Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the antialbuminuric and antihypertensive effects of aliskiren by monitoring home blood pressure (BP) in comparison with the effects of the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) valsartan in patients with hypertensive nephrosclerosis and albuminuria.
Methods
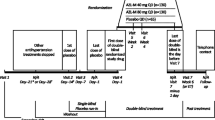
We conducted an open-label, randomized trial to compare the effects of aliskiren with those of valsartan. Patients with BP <150/90 mmHg, an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 90–30 mL/min/1.73 m2, and albuminuria >30 mg/g, despite treatment with a 160 mg daily dose of valsartan, were randomly assigned to the following two groups: the aliskiren group, who switched from 160 mg/day valsartan to 150 mg/day aliskiren, which was later increased to 300 mg/day (n = 20); and the valsartan group, who continued with 160 mg/day valsartan (n = 20).
Results
After 12 weeks of treatment, although there was no significant difference in clinic BP between groups, a significant reduction in morning and evening systolic BP was observed in the aliskiren group. The decrease in albuminuria in the aliskiren group was significantly better than that in the valsartan group, and a significant correlation was noted between the change in morning systolic BP and the change in albuminuria in the aliskiren group (r = 0.564, P = 0.0084).
Conclusion
We showed that aliskiren treatment leads to a greater reduction in albuminuria and home systolic BP values than valsartan in patients with nephrosclerosis. We propose that aliskiren therapy should be considered as a therapeutic modality to complement ARBs in hypertensive patients with nephrosclerosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Rohde RD. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1456–62.
Brenner BM, Cooper MD, De Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–9.
Ogihara T, Kikuchi K, Matsuoka H, Fujita T, Higaki J, Horiuchi M, Imai Y, Imaizumi T, Ito S, Iwao H, Kario K, Kawano Y, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Kimura G, Matsubara H, Matsuura H, Naruse M, Saito I, Shimada K, Shimamoto K, Suzuki H, Takishita S, Tanahashi N, Tsuchihashi T, Uchiyama M, Ueda S, Ueshima H, Umemura S, Ishimitsu T, Japanese Society of Hypertension Committee. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2009). Hypertens Res. 2009;32:3–107.
Pool JL, Schmieder RE, Azizi M, Aldigier JC, Januszewicz A, Zidek W, Chiang Y, Satlin A. Aliskiren, an orally effective renin inhibitor, provides antihypertensive efficacy alone and in combination of valsartan. Am J Hypertens. 2007;20:11–20.
Oparil S, Yarows SA, Patel S, Fang H, Zhang J, Satlin A. Efficacy and safety of combined use of aliskiren and valsartan in patients with hypertension: a randomized, double-blind trial. Lancet. 2007;370:221–9.
Ishibashi K, Kurisu S, Kato Y, Mitsuba N, Dohi Y, Nishioka K, Kihara Y. Effects of aliskiren on the fibrinolytic system in patients with coronary artery disease receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker. Heart Vessels. 2011 (in press).
Persson F, Lewis JB, Rossing P, Hollenberg NK, Parving HH. Aliskiren in combination with losartan reduces albuminuria independent of baseline blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6:1025–31.
Parving HH, Persson F, Lewis JB, Lewis EJ, Hollenberg NK, AVOID Study Investigators. Aliskiren combined with losartan in type-2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2433–46.
Rave K, Bender R, Heise T, Sawicki PT. Value of blood pressure self-monitoring as a predictor of progression of diabetic nephropathy. J Hypertens. 1999;17:597–601.
Suzuki H, Nakamoto H, Okada H, Sugahara S, Kanno Y. Self-measured systolic blood pressure in the morning is a strong indicator of clinical renal insufficiency. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2002;24:249–60.
Agarwal R, Andersen MJ. Prognostic importance of clinic and home blood pressure recordings in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2006;69:406–11.
Okada T, Nakao T, Matsumoto H, Nagaoka Y. Value of morning home blood pressure as a predictor of decline in renal function patients with chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2008;28:982–9.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, Yamagata K, Tomino Y, Yokoyama H, Hishida A. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:982–92.
Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, Zinman B, Dinneen SF, Hoogwerf B, Halle JP, Young J, Rashkow A, Joyce C, Nawaz S, Yusuf S, HOPE Study Investigators. Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. JAMA. 2001;286:421–6.
Ito S. Cardiorenal connection in chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012;16:8–16.
Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, Nahas ME, Astor BC, Matsushita K, Gansevoort RT, Kasiske BL, Eckardt KU. The definition, classification and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: a KDIGO Controversies Conference report. Kidney Int. 2011;80:17–28.
Astor BC, Matsushita K, Gansevoort RT, van der Velde M, Woodward M, Levey AS, Jong PE, Coresh J; Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium, Astor BC, Matsushita K, Gansevoort RT, van der Velde M, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, El-Nahas M, Eckardt KU, Kasiske BL, Wright J, Appel L, Greene T, Levin A, Djurdjev O, Wheeler DC, Landray MJ, Townend JN, Emberson J, Clark LE, Macleod A, Marks A, Ali T, Fluck N, Prescott G, Smith DH, Weinstein JR, Johnson ES, Thorp ML, Wetzels JF, Blankestijn PJ, van Zuilen AD, Menon V, Sarnak M, Beck G, Kronenberg F, Kollerits B, Froissart M, Stengel B, Metzger M, Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Heerspink HJ, Brenner B, de Zeeuw D, Rossing P, Parving HH, Auguste P, Veldhuis K, Wang Y, Camarata L, Thomas B, Manley T. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with mortality and end-stage renal disease. A collaborative meta-analysis of kidney disease population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011;79:1341–52.
Ibsen H, Olsen MH, Wachtell K, Borch-Johnsen K, Lindholm LH, Mogensen CE, Dahlof B, Snapinn SM, Wan Y, Lyle PA. Does albuminuria predict cardiovascular outcomes on treatment with losartan versus atenolol in patients with diabetes, hypertension, and left ventricular hypertrophy? The LIFE study. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:595–600.
Hillege HL, Jansen WM, Bak AA, Diercks GF, Grobbee DE, Crijns HJ, Van Gilst WH, De Zeeuw D, De Jong PE, Prevend Study Group. Microalbuminuria is common, also in a nondiabetic, nonhypertensive population, and independent indicator of cardiovascular risk factors and cardiovascular morbidity. J Intern Med. 2001;249:519–26.
Asselbergs FW, Diercks GF, Hillege HL, van Boven AJ, Janssen WM, Voors AA, de Zeeuw D, de Jong PE, van Veldhuisen DJ, van Gilst WH, Prevention of Renal and Vascular Endstage Disease Intervention Trial (PREVEND IT) Investigators. Effects of fosinopril and pravastatin on cardiovascular events in subjects with microalbuminuria. Circulation. 2004;110:2809–16.
Stehouwer CD, Nauta JJ, Zeldenrust GC, Hackeng WH, Donker AJ, den Ottolander GJ. Urinary albumin excretion, cardiovascular disease, and endothelial dysfunction in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1992;340:319–26.
Stehouwer CD, Smulders YM. Microalbuminuria and risk for cardiovascular disease: analysis of potential mechanisms. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2106–11.
Malik AR, Sultan S, Turner ST, Kullo IJ. Urinary albumin excretion is associated with impaired flow- and nitroglycerin-mediated brachial artery dilation in hypertensive adults. J Hum Hypertens. 2007;21:231–8.
Gradman AH, Schmieder RE, Lins RL, Nussberger J, Chiang Y, Bedigian MP. Aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor, provides dose-dependent antihypertensive efficacy and placebolike tolerability in hypertensive patients. Circulation. 2005;111:1012–8.
Strasser RH, Puig JG, Farsang C, Croket M, Li J, van Ingen H. A comparison of the tolerability of the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren and lisinopril in patients with severe hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2007;21:780–7.
Persson F, Rossing P, Schjoedt KJ, Juhl T, Tarnow L, Stehouwer CD, Schalkwijk C, Boomsma F, Frandsen E, Parving HH. Time course of the antiproteinuric and antihypertensive effects of direct renin inhibition in type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2008;73:1419–25.
Persson F, Rossing P, Reinhard H, Juhl T, Stehouwer CDA, Schalkwijk C, Danser AHJ, Boomsma F, Frandsen E, Parving HH. Renal effects of aliskiren compared to and in combination with irbesartan in patients with type 2 diabetes, hypertension and albuminuria. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:1873–9.
Kikuya M, Ohkubo T, Metoki H, Asayama K, Hara A, Obara T, Inoue R, Hoshi H, Hashimoto J, Totsune K, Satoh H, Imai Y. Day-by-day variability of blood pressure and heart rate at home as a novel predictor of prognosis: the Ohasama study. Hypertension. 2008;52:1045–50.
