Abstract
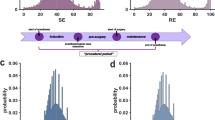
This paper analyses seizure detection features and their combinations using a probability-based scalp EEG seizure detection framework developed by Marc Saab and Jean Gotman. Our method was evaluated on 525 h of data, including 88 seizures in 21 patients. The individual performances of the three features used by Saab and Gotman were compared to six alternative features, and combinations of these nine features were analyzed in order to find a superior detector. On a testing set with the combination of their three features, Saab and Gotman reported a sensitivity of 0.78, a false positive rate of 0.86/h, and a median detection delay of 9.8 s. Based on 10-fold cross-validation the testing performance of our implementation of their method achieved a sensitivity of 0.79, a false positive rate of 0.62/h, and a median detection delay of 21.3 s. A detector based on an alternative combination of features achieved sensitivity of 0.81, a false positive rate of 0.60/h, and a median detection delay of 16.9 s. By including filtering techniques, it was possible to achieve performance levels similar to Saab and Gotman using our implementation of their method, although this involved increases in detection delays. Of the seizure detection measures investigated, relative average amplitude, relative power, relative derivative, and coefficent of variation of amplitude provided the best performing combinations. These better-performing features can be employed together to make robust and reliable seizure detectors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acir, N., I. Öztura, M. Kuntalp, B. Baklan, and C. Gützelis. Automatic detection of epileptiform events in EEG by a three-stage procedure based on artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 52(1):30–40, 2005.
Bayes, T. An essay towards solving a problem in the doctrine of chances. Philosophical Transactions, Giving Some Account of the Present Undertakings, Studies and Labours of the Ingenious in Many Considerable Parts of the World 53:370–418, 1763.
Blume, W., and S. Wiebe. “Periodic” seizures. Epilepsia 38(12):1355–1358, 1997.
Burrus, C., R. Gopinath, and H. Guo, editors. Introduction to Wavelets and Wavelet Transforms: A Primer. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1998.
Daubechies, I., editor. Ten Lectures on Wavelets. Montepelier, VT: Capital City Press, 1992.
Duda, R., P. Hart, and D. Stork. Pattern Classification. New York, NY: Wiley, 2001.
Feichtinger, M., H. Eder, A. Holl, E. Korner, G. Zmugg, R. Aigner, F. Fazekas, and E. Ott. Automatic and remote controlled ictal spect injection for seizure focus localization by use of a commercial contrast agent application pump. Epilepsia 48(7):1409–1413, 2007.
Firpi, H., E. Goodman, and J. Echauz. On prediction of epileptic seizures by means of genetic programming artificial features. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 34(3):515–529, 2006.
Firpi, H., E. Goodman, and J. Echauz. Epileptic seizure detection using genetically programmed artificial features. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 54(2):212–224, 2007.
Gabor, A. Seizure detection using a self-organizing neural network: validation and comparison with other detection strategies. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 107:27–32, 1998.
Ghosh-Dastidar, S., H. Adeli, and N. Dadmehr. Mixed-band wavelet-chaos-neural network methodology for epilepsy and epileptic seizure detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 54(9):1545–1551, 2007.
Ghosh-Dastidar, S., H. Adeli, and N. Dadmehr. Principal component analysis-enhanced cosine radial basis function neural network for robust epilepsy and seizure detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 55(2):512–518, 2008.
Gotman, J. Automatic recognition of epileptic seizures in the EEG. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 54:530–540, 1982.
Gotman, J. Automatic seizure detection: improvements and evaluation. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 76:317–324, 1990.
Gotman, J., and P. Gloor. Automatic recognition and quantification of interictal epileptic activity in the human scalp EEG. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 49:513–529, 1976.
Gotman, J., J. Ives, and P. Gloor. Frequency content of EEG and EMG at seizure onset: possibility of removal of EMG artifact by digital filtering. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 52(2):626–639, 1981.
Greene, B., S. Faula, W. Marnanea, G. Lightbodya, I. Korotchikova, and G. Boylan. A comparison of quantitative EEG features for neonatal seizure detection. Clin. Neurophysiol. 119:1248–1261, 2008.
Grewal, S., and J. Gotman. An automatic warning system for epileptic seizures recorded on intracerebral EEGs. Clin. Neurophysiol. 116:2460–2472, 2005.
Guye, M., J. Regis, F. Tamura, M. Wendling, A. Gonigal, P. Chauvel, and F. Bartolomei. The role of corticothalamic coupling in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 129:1917–1928, 2006.
Haas, S., M. Frei, and I. Osorio. Strategies for adapting automated seizure detection algorithms. Med. Eng. Phys. 29:895–909, 2007.
Haut, S., S. Shinnar, and S. Moshé. Seizure clustering: risks and outcomes. Epilepsia 41(1):146–149, 2005.
Hilfiker, P., and M. Egli. Detection and evolution of rhythmic components in ictal EEG using short segment spectra and discriminant-analysis. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 82:255–265, 1992.
