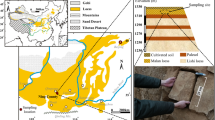
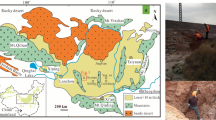
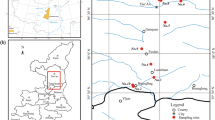
Abstract
Due to the monsoon climate, saline soils extensively spread over the arid or semi-arid area (e.g. NW China) and are featured with notable dissolution collapsibility and salt expandability. The features cause road hump and subgrade corrosion towards endangering the safety of passers. In this study, the microstructural evolution of the loess when subjected to alkaline and saline environments was investigated using a series of microscale tests, including scanning electron microscopic (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM–EDS), and mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP). The correspondence of the microstructural evolution with the macroscale mechanical properties using the reduced triaxial extension tests was studied. The test results showed that the alkaline and saline environments led to the microstructural evolution of the loess, involving the particle morphology, microstructural characteristics, pore distribution, and directionality of the pores. The increasing thickness of the diffuse double layer, induced by sodium sulphate, reduced the suction and deteriorated the microstructural characteristics, causing a degradation of the macroscale mechanical properties. Under sodium hydroxide conditions, a distinct transformation from granular structures to an agglomerated structure was attributed to the formation of sodium silicate, and the surface-surface connections were formed at the same time, which also indicated an enhancement of the microstructural characteristics. The enhanced microstructural characteristics contributed to the improvement in the macroscale mechanical properties. The findings of this study provide some design guideposts for preventing and mitigating the degradation of subgrade when exposed to saline environments.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assallay AM, Rogers CDF, Smalley IJ (1997) Formation and collapse of metastable particle packings and open structures in loess deposits. Eng Geol 48(1–2):101–115
Bai B, Long F, Rao DY, Xu T (2017) The effect of temperature on the seepage transport of suspended particles in a porous medium. Hydrol Process 31(2):382–393
Bai B, Rao DY, Chang T, Guo ZG (2019) A nonlinear attachment-detachment model with adsorption hysteresis for suspension-colloidal transport in porous media. J Hydrol 578:124080
Bai B, Xu T, Nie QK, Li PP (2020) Temperature-driven migration of heavy metal Pb2+ along with moisture movement in unsaturated soils. Int J Heat Mass Transf 153:119573
Bai XD, Cheng WC, Li G (2021a) A comparative study of different machine learning algorithms in predicting EPB shield behaviour: a case study at the Xi’an metro China. Acta Geotech 16(12):4061–4080
Bai XD, Cheng WC, Sheil BB, Li G (2021b) Pipejacking clogging detection in soft alluvial deposits using machine learning algorithms. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 113:103908
Blanck G, Cuisinier C, Masrouri F (2014) Soil treatment with organic non-traditional additives for the improvement of earthworks. Acta Geotech 9:1111–1112
Bolt GH (1956) Physical-chemical analysis of the compressibility of pure clays. Géotechnique 6(2):86–93
Bolt GH, Miller RD (1955) Compression studies of illite suspensions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 19(3):285–288
Deng LS, Fan W, Yin YP, Cao YB (2018) Case study of a collapse investigation of loess sites covered by very thick loess-paleosol interbedded strata. Int J Geomech 18(11):05018009
Du YJ, Fan RD, Reddy KR, Liu SY, Yang YL (2015) Impacts of presence of lead contamination in clayey soil-calcium bentonite cutoff wall backfills. Appl Clay Sci 108:111–122
Du YJ, Wei ML, Reddy KR, Wu HL (2016) Effect of carbonation on leachability, strength and microstructural characteristics of KMP binder stabilized Zn and Pb contaminated soils. Chemosphere 144:1033–1042
Du YJ, Wu J, Bo YL, Jiang NJ (2020) Effects of acid rain on physical, mechanical and chemical properties of GGBS–MgO-solidified/stabilized Pb-contaminated clayey soil. Acta Geotech 15:923–932