Tatasciore A, Renda G, Zimarino M, Soccio M, Bilo G, Parati G, Schillaci G, De Caterina R. Awake systolic blood pressure variability correlates with target-organ damage in hypertensive subjects. Hypertension. 2007;50:325–32.
Nagai M, Hoshide S, Ishikawa J, Shimada K, Kario K. Visit-to-visit blood pressure variations: new independent determinants for carotid artery measures in the elderly at high risk of cardiovascular disease. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2011;5:184–92.
Matsui Y, Ishikawa J, Eguchi K, Shibasaki S, Shimada K, Kario K. Maximum value of home blood pressure: a novel indicator of target organ damage in hypertension. Hypertension. 2011;57:1087–93.
Ichihara A, Sakoda M, Kurauchi-Mito A, Narita T, Kinouchi K, Bokuda K, Itoh H. New approaches to blockade of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system: characteristics and usefulness of the direct renin inhibitor aliskiren. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;113:296–300.
Hollenberg NK, Fisher NDL, Price DA. Pathways for angiotensin II generation in intact human tissue. Evidence from comparative pharmacological interruption of the renin system. Hypertension. 1998;32:387–92.
Hollenberg NK. Pharmacologic interruption of the renin-angiotensin system and the kidney: differential responses to angiotensin converting enzyme and renin inhibition. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:S239–42.
Foster RH, MacFarlane CH, Bustamante MO. Resent progress in understanding aldosterone secretion. Gen Pharmacol. 1997;28:647–51.
Rossi GP. Aldosterone breakthrough during RAS blockade: a role for endothelins and their antagonists? Curr Hypertens Rep. 2006;8:262–8.
Bomback AS, Rekhtman Y, Klemmer PJ, Canetta PA, Radhakrishnan J, Appel GB. Aldosterone breakthrough during aliskiren, valsartan, and combination (aliskiren + valsartan) therapy. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2012;6:338–45.
Pouleur AC, Uno H, Prescott MF, Desai A, Appelbaum E, Lukashevich V, Smith BA, Dahlof B, for the ALLAY investigators. Suppression of aldosterone mediates regression of left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with hypertension. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2011;12:483–90.
Abe M, Maruyama N, Suzuki H, Fujii Y, Ito M, Yoshida Y, Okada K, Soma M. Additive renoprotective effects of aliskiren on angiotensin receptor blocker and calcium channel blocker treatments for type 2 diabetic patients with albuminuria. Hypertens Res. 2012;35:874–81.
Persson F, Lewis JB, Lewis EJ, Rossing P, Hollenberg NK, Hans-Henrik P. Impact of aliskiren treatment on urinary aldosterone levels in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy: an AVOID substudy. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012;13:118–21.
Ichihara A, Kaneshiro Y, Takemitsu T, Sakoda M, Itoh H. The (pro)renin receptor and the kidney. Semin Nephrol. 2007;27:524–8.
Balakumar P, Jagadeesh G. Cardiovascular and renal pathologic implications of prorenin, renin, and the (pro)renin receptor: promising young players from the old renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010;56:570–9.
Persson F, Lewis JB, Lewis EJ, Rossing P, Hollenberg NK, AVOID Study Investigators. Impact of baseline renal function on the efficacy and safety of aliskiren added to losartan in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:2304–9.
Harel Z, Gilbert C, Wald R, Bell C, Perl J, Juurlink D, Beyene J, Shah PS.The effect of combination treatment with aliskiren and blockers of the renin–angiotensin system on hyperkalaemia and acute kidney injury: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;344:e42. doi:10.1136/bmj.e42.
Novartis International AG (2011) Novartis announces termination of ALTITUDE study with Rasilez/Tekturna in high-risk patients with diabetes and renal impairment. http://www.novartis.com/newsroom/media-releases/en/2011/1572562.shtml. Accessed 20 Dec 2011.
Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JJ, de Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon SD, Chaturvedi N, Ghadanfar M, Weissbach N, Xiang Z, Armbrecht J, Pfeffer MA. Aliskiren trial in type 2 diabetes using cardio-renal endpoints (ALTITUDE): rationale and study design. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:1663–71.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, H., Okada, K., Abe, M. et al. Aliskiren reduces home blood pressure and albuminuria in patients with hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Clin Exp Nephrol 17, 386–395 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0721-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0721-4