Abstract
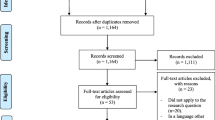
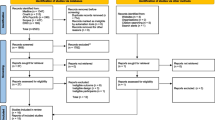
Despite the increasing awareness of the relevance of empathy in patient care, some findings suggest that medical schools may be contributing to the deterioration of students’ empathy. Therefore, it is important to clarify the magnitude and direction of changes in empathy during medical school. We employed a scoping review to elucidate trends in students’ empathy changes/differences throughout medical school and examine potential bias associated with research design. The literature published in English, Spanish, Portuguese and French from 2009 to 2016 was searched. Two-hundred and nine potentially relevant citations were identified. Twenty articles met the inclusion criteria. Effect sizes of empathy scores variations were calculated to assess the practical significance of results. Our results demonstrate that scoped studies differed considerably in their design, measures used, sample sizes and results. Most studies (12 out of 20 studies) reported either positive or non-statistically significant changes/differences in empathy regardless of the measure used. The predominant trend in cross-sectional studies (ten out of 13 studies) was of significantly higher empathy scores in later years or of similar empathy scores across years, while most longitudinal studies presented either mixed-results or empathy declines. There was not a generalized international trend in changes in students’ empathy throughout medical school. Although statistically significant changes/differences were detected in 13 out of 20 studies, the calculated effect sizes were small in all but two studies, suggesting little practical significance. At the present moment, the literature does not offer clear conclusions relative to changes in student empathy throughout medical school.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arksey, H., & O’Malley, L. (2005). Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 8(1), 19–32. doi:10.1080/1364557032000119616.
Austin, E. J., Evans, P., Magnus, B., & O’Hanlon, K. (2007). A preliminary study of empathy, emotional intelligence and examination performance in MBChB students. Medical Education, 41(7), 684–689. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2923.2007.02795.x.
Bratek, A., Bulska, W., Bonk, M., Seweryn, M., & Krysta, K. (2015). Empathy among physicians, medical students and candidates. Psychiatria Danubina, 27(Suppl 1), S48–S52.
Chen, D., Lew, R., Hershman, W., & Orlander, J. (2007). A cross-sectional measurement of medical student empathy. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 22(10), 1434–1438. doi:10.1007/s11606-007-0298-x.
Chen, D. C. R., Kirshenbaum, D. S., Yan, J., Kirshenbaum, E., & Aseltine, R. H. (2012). Characterizing changes in student empathy throughout medical school. Medical Teacher, 34(4), 305–311. doi:10.3109/0142159X.2012.644600.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Colliver, J. A., Conlee, M. J., Verhulst, S. J., & Dorsey, J. K. (2010). Reports of the decline of empathy during medical education are greatly exaggerated: A reexamination of the research. Academic Medicine, 85(4), 588–593.
Costa, P., Alves, R., Neto, I., Marvão, P., Portela, M., & Costa, M. J. (2014). Associations between medical student empathy and personality: A multi-institutional study. PLoS One, 9(3), e89254. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089254.
Costa, P., Magalhães, E., & Costa, M. J. (2013). A latent growth model suggests that empathy of medical students does not decline over time. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 18(3), 509–522. doi:10.1007/s10459-012-9390-z.
Davis, M. H. (1983). Measuring individual differences in empathy: Evidence for a multidimensional approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44(1), 113–126. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.44.1.113.
Duarte, M. I., Branco, M. C., Raposo, M. L., & Rodrigues, P. J. (2015). Empathy in medical students as related to gender, year of medical school and specialty interest. South East Asian Journal of Medical Education, 9(1), 51.
Esquerda, M., Yuguero, O., Viñas, J., & Pifarré, J. (2016). La empatía médica, ¿nace o se hace? Evolución de la empatía en estudiantes de medicina. Atención Primaria, 48(1), 8–14. doi:10.1016/j.aprim.2014.12.012.