Iasemidis, L., D.-S. Shiau, P. Pardalos, W. Chaovalitwongse, K. Narayanan, A. Prasad, K. Tsakalis, P. Carney, and J. Sackellares. Long-term prospective on-line real-time seizure prediction. Clin. Neurophysiol. 116:532–544, 2005.
Khan, Y., and J. Gotman. Wavelet-based automatic seizure detection in intracerebral electroencephalogram. Clin. Neurophysiol. 114(5):898–908, 2003.
Kuhlmann, L., A. Burkitt, M. Cook, K. Fuller, D. Grayden, and I. Mareels. Correlation analysis of seizure detection features. In: 4th International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing, pp. 898–908, 2008.
Lai, A., T. Nelson, A. Halliday, D. Freestone, A. Burkitt, and M. Cook. Synchronisation in intracranial electrical activity recordings from rats with the tetanus toxin model of temporal lobe epilepsy. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Scientific Meeting of the Epilepsy Society of Australia, pp. 36, P57, 2007.
Le Van Quyen, M., J. Martinerie, M. Baulac, F. Varela. Anticipating epileptic seizures in real time by a non-linear analysis of similarity between eeg recordings. NeuroReport 10:2149–2155, 1999.
Lehnertz, K., and C. Elger. Can epileptic seizures be predicted? Evidence from nonlinear time series analysis of brain electrical activity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80:5019–5022, 1998.
Ocak, H. Automatic detection of epileptic seizures in eeg using discrete wavelet transform and approximate entropy. Expert Syst. Appl. 36:2027–2036, 2009.
Osorio, I., M. Frei, J. Giftakis, T. Peters, J. Ingram, M. Turnbull, M. Herzog, M. Rise, S. Schaffner, R. Wennberg, T. Walczak, M. Risinger, and C. Ajmone-Marsan. Performance reassessment of a real-time seizure-detection algorithm for long ECoG series. Epilepsia 43(12):1522–1535, 2002.
Osorio, I., M. Frei, and S. Wilkinson. Real-time automated detection and quantitative analysis of seizures and short-term prediction of clinical onset. Epilepsia 39(6):615–627, 1998.
Päivinen, N., S. Lammi, A. Pitkänen, J. Nissinen, M. Penttonen, and T. Grönfors. Epileptic seizure detection: a nonlinear viewpoint. Comp. Meth. Prog. Biomed. 79:151–159, 2005.
Pauri, F., F. Pierelli, G. Chartrian, and W. Erdly. Long-term EEG-video-audio monitoring: computer detection of focal EEG seizure patterns. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 82:1–9, 1992.
Proakis, J., and D. Manolakis. Digital Signal Processing: Principles, Algorithms and Applications, 3rd edn. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1996.
Qu, H., and J. Gotman. A seizure warning system for long-term epilepsy monitoring. Neurology 45(12):2250–2254, 1995.
Rabiner, L., and B. Gold. Theory and Application of Digital Signal Processing. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1975.
Rangayyan, R. Biomedical Signal Analysis: A Case-Study Approach. IEEE Press Series on Biomedical Engineering. New York, NY: Wiley, 2002.
Rosso, O., M. Martin, and A. Plastino. Brain electrical activity analysis using wavelet-based informational tools. Physica A 313(3–4):587–608, 2002.
Saab, M., and J. Gotman. A system to detect the onset of epileptic seizures in scalp EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 116:427–442, 2005.
Schindler, K., H. Leung, C. Elger, and K. Lehnertz. Assessing seizure dynamics by analysing the correlation structure of multichannel intracranial EEG. Brain 130:65–77, 2007.
Schuyler, R., A. White, K. Staley, and J. Krzysztof. Epileptic seizure detection: identification of ictal and pre-ictal states using rbf networks with wavelet-decomposed eeg data. IEEE EMBS Mag. March/April:74–81, 2007.
Shoeb, A., H. Edwards, J. Connolly, B. Bourgeois, S. Treves, and J. Guttag. Patient-specific seizure onset detection. Epil. Beh. 5:483–498, 2004.
Srinivasan, V., C. Eswaran, and N. Sriraam. Approximate entropy-based epileptic eeg detection using artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 11(3):288–295, 2007.
Tezel, G., and Y. Özbay. A new approach for epileptic seizure detection using adaptive neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 36:172–180, 2009.
Varsavsky, A., and I. Mareels. Patient un-specific detection of epileptic seizures through changes in variance. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2006. EMBS ’06. 28th Annual International Conference of the IEEE, pp. 3747–3750, 2006.
Wilson, S. Algorithm architectures for patient dependent seizure detection. Clin. Neurophysiol. 117(6):1204–1216, 2006.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an Australian Research Council Linkage Project Grant (LP0560684), The Bionic Ear Institute and St. Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne. We are grateful for the EEG data provided by the patients, and to the St. Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne Neurophysiology Clinic for collecting the data. EEG data collection was approved by the St. Vincent’s Hospital Melbourne Ethics Committee. We also thank Michael Eager for helping to format the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhlmann, L., Burkitt, A.N., Cook, M.J. et al. Seizure Detection Using Seizure Probability Estimation: Comparison of Features Used to Detect Seizures. Ann Biomed Eng 37, 2129–2145 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-009-9755-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-009-9755-5