Abstract
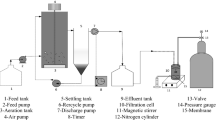
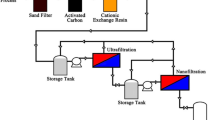
The present study was carried out for the treatment of paper mill effluent using combination of activated sludge process and membrane separation. An integrated paper mill employing OCEOPHH sequence (oxidation, chlorination, alkali extraction re-enforced by oxygen and peroxide, hypo-1, and hypo-2) for the bleaching of hardwood pulp was selected for the study. The purpose of this work was to examine the water quality and membrane performance when combining activated sludge process with different membrane separation processes in series. Pollutant removal including adsorbable organic halides (AOX) was compared among different treatment combinations; (i) ASP + microfiltration (MF), (ii) ASP +MF + ultrafiltration (UF), (iii) ASP +MF + UF + nanofiltration (NF), and (iv) ASP +MF + UF + NF + reverse osmosis (RO) to select the optimal treatment scheme for water recycling in the paper mill. Different initial inlet pressures were used for the UF and NF (6.8, 10.3, and 13.7 bar) and for RO (10.3, 13.7, and 17.2) The retentate from each membrane was recycled back to the feed and retreated until the inlet pressure increased to the maximum cut-off pressure for each membrane. After separation, 100 % total suspended solids, total dissolved solids, color removal and 94.2 % chemical oxygen demand, and 86 % AOX removal was observed. This study suggests the potential application of the combination of membrane separation with activated sludge process for recycling water in the paper industry.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi GY, Abbassi BE (2004) Environmental assessment for paper and cardboard industry in Jordan: a cleaner production concept. J Clean Prod 12(4):321–326
Abou-Elela SI, Nasr FA, Ibrahim HS, Badr NM, Askalany ARM (2008) Pollution prevention pays off in a board paper mill. J Clean Prod 16(3):330–334
APHA and AWWA aW (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C
Ataberk S, Gokcay CF (1997) Removal of chlorinated organics from pulping effluents by activated sludge process. Fersenius Environ Bull 6:147–153
Azbar N (2004) Upgrading an existing treatment system to adopt cleaner production principals. J Clean Prod 12(7):789–795
Bajpai P (2012) Biological treatment of pulp and paper mill effluents. In: Biotechnology for pulp and paper processing. Springer, New York, USA, pp 211–261
Beril Gönder Z, Arayici S, Barlas H (2011) Advanced treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewater by nanofiltration process: effects of operating conditions on membrane fouling. Sep Purif Technol 76(3):292–302
Blöcher C, Noronha M, Fünfrocken L, Dorda J, Mavrov V, Janke HD, Chmiel H (2002) Recycling of spent process water in the food industry by an integrated process of biological treatment and membrane separation. Desalination 144(1–3):143–150
Bulow C, Pingen G, Hamm U (2003) Complete water system closure. In: Pulp and Paper International, 12:14–17
Buyukkamaci N, Koken E (2010) Economic evaluation of alternative wastewater treatment plant options for pulp and paper industry. Sci Total Environ 408(24):6070–6078
Choi J-H, Dockko S, Fukushi K, Yamamoto K (2002) A novel application of a submerged nanofiltration membrane bioreactor (NF MBR) for wastewater treatment. Desalination 146(1–3):413–420
Galil NI, Levinsky Y (2007) Sustainable reclamation and reuse of industrial wastewater including membrane bioreactor technologies: case studies. Desalination 202(1–3):411–417
Gergov M, Priha M, Talka E, Valttila O, Kangas A, Kukkonen K (1988) Chlorinated organic compounds in effluent treatment at kraft mills. Tappi J 71(12):175–184
Hamm U, Schabel S (2007) Effluent-free papermaking: industrial experiences and latest developments in the German paper industry. Water Sci Technol 55(6):205–211
Hernández-Sancho F, Sala-Garrido R (2009) Technical efficiency and cost analysis in wastewater treatment processes: a DEA approach. Desalination 249(1):230–234
Karthik M, Dhodapkar R, Manekar P, Aswale P, Nandy T (2011) Closing water loop in a paper mill section for water conservation and reuse. Desalination 281:172–178
Khansorthong S, Hunsom M (2009) Remediation of wastewater from pulp and paper mill industry by the electrochemical technique. Chem Eng J 151(1–3):228–234
