Abstract
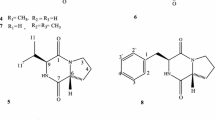
A novel diketopiperazine, named cyclo-(D-pipecolinyl-L-isoleucine) (DKP 1), and 7 known diketopiperazines were isolated from the cell-free culture supernatant of the Antarctic psychrophilic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125. Two diketopiperazines containing pipecolinyl moiety were isolated for the first time from a natural source. Two new linear peptides, stable to bacterial proteolytic enzymes, were also characterized. The structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated by means of spectroscopic data (1D-, 2D-NMR, EIMS, FABMS, and ESIMS/MS) and chiral high-performance liquid chromatography. The potential antioxidant activity of the isolated compounds was evaluated by a DPPH free radical scavenging assay.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczeski M, Reed AR, Crews P. (1995). New and known diketopiperazines from the carribbean sponge, Calyx CF podatypa. J Nat Prod 58:201–208
Sannia G, Vinci F, Marino G. (2000). Aspartate aminotransferase from the Antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC 125: cloning, expression, properties, and molecular modelling. Eur J Biochem 267:2790–2802
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Munro MHG, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR. (2004). Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 21:1–49, and earlier series
Boldyrev AA, Dupin AM, Batrukova MA, Bavykina NI, Korshunova GA, Shvachkin YuP. (1989). A comparative study of synthetic carnosine analogs as antioxidants Comp Biochem Physiol 94B:237–240
Cavicchioli R, Siddiqui KS, Andrews D, Sowers KR. (2002). Low-temperature extremophiles and their applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:253–61
Corsaro MM, Lanzetta R, Parrilli E, Parrilli M, Tutino ML, Ummarino S. (2004) Influence of growth temperature on lipid and phosphate contents of su polysaccharides from Antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC 125. J Bacteriol 186:29–34
Davies DB, Abu Khaled Md. (1976). Conformations of peptides in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, part II: homoallylic coupling in cyclic dipeptides. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2:187–196
Degrassi G, Aguilar C, Bosco M, Zahariev S, Pongor S, Venturi V. (2002). Plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas putida WCS358 produces and secretes four cyclic dipeptides: cross-talk with quorum sensing bacterial sensors. Curr Microbiol 45:250–254
De Rosa S, Mitova M, Tommonaro G. (2003). Marine bacteria associated with sponge as source of cyclic peptides. Biomol Eng 20:311–316
Fenical W. (1993). Chemical studies of marine bacteria: developing a new resource. Chem Rev 93:1673–1683
Ferroni GDJ. (1989). The conditions required for exopolymer production by a psychrotrophic bacterium. Gen Appl Microbiol 35:393–406
Gautschi M, Schmid JP, Peppard TL, Ryan TP, Tuorto RM, Yang X. (1997) Chemical characterization of diketopiperazines in beer. J Agric Food Chem 45:3183–3189
Ginz M, Engelhardt UH. (2000). Identification of proline-based diketopiperazines in roasted coffee. J Agric Food Chem 48:3528–3532
Holden MTG, Chhabra SR, de Nys R, Stead P, Bainton NJ, Hill PJ, Manefield M, Kumar N, Labatte M, England D, Rice S, Givskov M, Salmond GPC, Stewart GSAB, Bycroft BW, Kjelleberg S, Williams P. (1999). Quorum-sensing cross talk: isolation and chemical characterization of cyclic dipeptides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol 33:1254–1266
Holmstroem C, Kjelleberg S. (1999). Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30:285–293
Huang Z, Zhou S, Wu X, Jiang G, Lin Y. (1997). Study on metabolites of bacteria 110 from the South China Sea. Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao, Ziran Kexueban 36:127–128
Hugenholtz P, Goebel BM, Pace NR. (1998). Impact of culture-independent studies on the emerging phylogenetic view of bacterial diversity. J Bacteriol 180:4765–4774
Imamura M, Prasad C. (2001). Role of endogenous cyclo-(histidyl-proline) in voluntary alcohol consumption by alcohol-preferring C57BL mice. Peptides 22:2113–2117
Jayatilake GS, Thornton MP, Leonard AC, Grimwade JE, Baker BJ. (1996) Metabolites from an Antarctic sponge-associated bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Nat Prod 59: 293–296, and references therein
Jensen PR, Fenical W. (2000). Marine microorganisms and drug discovery: current status and future potential. In:Fusetani N. (ed) Drugs from the Sea, Basel, Switzerland: Karger Publishers, 6–29