Duan Z, Cheng WC, Peng JB, Rahman MM, Tang H (2021) Interactions of landslide deposit with terrace sediments: Perspectives from velocity of deposit movement and apparent friction angle. Eng Geol 280:105913
Duan Z, Cheng WC, Peng JB, Wang QY, Chen W (2019) Investigation into the triggering mechanism of loess landslides in the south Jingyang platform, Shaanxi province. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:4919–4930
Estabragh AR, Beytolahpour I, Moradi M, Javadi AA (2014) Consolidation behavior of two fine-grained soils contaminated by glycerol and ethanol. Eng Geol 178:102–108
Fan X, Xu Q, Scaringi G, Li S, Peng D (2017) A chemo-mechanical insight into the failure mechanism of frequently occurred landslides in the Loess Plateau, Gansu Province, China. Eng Geol 228:337–345
Gao Y, Qian H, Li X, Chen J, Jia H (2018) Effects of lime treatment on the hydraulic conductivity and microstructure of loess. Environ Earth Sci 77:529
Gao S, Liang J, Teng T, Zhang M (2019) Petroleum contamination evaluation and bacterial community distribution in a historic oilfield located in Loess Plateau in China. Appl Soil Ecol 136:30–42
Ghirian A, Fall M (2013) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical behavior of cemented paste backfill in column experiments. Part I: Physical, hydraulic and thermal processes and characteristics. Eng Geol 164:195–207
Ghirian A, Fall M (2014) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical behavior of cemented paste backfill in column experiments: Part II: Mechanical, chemical and microstructural processes and characteristics. Eng Geol 170:11–23
Gratchev I, Towhata I (2011) Compressibility of natural soils subjected to long-term acidic contamination. Environ Earth Sci 64(1):193–200
Gratchev I, Towhata I (2013) Stress–strain characteristics of two natural soils subjected to long-term acidic contamination. Soils Found 53(3):469–476
Hu WL, Cheng WC, Wen SJ, Rahman, MM (2021a) Effects of chemical contamination on microscale structural characteristics of intact loess and resultant macroscale mechanical properties. Catena 203, 105361.
Hu WL, Cheng WC, Wen SJ, Yuan K (2021b) Revealing enhancement and degradation mechanisms affecting calcite precipitation in EICP process. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:750258
Lei H, Wang L, Jia R, Jiang M, Zhang W, Li C (2020) Effects of chemical conditions on the engineering properties and microscopic characteristics of Tianjin dredged fill. Eng Geol 269: 105548.
Li P, Xie WL, Pak RYS, Vanapalli SK (2019) Microstructural evolution of loess soils from the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 173:276–288
Liu JY, Li XA, Xue Q, Guo ZZ (2020) Experimental study on air permeability and microscopic mechanism of intact and remolded Malan loess, Loess Plateau, China. Bull Eng Geol Env 79:3909–3919
Meng J, Li XA (2019) Effects of carbonate on the structure and properties of loess and the corresponding mechanism: an experimental study of the Malan loess, Xi’an area, China. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:4965–4976
Mitchell JK, Soga K (1976) Fundamentals of soil behavior. Wiley, New York
Moore CA, Donaldson CF (1995) Quantifying soil microstructure using fractals. Geotechnique 45(1):105–116
Nguyen XP, Cui YJ, Tang AM, Deng YF, Li XL, Wouters L (2013) Effects of pore water chemical composition on the hydro-mechanical behavior of natural stiff clays. Eng Geol 166:52–64
Safehian H, Rajabi AM, Ghasemzadeh H (2018) Effect of diesel-contamination on geotechnical properties of illite soil. Eng Geol 241:55–63
Shao X, Zhang H, Tan Y (2018) Collapse behavior and microstructural alteration of remolded loess under graded wetting tests. Eng Geol 233:11–22
Smalley I, Marković SB (2014) Loessification and hydroconsolidation: there is a connection. Catena 117:94–99
Smalley I, O’Hara-Dhand K, Kwong J (2014) China: material for a loess landscape. Catena 117:100–107
Sridharan A, Choudhury D (2002) Swelling Pressure of Sodium Montmorillonites Géotechnique 52(6):459–462
Suksiripattanapong C, Horpibulsuk S, Yeanyong C, Arulrajah A (2021) Evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol and high calcium fly ash based geopolymer for the improvement of soft Bangkok clay. Transport Geotech 27: 100476.