Liu G, Liu Y, Ni J, Shi H, Qian Y (2004) Treatability of kraft spent liquor by microfiltration and ultrafiltration. Desalination 160(2):131–141
Mänttäri M, Nuortila-Jokinen J, Nyström M (1997) Influence of filtration conditions on the performance of NF membranes in the filtration of paper mill total effluent. J Membr Sci 137(1–2):187–199
Mänttäri M, Viitikko K, Nyström M (2006) Nanofiltration of biologically treated effluents from the pulp and paper industry. J Membr Sci 272(1–2):152–160
Mobius CH, Helble A (2003) Combined ozonation and biofilm treatment for reuse of paper mill wastewaters. In: Third International Conference on Oxidation Technologies for Water and Wastewater Treatment, Goslar, Special Topic: AOP’s for Recycling and Reuse,. pp 276–280
Nandy T, Kaul SN, Shastry S (2002) Upgrading a paper industry effluent treatment plant for capacity expansion with recourse to recycling effluent. Resour Conserv Recycl 34(3):209–228
Nassar MM (2003) Studies on internal and external water treatment at a paper and cardboard factory. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 78(5):572–576
Negaresh E, Antony A, Bassandeh M, Richardson DE, Leslie G (2012) Selective separation of contaminants from paper mill effluent using nanofiltration. Chem Eng Res Des 90(4):576–583
Parthasarathy G, Krishnagopalan G (1999) Effluent reduction and control of non-process elements towards a cleaner Kraft pulp mill. Clean Prod Process 1(4):264–277
Patoczka J (2006) TDS and sludge generation impacts from use of chemicals in wastewater treatment. In: WEFTEC®.06. Water Environment Foundation, NJ, 5209–5214
Paul D, Sikdar SK (1998) Clean production with membrane technology. Clean Prod Process 1(1):39–48
Pizzichini M, Russo C, Meo CD (2005) Purification of pulp and paper wastewater, with membrane technology, for water reuse in a closed loop. Desalination 178(1–3):351–359
Raj A, Reddy MMK, Chandra R (2007) Decolourisation and treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent by lignin-degrading Bacillus sp. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82(4):399–406
Sattler C, de Oliveira L, Tzschirner M, Machado AEH (2004) Solar photocatalytic water detoxification of paper mill effluents. Energy 29(5–6):835–843
Shukla SK, Kumar V, Bansal MC (2010) Treatment of combined bleaching effluent by membrane filtration technology for system closure in paper industry. Desalin Water Treat 13(1–3):464–470
Shukla S, Kumar V, Kim T, Bansal MC (2013a) Membrane filtration of chlorination and extraction stage bleach plant effluent in Indian paper Industry. Clean Technol Environ Policy 15(2):235–243
Shukla SK, Kumar V, Chakradhar B, Kim T (2013b) Recycling of regenerated wastewater in the process using water cascade analysis in pulp and paper mills. In: Recycling: Technological Systems, Management Practices and Environmental Impact, 209–224
Shukla SK, Kumar V, Chakradhar B, Kim T, Bansal MC (2013c) Designing plant scale process integration for water management in an Indian paper mill. J Environ Manag 128:602–614
Sumathi S, Hung Y-T (2006) Treatment of pulp and paper mill wastes. In: Wang LK, Hung Y-T, Lo HH, Yapijakis C (eds) Waste treatment in the process industries. Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp 453–497
Tansel B, Bao WY, Tansel IN (2000) Characterization of fouling kinetics in ultrafiltration systems by resistances in series model. Desalination 129(1):7–14
Zhang Y, Ma C, Ye F, Kong Y, Li H (2009) The treatment of wastewater of paper mill with integrated membrane process. Desalination 236(1–3):349–356
Acknowledgments
Sudheer Kumar Shukla was supported by the Yonsei University Research Fund of 2014. Van Doan, Kim and Park were supported by NRF-2013R1A2A03016475 (Biological production of combustion propellant N2O from high N-loading wastewater and its microbial ecological metabolism engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, S.K., Kumar, V., Van Doan, T. et al. Combining activated sludge process with membrane separation to obtain recyclable quality water from paper mill effluent. Clean Techn Environ Policy 17, 781–788 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0836-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-014-0836-2