Abstract
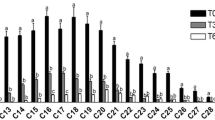
Viable microorganisms were found in Miocene lacustrine clays of the cypris formation excavated from 200-m below the surface as spoil during open-cast brown coal mining (Sokolov Brown Coal Basin, North-Western Bohemia, Czech Republic). Both saprotrophic microfungi of the genera Penicillium, Verticillium, Cladosporium and Aspergillus as well as heterotrophic bacteria were isolated from an intact sediment cores. Heterotrophic bacteria were classified by the MIS Sherlock System as representatives of genera Nocardiopsis, Arthrobacter, Micrococcus, Kocuria, Rothia, Clavibacter, Bacillus, Paenibacillus, Brevibacillus, Microbacterium, Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas. A bacterium found among the strains had an atypical fatty acids profile enriched by branched fatty acids and polyunsaturated fatty acid (18:3\(\omega\)6) and gave no MIS Sherlock match. Phospholipid fatty acids analysis indicates a relatively high (535 pmol g−1) but inhomogeneously distributed viable microbial biomass. Fatty acids analyses of non-fractioned lipids (representing viable, storage and dead biomass; 8390 pmol g−1) detected rich and homogenous profiles with fungal, bacterial and actinomycetal markers but no protozoan and algal fatty acids markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas R.M. 1993. In: Parkers L.C. (ed.), Handbook of Microbiological Media. CRC Press, London.
Balkwill D.L., Reeves R.H., Drake G.R., Reeves J.Y., Crocker F.H., King M.B. and Boone D.R. (1997). Phylogenetic characterization of bactetria in the subsurface microbial culture collection. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 20:201–216
Bloem J. (1995). Fluorescent staining of microbes for total counts. In: Akkermans A.D.L., Elsas J.D., Bruijn F.J. (eds), Molecular Microbial Ecology Manual. Kluwer Academic Press, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 1–12
Bloem J., Bolhuis P.R., Veninga M.R. and Wieringa J. (1995). Microscopic methods for counting bacteria and fungi in soil. In: Alef K., Nannipieri P. (eds), Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry. Academic Press, London, pp. 162–170
Brockman F.J. and Murray Ch.J. (1997). Subsurface microbiological heterogeneity: current knowledge, descriptive approaches and applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 20:231–247
Brockman F.J., Li S.W., Frederickson J.K., Ringelberg D.B., Kieft T.I., Spandoni C.M., White D.C. and McKinley J.P. (1998). Post-Sampling changes in microbial community composition and activity in a subsurface paleosol. Microbiol Ecol. 36:152–164
Chandler D.P., Brockman T.J., Bailey J.F. and Fredirckson J.K. (1998). Phylogenetic diversity of Archae and bacteria in deep subsurface paleosol. Microbiol. Ecol. 36:37–50
Chroňáková A., Elhottová D., Malý S. and Krištůfek V. (2004). Approaches applied in study of soil microbial diversity in brown coal post-mining chronosequences. Phytopedon 3:35–39
Colwell F.S., Onstott T.C., Delwiche M.E., Chandler D., Frederickson J.K., Yao Q.J., McKingley J.P., Boone D.R., Griffiths R., Phelps T.J., Ringelberg D., White D.C., LaFreniere, Balkwill D., Lehman R.M., Konisky J. and Long P.E. (1997). Microorganisms from deep, high temperature sandstones: constraints on microbial colonization. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 20:425–435
Crocker F.H., Frederickson J.K., White D.C., Ringelberg D.B. and Balkwill D.L. (2000). Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of Arthrobacter strains isolated from unconsolidated subsurface sediments. Microbiology 146:1295–1310
Frederickson J.K., McKinley J.P., Nierwicki-Bauer S.A., White D.C., Ringelberger D.B., Rawson S.A., Li S.A., Brockman F.J. and Bjornstad B.N. (1995). Microbial community structure and biochemistry of Miocene subsurface sediments: implications for long-term microbial survival. Mol. Ecol. 4:619–626
Greenblatt C.L., Davis A., Clement B.G., Kitts C.L., Cox, T. and Cano, R.J. (1999). Diversity of microorganisms isolated from amber. Microbiol. Ecol. 38:58–68
Kříbek B., Strnad M., Boháček Z., Sýkorová I., Čejka J. and Sobalik Z. (1998). Geochemistry of Miocene lacustrine sediments from the Sokolov Coal Basin (Czech Republic). Int. J. Coal Geol. 37:207–233
Nichols D.S. and McMeekin (2002). Biomarker techniques to screen for bacteria that produce polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Microbiol. Meth. 48:161–170
Nováková A. (2001). Soil microfungi in two post-mining chronosequences with different vegetation types. Restor. Ecol. 9:351–358
Oravecz O., Elhottová D., Krištůfek V., Šustr V., Frouz J., Tříska J. and Márialigeti K. (2004). Application of ARDRA and PLFA analysis in characterisation of the food, gut and excrement of saprophagous larvae of Penthetria holosericea (Diptera: Bibionidae): a pilot study. Folia Microbiol. 49:83–93
Parkes R.J., Cragg B.A., Bale S.J., Getliff J.M., Goodman K., Rochelle P.A., Fry J.C., Weightman A.J. and Harvey S.M. (1994). Deep bacterial biosphere in Pacific Ocean sediments. Nature 371:410–413
Pedersen K. (1997). Microbial life in deep granitic rock. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 20:399–414
Raghlukumar C., Raghlukumar S., Sheelu G., Gupta S.M, Nath B.N. and Rao B.R. (2004). Burried in time: culturable fungi in a deep-sea sediment core from the Chagos Trench, Indian Ocean. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 51:1759–1768
Ringelberg D.B., Sutton S. and White D.C. (1997). Biomass, bioactivity and biodiversity: microbial ecology of the deep subsurface: analysis of ester-linked phospholipids fatty acids. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 20:371–377
Russell N.J. and Nichols D.S. (1999). Polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine bacteria – a dogma rewritten. Microbiology 145:767–779
Yakimov M.M., Ventile G., Bruni V., Cappello S., D’Auria G., Golyshin P.N. and Giuliano L. (2004). Trude oil-indiced structural shift of coastal bacterial communities of rod bay (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea, Antarctica) and characterization of cultured cold-adapted hydrocarbvonoclastic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 49:419–432
Acknowledgements
This work was founded through projects 526/03/1259 from the Czech Science Foundation, S600660505 from Czech Academy of Sciences and AV 0Z 606 605 21 Research Plan of ISB AS CR. Authors thank to Mr. Patrick Hill for language revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elhottová, D., Krištůfek, V., Frouz, J. et al. Screening for microbial markers in Miocene sediment exposed during open-cast brown coal mining. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 89, 459–463 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-005-9044-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-005-9044-8