curr Top Med Chem 2(8):795–816
Johnston GA (2005) GABA(A) receptor channel pharmacology. Curr Pharm Des 11(15):1867–1885
Mehta AK, Ticku MK (1999) An update on GABAA receptors. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 29(2–3):196–217
Davies PA, Hanna MC, Hales TG, Kirkness EF (1997) Insensitivity to anaesthetic agents conferred by a class of GABA(A) receptor subunit. Nature 385(6619):820–823
Korpi ER, Sinkkonen ST (2006) GABA(A) receptor subtypes as targets for neuropsychiatric drug development. Pharmacol Ther 109(1–2):12–32
Rudolph U, Crestani F, Mohler H (2001) GABA(A) receptor subtypes: dissecting their pharmacological functions. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(4):188–194
Sarto-Jackson I, Sieghart W (2008) Assembly of GABA(A) receptors (Review). Mol Membr Biol 25(4):302–310
Hibbs RE, Gouaux E (2011) Principles of activation and permeation in an anion-selective Cys-loop receptor. Nature 474(7349):54–60
Morlock EV, Czajkowski C (2011) Different residues in the GABAA receptor benzodiazepine binding pocket mediate benzodiazepine efficacy and binding. Mol Pharmacol 80(1):14–22
Xie HB, Wang J, Sha Y, Cheng MS (2013) Molecular dynamics investigation of Cl transport through the closed and open states of the 2alpha2betagamma GABA receptor. Biophys Chem 180–181C:1-9.
Nestoros JN (1982) Benzodiazepine and gaba receptors are functionally related: further electrophysiological evidence in vivo. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6(4–6):417–420
McLeod M, Pralong D, Copolov D, Dean B (2002) The heterogeneity of central benzodiazepine receptor subtypes in the human hippocampal formation, frontal cortex and cerebellum using [3H]flumazenil and zolpidem. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 104(2):203–209
Blanchard JC, Boireau A, Julou L (1982) Brain receptors and zopiclone. Int Pharmacopsychiatry 17(Suppl 2):59–69
Gohlke H, Case DA (2004) Converging free energy estimates: MM-PB(GB)SA studies on the protein-protein complex Ras-Raf. J Comput Chem 25(2):238–250
Hou T, Wang J, Li Y, Wang W (2011) Assessing the performance of the MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods. 1. The accuracy of binding free energy calculations based on molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Inf Model 51(1):69–82
Everitt AB, Seymour VA, Curmi J, Laver DR, Gage PW, Tierney ML (2009) Protein interactions involving the gamma2 large cytoplasmic loop of GABA(A) receptors modulate conductance. FASEB J 23(12):4361–4369
O'Toole KK, Jenkins A (2011) Discrete M3-M4 intracellular loop subdomains control specific aspects of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor function. J Biol Chem 286(44):37990–37999
Discovery Studio 3.0 (2011). Accelrys, San Diego, CA
Eramian D, Shen MY, Devos D, Melo F, Sali A, Marti-Renom MA (2006) A composite score for predicting errors in protein structure models. Protein Sci 15(7):1653–1666
Baumann SW, Baur R, Sigel E (2002) Forced subunit assembly in alpha1beta2gamma2 GABAA receptors. Insight into the absolute arrangement. J Biol Chem 277(48):46020–46025
Sigel E, Luscher BP (2011) A closer look at the high affinity benzodiazepine binding site on GABAA receptors. Curr Top Med Chem 11(2):241–246
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30(16):2785–2791
AMBER 12 (2012). University of California, San Francisco
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem 25(9):1157–1174
Jakalian A, Jack DB, Bayly CI (2002) Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J Comput Chem 23(16):1623–1641
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, DiNola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81(7):3684–3693
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle mesh Ewald: An N. log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98(12):10089–10092
Kräutler V, van Gunsteren WF, Hünenberger PH (2001) A fast SHAKE algorithm to solve distance constraint equations for small molecules in molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 22(5):501–508
Onufriev A, Bashford D, Case DA (2004) Exploring protein native states and large-scale conformational changes with a modified generalized born model. Proteins 55(2):383–394