Handford, C., Lemon, J., Grimm, M. C., & Vollmer-Conna, U. (2013). Empathy as a function of clinical exposure-reading emotion in the eyes. PLoS One, 8(6), e65159. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065159.
Hegazi, I., & Wilson, I. (2013). Maintaining empathy in medical school: It is possible. Medical Teacher, 35(12), 1002–1008. doi:10.3109/0142159X.2013.802296.
Hojat, M., Gonnella, J. S., Mangione, S., Nasca, T. J., Veloski, J. J., Erdmann, J. B., et al. (2002). Empathy in medical students as related to academic performance, clinical competence and gender. Medical Education, 36(6), 522–527. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2923.2002.01234.x.
Hojat, M., Mangione, S., Nasca, T. J., Rattner, S., Erdmann, J. B., Gonnella, J. S., et al. (2004). An empirical study of decline in empathy in medical school. Medical Education, 38(9), 934–941. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.01911.x.
Hojat, M., Vergare, M. J., Maxwell, K., Brainard, G., Herrine, S. K., Isenberg, G. A., et al. (2009). The devil is in the third year: A longitudinal study of erosion of empathy in medical school. Academic Medicine, 84(9), 1182–1191.
Kataoka, H. U., Koide, N., Ochi, K., Hojat, M., & Gonnella, J. S. (2009). Measurement of empathy among Japanese medical students: Psychometrics and score differences by gender and level of medical education. Academic Medicine, 84(9), 1192–1197.
Kliszcz, J., Hebanowski, M., & Rembowski, J. (1998). Emotional and cognitive empathy in medical schools. Academic Medicine, 73, 541.
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., & O’Brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science, 5(1), 69. doi:10.1186/1748-5908-5-69.
Lim, B. T., Moriarty, H., Huthwaite, M., Gray, L., Pullon, S., & Gallagher, P. (2013). How well do medical students rate and communicate clinical empathy? Medical Teacher, 35(2), e946–e951. doi:10.3109/0142159X.2012.715783.
Loureiro, J., Gonçalves-Pereira, M., Trancas, B., Caldas-de-Almeida, J. M., & Castro-Caldas, A. (2011). Empathy in the doctor-patient relationship as viewed by first-year medical students: Data on validity and sensibility to change of the Jefferson measure in Portugal. Acta Médica Portuguesa, 24, 431–442.
Magalhães, E., Salgueira, A. P., Costa, P., & Costa, M. J. (2011). Empathy in senior year and first year medical students: A cross-sectional study. BMC Medical Education, 11(1), 52.
Mays, N., Roberts, E., & Popay, J. (2001). Synthesising research evidence. In N. Fulop, P. Allen, A. Clarke, & N. Black (Eds.), Studying the organisation and delivery of health services: research methods (pp. 188–220.). London, UK: Routledge.
Montilva, M., García, M., Torres, A., Puertas, M., & Zapata, E. (2015). Empatía según la escala de Jefferson en estudiantes de Medicina y Enfermería en Venezuela. Investigación en Educación Médica, 4(16), 223–228. doi:10.1016/j.riem.2015.04.006.
Newton, B. W., Barber, L., Clardy, J., Cleveland, E., & OʼSullivan, P. (2008). Is there hardening of the heart during medical school? Academic Medicine, 83(3), 244–249. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181637837.
Nunes, P., Williams, S., Sa, B., & Stevenson, K. (2011). A study of empathy decline in students from five health disciplines during their first year of training. International Journal of Medical Education, 2, 12–17. doi:10.5116/ijme.4d47.ddb0.
Pedersen, R. (2009). Empirical research on empathy in medicine—A critical review. Patient Education and Counseling, 76(3), 307–322. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2009.06.012.
Pham, M. T., Rajić, A., Greig, J. D., Sargeant, J. M., Papadopoulos, A., & McEwen, S. A. (2014). A scoping review of scoping reviews: Advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Research Synthesis Methods, 5(4), 371–385. doi:10.1002/jrsm.1123.
