Abstract
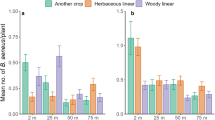
Halotydeus destructor and Penthaleus major are species of earth mite commonly found at high densities in agricultural fields in Australia and other parts of the world. These mites pose a risk to a range of winter crops and pastures when seedlings emerge in autumn. In order to predict likely mite pressure, we investigated whether autumn densities in pastures can be determined from agronomic and environmental field variables. For H. destructor, field densities showed little association with a range of vegetation variables but could largely be explained using the variable field type, with high densities present when fields had mixtures of grass, clover and weeds. For P. major, we found a regional effect. In the region where most data were available, P. major field densities were associated with grass abundance, whereas an association with field type was significant but different to that found for H. destructor. For both species, densities were not associated with rainfall, but there was a weak association with soil moisture capacity. We discuss how these results can help in managing these important pest mites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annells A, Ridsdill-Smith T (1994) Host plant species and carbohydrate supplements affecting rate of multiplication of redlegged earth mite. Exp Appl Acarol 18:521–530
Arthur AL, McColl SA, Umina PA (2013) Synthetic pesticides show little efficacy against Balaustium medicagoense (Prostigmata: Erythraeidae) in the field compared with other pest mites. Aust J Entomol 52:259–267
Arthur AL, Hoffmann AA, Umina PA (2014) Estimating densities of the pest Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae) in canola. J Econ Entomol 107:2204–2212
Arthur AL, Hoffmann AA, Umina PA (2015) Challenges in devising economic spray thresholds for a major pest of Australian canola, the redlegged earth mite (Halotydeus destructor). Pest Manag Sci 71:1462–1470
ASRIS (2011) Australian soil resource information system. http://www.asris.csiro.au. Accessed 10 Aug 2017
Cheng X, Hoffmann AA, Maino JL, Umina PA (2018a) A cryptic diapause strategy in Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) (Trombidiformes: Penthaleidae) induced by multiple cues: Unraveling summer diapause in redlegged earth mites. Pest Manag Sci 74:2618–2625
Cheng X, Umina PA, Hoffmann AA, Reisig D (2018b) Influence of previous host plants on the reproductive success of a polyphagous mite pest, Halotydeus destructor (Trombidiformes: Penthaleidae). J Econ Entomol 111:1–9
Doxon ED, Davis CA, Fuhlendorf SD (2011) Comparison of two methods for sampling invertebrates: vacuum and sweep-net sampling. J Field Ornithol 82:60–67
Gaull K, Ridsdill-Smith T (1996) The foraging behaviour of redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor (Acarina: Penthaleidae), in an annual subterranean clover pasture. Bull Entomol Res 86:247–252
Gower JM, Hoffmann AA, Weeks AR (2008) Effectiveness of spring spraying targeting diapause egg production for controlling redlegged earth mites and other pests in pasture. Anim Prod Sci 48:1118–1125
Grimm M, Hyder M, Doyle P, Michael P (1995) The effect of pasture feed on offer in spring on pest populations and pasture production. Proc Aust Soc Anim Prod 20:233–236
Halliday R (2005) Predatory mites from crops and pastures in South Africa: potential natural enemies of redlegged earth mite Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae). Zootaxa 1079:11–64
Hill MP, Hoffmann AA, McColl SA, Umina PA (2012a) Distribution of cryptic blue oat mite species in Australia: current and future climate conditions. Agric For Entomol 14:127–137
Hill MP, Hoffmann AA, Macfadyen S, Umina PA, Elith J (2012b) Understanding niche shifts: using current and historical data to model the invasive redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor: investigating niche shifts in an invasive mite. Divers Distrib 18:191–203
Hill MP, Chown SL, Hoffmann AA (2013) A predicted niche shift corresponds with increased thermal resistance in an invasive mite, Halotydeus destructor. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 22:942–951
Hill MP, Hoffmann AA, Umina PA, Cheng X, Miller AD (2016) Genetic analysis along an invasion pathway reveals endemic cryptic taxa, but a single species with little population structure in the introduced range. Divers Distrib 22:57–72
James DG, O’Malley KJ (1991) Oversummering of eggs of Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) (Acari: Penthaleidae): Diapause termination and mortality. Aust Entomol 1:35–41
James D, McDonald G, Hoffmann AA (1995) Biological control of earth mites in pasture using endemic natural enemies. Plant Prot Q 10:58–59
Maclennan KE, McDonald G, Ward SA (1998) Soil microflora as hosts of redlegged earth mite (Halotydeus destructor). Entomol Exp Appl 86:319–323
Maino JL, Binns M, Umina P (2018a) No longer a west-side story—pesticide resistance discovered in the eastern range of a major Australian crop pest, Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae). Crop Pasture Sci 69:216–221
Maino JL, Umina PA, Hoffmann AA (2018b) Climate contributes to the evolution of pesticide resistance. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 27:223–232
McDonald G, Umina PA, Macfadyen S, Mangano P, Hoffmann AA (2015) Predicting the timing of first generation egg hatch for the pest redlegged earth mite Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae). Exp Appl Acarol 65:259–276
Michael P (1995) Biological control of redlegged earth mite and lucerne flea by the predators Anystis wallacei and Neomulgus capillatus. Plant Prot Q 10:55–57