Luu T, Cromer B, Gage PW, Tierney ML (2005) A role for the 2' residue in the second transmembrane helix of the GABA A receptor gamma2S subunit in channel conductance and gating. J Membr Biol 205(1):17–28
Gonzales EB, Bell-Horner CL, Dibas MI, Huang RQ, Dillon GH (2008) Stoichiometric analysis of the TM2 6' phenylalanine mutation on desensitization in alpha1beta2 and alpha1beta2gamma2 GABA A receptors. Neurosci Lett 431(2):184–189
Horenstein J, Wagner DA, Czajkowski C, Akabas MH (2001) Protein mobility and GABA-induced conformational changes in GABA(A) receptor pore-lining M2 segment. Nat Neurosci 4(5):477–485
Pritchett DB, Seeburg PH (1990) Gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor alpha 5-subunit creates novel type II benzodiazepine receptor pharmacology. J Neurochem 54(5):1802–1804
Sancar F, Ericksen SS, Kucken AM, Teissere JA, Czajkowski C (2007) Structural determinants for high-affinity zolpidem binding to GABA-A receptors. Mol Pharmacol 71(1):38–46
Hanson SM, Morlock EV, Satyshur KA, Czajkowski C (2008) Structural requirements for eszopiclone and zolpidem binding to the gamma-aminobutyric acid type-A (GABAA) receptor are different. J Med Chem 51(22):7243–7252
Teissere JA, Czajkowski C (2001) A (beta)-strand in the (gamma)2 subunit lines the benzodiazepine binding site of the GABA A receptor: structural rearrangements detected during channel gating. J Neurosci 21(14):4977–4986
Davies M, Bateson AN, Dunn SM (1998) Structural requirements for ligand interactions at the benzodiazepine recognition site of the GABA(A) receptor. J Neurochem 70(5):2188–2194
Ogris W, Poltl A, Hauer B, Ernst M, Oberto A, Wulff P, Hoger H, Wisden W, Sieghart W (2004) Affinity of various benzodiazepine site ligands in mice with a point mutation in the GABA(A) receptor gamma2 subunit. Biochem Pharmacol 68(8):1621–1629
Buhr A, Sigel E (1997) A point mutation in the gamma2 subunit of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors results in altered benzodiazepine binding site specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(16):8824–8829
Sigel E, Schaerer MT, Buhr A, Baur R (1998) The benzodiazepine binding pocket of recombinant alpha1beta2gamma2 gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors: relative orientation of ligands and amino acid side chains. Mol Pharmacol 54(6):1097–1105
Castellano S, Taliani S, Milite C, Pugliesi I, Da Pozzo E, Rizzetto E, Bendinelli S, Costa B, Cosconati S, Greco G, Novellino E, Sbardella G, Stefancich G, Martini C, Da Settimo F (2012) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-phenylquinazoline-2-carboxamides designed as a novel class of potent ligands of the translocator protein. J Med Chem 55(9):4506–4510
Chambon JP, Perio A, Demarne H, Hallot A, Dantzer R, Roncucci R, Biziere K (1985) Ethyl loflazepate: a prodrug from the benzodiazepine series designed to dissociate anxiolytic and sedative activities. Arzneimittelforschung 35(10):1573–1577
Dubinsky B, Vaidya AH, Rosenthal DI, Hochman C, Crooke JJ, DeLuca S, DeVine A, Cheo-Isaacs CT, Carter AR, Jordan AD, Reitz AB, Shank RP (2002) 5-ethoxymethyl-7-fluoro-3-oxo-1,2,3,5-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2a]pyridine-4 -N-(2-fluorophenyl)carboxamide (RWJ-51204), a new nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303(2):777–790
Fujimoto M, Hirai K, Okabayashi T (1982) Comparison of the effects of GABA and chloride ion on the affinities of ligands for the benzodiazepine receptor. Life Sci 30(1):51–57
Vinkers CH, Korte-Bouws GA, Torano JS, Mirza NR, Nielsen EO, Ahring PK, de Jong GJ, Olivier B (2010) The rapid hydrolysis of chlordiazepoxide to demoxepam may affect the outcome of chronic osmotic minipump studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 208(4):555–562
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Program for Innovative Research Team of the Ministry of Education and Program for Liaoning Innovative Research Team in University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1568 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, HB., Sha, Y., Wang, J. et al. Some insights into the binding mechanism of the GABAA receptor: a combined docking and MM-GBSA study. J Mol Model 19, 5489–5500 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-013-2049-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-013-2049-8