Quince, T. A., Parker, R. A., Wood, D. F., & Benson, J. A. (2011). Stability of empathy among undergraduate medical students: A longitudinal study at one UK medical school. BMC Medical Education, 11(1), 90.
Roff, S. (2015). Reconsidering the “decline” of medical student empathy as reported in studies using the Jefferson Scale of Physician Empathy-Student version (JSPE-S). Medical Teacher,. doi:10.3109/0142159X.2015.1009022.
Roh, M.-S., Hahm, B.-J., Lee, D. H., & Suh, D. H. (2010). Evaluation of empathy among Korean medical students: A cross-sectional study using the Korean version of the Jefferson scale of physician empathy. Teaching and Learning in Medicine, 22(3), 167–171. doi:10.1080/10401334.2010.488191.
Schwellnus, H., & Carnahan, H. (2014). Peer-coaching with health care professionals: What is the current status of the literature and what are the key components necessary in peer-coaching? A scoping review. Medical Teacher, 36(1), 38–46. doi:10.3109/0142159X.2013.836269.
Shariat, S. V., & Habibi, M. (2013). Empathy in Iranian medical students: Measurement model of the Jefferson scale of empathy. Medical Teacher, 35(1), e913–e918. doi:10.3109/0142159X.2012.714881.
Shashikumar, R., Chaudhary, R., Ryali, V. S. S. R., Bhat, P. S., Srivastava, K., Prakash, J., & Basannar, D. (2014). Cross sectional assessment of empathy among undergraduates from a medical college. Medical Journal Armed Forces India, 70(2), 179–185. doi:10.1016/j.mjafi.2014.02.005.
Silva, M. G., Arboleda Castillo, J., & Díaz Narváez, V. P. (2014). Orientación empática en estudiantes de Medicina en una universidad de República Dominicana. Educación Médica Superior, 28(1), 74–83.
Stansfield, R. B., Schwartz, A., O’Brien, C. L., Dekhtyar, M., Dunham, L., & Quirk, M. (2015). Development of a metacognitive effort construct of empathy during clinical training: A longitudinal study of the factor structure of the Jefferson scale of empathy. Advances in Health Sciences Education,. doi:10.1007/s10459-015-9605-1.
Thomazi, L., Moreira, F. G., & Marco, M. A. (2014). Avaliação da evolução da empatia em alunos do quarto ano da graduação em medicina da Unifesp em 2012. Revista Brasileira de Educação Médica, 38(1), 87–93.
Todres, M., Tsimtsiou, Z., Stephenson, A., & Jones, R. (2010). The emotional intelligence of medical students: An exploratory cross-sectional study. Medical Teacher, 32(1), e42–e48. doi:10.3109/01421590903199668.
Toto, R. L., Man, L., Blatt, B., Simmens, S. J., & Greenberg, L. (2015). Do empathy, perspective-taking, sense of power and personality differ across undergraduate education and are they inter-related? Advances in Health Sciences Education: Theory and Practice, 20(1), 23–31. doi:10.1007/s10459-014-9502-z.
Wen, D., Ma, X., Li, H., Liu, Z., Xian, B., & Liu, Y. (2013). Empathy in Chinese medical students: Psychometric characteristics and differences by gender and year of medical education. BMC Medical Education, 13(1), 130.
Youssef, F. F., Nunes, P., Sa, B., & Williams, S. (2014). An exploration of changes in cognitive and emotional empathy among medical students in the Caribbean. International Journal of Medical Education, 5, 185–192. doi:10.5116/ijme.5412.e641.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Thelma Quince and Mohammadreza Hojat for critically reviewing the text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira-Valente, A., Monteiro, J.S., Barbosa, R.M. et al. Clarifying changes in student empathy throughout medical school: a scoping review. Adv in Health Sci Educ 22, 1293–1313 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-016-9704-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-016-9704-7