Tandy S, Ammann A, Schulin R, Nowack B (2006) Biodegradation and speciation of residual SS-ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid (EDDS) in soil solution left after soil washing. Environ Pollut 142:191–199
Trzciński J, Williams DJ, Żbik MS (2015) Can hydrocarbon contamination influence clay soil grain size composition? Appl Clay Sci 109–110:49–54
Wang L, Cheng WC, Xue ZF (2022) The effect of calcium source on Pb and Cu remediation using enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:849631
Wei W, Shao ZS, Qiao RJ, Chen WW, Zhang PJ, Cheng JX (2021) Workability and mechanical properties of microwave heating for recovering high quality aggregate from concrete. Constr Build Mater 276:122237
Wei Y, Fan W, Yu B, Deng L, Wei T (2020) Characterization and evolution of three dimensional microstructure of Malan loess. Catena 192: 104585.
Xu P, Zhang Q, Qian H, Li M, Yang F (2021) An investigation into the relationship between saturated permeability and microstructure of remolded loess: a case study from Chinese Loess Plateau. Geoderma 382: 114774.
Xue ZF, Cheng WC, Wang L, Hu WL (2022) Effects of bacterial inoculation and calcium source on microbial-induced carbonate precipitation for lead remediation. J Hazard Mater 426:128090
Xue ZF, Cheng WC, Wang L, Song GY (2021) Improvement of the shearing behaviour of loess using recycled straw fiber reinforcement. KSCE J Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-2263-3
Ye X, Wang S, Yang J, Sheng D, Xiao C (2017) Soil conditioning for EPB shield tunneling in argillaceous siltstone with high content of clay minerals: case study. Int J Geomech 17(4):05016002
Yuan Y, Shao ZS, Qiao RJ, Fei XS, Cheng JX, Wei W (2021) Fracture behavior of concrete coarse aggregates under microwave irradiation influenced by mineral components. Constr Build Mater 286:122944
Zhang F, Wang G, Kamai T, Chen W, Zhang D, Yang J (2013) Undrained shear behavior of loess saturated with different concentrations of sodium chloride solution. Eng Geol 155:69–79
Zhang SC, Liu H, Chen WH, Niu FJ, Niu ZL (2020) Strength deterioration model of remolded loess contaminated with acid and alkali solutions under freeze-thaw cycles. Bull Eng Geol Env 11(1):11–12
Zhang T, Deng Y, Cui Y, Lan H, Zhang F, Zhang H (2019) Porewater salinity effect on flocculation and desiccation cracking behaviour of kaolin and bentonite considering working condition. Eng Geol 251:11–23
Zhang Y, Hu Z, Li L, Xue Z (2018) Improving the structure and mechanical properties of loess by acid solutions–an experimental study. Eng Geol 244:132–145
Zhao YD, Hu X, Li XY (2020) Analysis of the intra-aggregate pore structures in three soil types using X-ray computed tomography. Catena 193: 104622.
Zhu CP, Liu HL, Shen Y (2011) Laboratory tests on shear strength properties of soil polluted by acid and alkali. Chinese J Geotech Eng 33(7):164–170 (in Chinese)
Funding
This paper is supported by the Shaanxi Educational Department under Grant No. 2020TD-005 through the innovative ability support scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lin Wang: data curation, formal analysis, validation, software, writing–original draft. Wen-Chieh Cheng: conceptualisation, methodology, writing–review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition. Zhong-Fei Xue: data curation, formal analysis, validation, software, writing–original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Cheng, WC. & Xue, ZF. Investigating microscale structural characteristics and resultant macroscale mechanical properties of loess exposed to alkaline and saline environments. Bull Eng Geol Environ 81, 146 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02640-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02640-z