Abstract
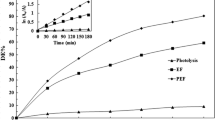
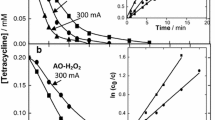
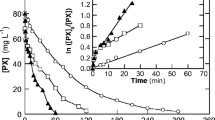
Aqueous solutions of organophosphorus pesticides were completely mineralized via in-situ generated hydroxyl radicals (HO·) by the Electro-Fenton process. Formation of Fenton's reagent (H2O2, Fe2+) was carried out by simultaneous reduction of O2 and Fe3+ on carbon cathode in acidic medium. The electrochemistry combined with Fenton's reagent provides an excellent way to continuously produce the hydroxyl radical, a powerful oxidant. We demonstrate the efficiency of the Electro-Fenton process to degrade three organophosphorus insecticides: malathion, parathion ethyl and tetra-ethyl-pyrophosphate (TEPP). Degradation kinetics and removals of chemical oxygen demand (COD) have been investigated. Here we show that the mineralization efficiency was over 80% for three organophosphorus pesticides.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron JJ, Oturan MA (2001) New photochemical and electrochemical methods for the degradation of pesticides in aqueous media. Turk J Chem 25:509–520
Bucheli TD, Grubler FC, Müller SR, Schwarzenbach RP (1997) Simultaneous determination of neutral and acidic pesticides in natural waters at the low nanogram per liter level. Anal Chem 69:1569–1576
Dzyadevych S, Chovelon JM (2002) A comparative photodegradation studies of methyl parathion by using lumistox test and conductometric biosensor technique. Mater Sci Eng 21:55–60
Haag WR, Yao CCD (1992) Rate constant for reaction of hydroxyl radicals with several drinking water contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 26:1005–1013
Hermann JM, Guillard C, Arguello M, Agüera A, Tejedor A, Piedra L, Fernandez-Alba A (1999) Photocatalytic degradation of pesticides pirimiphos-methyl: determination of the reaction pathway and identification of intermediate products by various analytical methods. Catalys Today 54:353–367
Kuo WG (1992) Decolorizing dye wastewater with Fenton's reagent. Water Res 26:881–886
Matsue T, Fujihira M, Osa T (1981) Oxidation of alkylbenzenes by electrogenerated hydroxyl radical. J Electrochem Soc 128:2565–2569
Nigam P, Banat IM, Singh D, Marchant R (1995) Microbial process for the decolorization of textile effluent containing azo, diazo and reactive dyes. Process Biochem 31:435–442
Oturan MA (2000) An ecologically effective water treatment technique using electrochemically generated hydroxyl radicals for in situ destruction of organic pollutants: Application to the herbicide 2,4-D. J Appl Electrochem 30:475–482
Oturan MA, Aaron JJ, Oturan N, Pinson J (1999) Degradation of chlorophenoxyacid herbicides in aqueous media, using a novel electrochemical method. Pestic Sci 55:558–562
Plumb JA, Areechon N (1990) Effect of malathion on humoral immune response of channel catfish. Dev Comp Immunol 14:355–358
Sauleda R, Brillas E (2001) Mineralization of aniline and 4-chlorophenol in acidic solution by ozonation catalyzed with Fe2+ and UVA light. Appl Catal B-Environ 29:135–145
Spadaro JT, Lorne I, Renganathan V (1994) Hydroxyl radical mediated degradation of azo dyes: evidence for benzene generation. Environ Sci Technol 28:1389–1393
Trucker JW, Thompson CQ (1987) Danger of using organophosphorus pesticides and diesel oil in fish ponds. Aquacult Mag 13:62–63
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guivarch, E., Oturan, N. & Oturan, M.A. Removal of organophosphorus pesticides from water by electrogenerated Fenton's reagent. Environ Chem Lett 1, 165–168 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-003-0029-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-003-0029-4