Kalinovskaya NI, Kuznetsova TA, Ivanova EP, Romanenko LA, Voinov VG, Huth F, Laatsch H. (2002). Characterization of surfactine-like cyclic depsipeptides synthesized by Bacillus pumilis from ascidian Halocynthia aurantium. Mar Biotechnol 4:179–188
Kawamura Sh, Sakurada Sh, Sakurada Ts, Kisara K, Sasaki Yu, Suzuki K. (1985). The antinociceptive effects of histidyl-proline diketopiperazine and thyrotropin-releasing hormone in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol 112:287–294
Lazzazera BA. (2000). Quorum sensing and starvation: signals for entry into stationary phase. Curr Opin Microbiol 3:177–182
Lazazzera BA, Grossman AD. (1998). The ins and outs of peptide signaling. Trends Microbiol 6:288–294
Mitova M, Tommonaro G, De Rosa S. (2003). A new cyclopeptide from a bacterium associated with the marine sponge Ircinia muscarum. Z Naturforsch 58c:740–745, and references therein
Mitova M, Tommonaro G, Hentschel U, Müller WEG, De Rosa S. (2004a). Exocellular cyclic dipeptides from a Ruegeria strain associated with cell cultures of Suberites domuncula. Mar Biotechnol 6:95–103
Mitova M, Popov S, De Rosa S. (2004b). Cyclic peptides from a Ruegeria strain of bacteria associated with the sponge Suberites domuncula. J Nat Prod 67:1178–1181
Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Snader KM. (2003). Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J Nat Prod 66:1022–1037
Prasad C. (1995). Bioactive cyclic dipeptides Peptides 16:151–164
Prasad Ch, Mizuma H, Brock JW, Porter JR, Svec F, Hilton Ch. (1995). A paradoxical elevation of brain cyclo-(His-Pro) levels in hyperphagic obese Zucker rats. Brain Res 699:149–153
Rudi A, Kashman Y, Benayahu Y, Schleyer M. (1994). Amino acid derivatives from the marine sponge Jaspis digonoxea. J Nat Prod 57:829–832
Schmitz F, Vanderah D, Hollenbeak K, Enwall C, Gopichand Y, SenGupta P, Hossain M, van der Helm D. (1983). Metabolites from the marine sponge Tedania ignis: a new atisanediol and several known diketopiperazines. J Org Chem 48:3941–3945
Seebach D, Ryeping M, Arvidsson PI, Kimmerlin T, Micuch P, Noti C, Langenegger D, Hoyer D. (2001). Linear, peptidase-resistant β2/β3-di- and ?/β3-tetrapeptide derivatives with nanomolar affinities to a human somatostatin receptor. Helv Chim Acta 84:3503–3510
Shi LY, Ku BS, Yao HY. (1991). Antidepressant effects of several overshort peptides. Yaoxue Xuebao 26:546–547
Siemon IZ, Kolasa T, Paradowsky A. (1979). On the taste of stereoisomeric cyclic dipeptides containing a proline residue. Chem Senses Flavour 4:127–133
Song MK, Hwang IK, Rosenthal MJ, Harris DM, Yamaguchi DT, Yip I, Go VLW (2003). Anti-hyperglycemic activity of zink plus cyclo-(His-Pro) in genetically diabetic goto-kakizaki and aged rats. Exp Biol Med 228:1338–1345
Stierle A, Cardellina J, Singleton F. (1988). A marine Micrococcus produces metabolites ascribed to the sponge Tedania ignis. Experientia 44:1021
Trischman JA, Oeffner RE, de Luna MG, Kazaoka M. (2004). Competitive induction and enhancement of indole and a diketopiperazine in marine bacteria. Mar Biotechnol 6:215–220
Vicar J, Budesinsky M, Blaha K. (1973a). Amino acids and peptides, CXIV: proton magnetic resonance studies of cyclodipeptides containing pipecolic acid, proline and/or 2-azetidinecarboxylic acid. Collection Czechoslov Chem Comm 38:1940–1956
Vicar J, Smolikova J, Blaha K. (1973b). Amino acids and peptides, CXV: 2,5-piperazinediones with an anneled azetidine ring; synthesis and infrared spectra. Collection Czechoslov Chem Comm 38:1957–1970
Yamano N, Higashida N, Endo C, Sakata N, Fujishima S, Maruyama A, Higashihara T (2000). Purification and characterization of N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate deacetylase from a psychrotrophic marine bacterium, Alteromonas species. 2:57–64
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Marie Curie Research Training Grant of the European Community programme “Quality of life and management of living resources” contract No QLK5-CT-2001-50974, a grant of Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca Scientifica (Progetti di Rilevante Interesse Nazionale 2002 – UO G. Marino) and by CNR-Roma. “Servizio di Spettrometria di Massa del CNR-Napoli and Servizio NMR, ICB-CNR” provided the MS and NMR spectra, respectively. The technical assistance of Ms. M. Bianco, Mr. C. Iodice, Mr. V. Mirra, and Dr. R. Varlese is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitova, M., Tutino, M.L., Infusini, G. et al. Exocellular Peptides from Antarctic PsychrophilePseudoalteromonas Haloplanktis. Mar Biotechnol 7, 523–531 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-004-5098-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-004-5098-2