Michael PJ, Dutch ME, Pekin CJ (1991) A review of the predators of redlegged earth mite, blue oat mite and lucerne flea. Plant Prot Q 6:178–180
Micic S, Hoffmann AA, Strickland G, Weeks AR, Bellati J, Henry K, Nash MA, Umina PA (2008) Pests of germinating grain crops in southern Australia: an overview of their biology and management options. Aust J Exp Agric 48:1560–1573
Murray DAH, Clarke MB, Ronning DA (2013) Estimating invertebrate pest losses in six major Australian grain crops. Aust J Entomol 52:227–241
Nansen C, Gumley J, Groves L, Nansen M, Severtson D, Ridsdill-Smith TJ (2015) Development of ‘best practices’ for sampling of an important surface-dwelling soil mite in pastoral landscapes. Exp Appl Acarol 66:399–414
Paydar Z, Cresswell HP (1996) Water retention in Australian soils. 2.* Prediction using particle size, bulk density, and other properties. Soil Res 34:679–693
Qin T (1997) Population genetics of redlegged earth mites Halotydeus destructor and H. anthropus (Acarina: Penthaleidae) from Australia and or South Africa. Bull Entomol Res 87:289–298
R Core Team (2016) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 3 Nov 2016
Raupach MR, Briggs PR, Haverd V, King EA, Paget M, Trudinger CM (2012) Australian water availability project. CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research, Canberra
Ridsdill-Smith TJ (1997) Biology and control of Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) (Acarina: Penthaleidae): a review. Exp Appl Acarol 21:193–223
Ridsdill-Smith TJ, Annells AJ (1997) Seasonal occurrence and abundance of redlegged earth mite Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae) in annual pastures of southwestern Australia. Bull Entomol Res 87:413–423
Ridsdill-Smith T, Gaull K (1995) An improved method for rearing Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae) in the laboratory. Exp Appl Acarol 19:337–345
Ridsdill-Smith T, Pavri C (2000) Feeding life style of redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae), in pastures and the role of broad-leafed weeds. Exp Appl Acarol 24:397–414
Ridsdill-Smith J, Pavri C, De Boer E, Kriticos D (2005) Predictions of summer diapause in the redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae), in Australia. J Insect Physiol 51:717–726
Ridsdill-Smith TJ, Smith RH, Read J, Pavri CC (2013) Population ecology of Halotydeus destructor in pastures. Integr Control Plant Feed Mites IOBC-WPRS Bull 93:91–101
Robinson MT, Hoffmann AA (2000) Additional tests on the effects of pesticides on cryptic species of blue oat mite (Penthaleus spp.) and the redlegged earth mite (Halotydeus destructor). Aust J Exp Agric 40:671–678
Robinson MT, Hoffmann AA (2001) The pest status and distribution of three cryptic blue oat mite species (Penthaleus spp.) and redlegged earth mite (Halotydeus destructor) in southeastern Australia. Exp Appl Acarol 25:699–716
Robinson MT, Weeks AR, Hoffmann AA (2002) Geographic patterns of clonal diversity in the earth mite species Penthaleus major with particular emphasis on species margins. Evolution 56:1160–1167
Solomon M (1937a) Behaviour of the red-legged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor, in relation to environmental conditions. J Anim Ecol 6:340–361
Solomon M (1937b) Experiments on the effects of temperature and humidity on the survival of Halotydeus destructor (Tucker), Acarina family Penthaleidae. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 15:1–16
Swan D (1934) The red-legged earth mite Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) in South Australia: with remarks upon Penthaleus major (Dugès). J Dep Agric S Aust 38:353–367
Umina PA (2007) Pyrethroid resistance discovered in a major agricultural pest in southern Australia: the redlegged earth mite Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae). Pest Manag Sci 63:1185–1190
Umina P, Hoffmann A (1999) Tolerance of cryptic species of blue oat mites (Penthaleus spp.) and the redlegged earth mite (Halotydeus destructor) to pesticides. Anim Prod Sci 39:621–628
Umina PA, Hoffmann AA (2003) Diapause and implications for control of Penthaleus species and Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae) in southeastern Australia. Exp Appl Acarol 31:209–223
Umina PA, Hoffmann AA (2004) Plant host associations of Penthaleus species and Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Penthaleidae) and implications for integrated pest management. Exp Appl Acarol 33:1–20
Umina P, Hoffmann AA (2005) Competitive interactions among four pest species of earth mites (Acari:Penthaleidae). J Econ Entomol 98:307–316
Umina PA, Hoffmann AA, Weeks AR (2004) Biology, ecology and control of the Penthaleus species complex (Acari: Penthaleidae). Exp Appl Acarol 34:211–237
Umina PA, Arthur AL, McColl SA, Hoffmann AA, Roberts JMK (2010) Selective control of mite and collembolan pests of pastures and grain crops in Australia. Crop Prot 29:190–196
Umina PA, Weeks AR, Roberts J, Jenkins S, Mangano GP, Lord A, Micic S (2012) The current status of pesticide resistance in Australian populations of the redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor. Pest Manag Sci 68:889–896
Umina PA, Lord A, Micic S, Edwards O (2017) Discovery and characterisation of field resistance to organophosphorus chemicals in a major mite pest, Halotydeus destructor. Pest Manag Sci 73:1719–1724
Wallace MMH (1970) The influence of temperature on the post-diapausal development and survival in the aestivating eggs of Halotydeus destructor (Acari: Eupodidae). Aust J Zool 18:315–329
Wallace MMH, Mahon JA (1971) The distribution of Halotydeus destructor and Penthaleus major (Acari:Eupodidae) in Australia in relation to climate and land use. Aust J Zool 19:65–76
Weeks AR, Hoffmann AA (1999) The biology of Penthaleus species in southeastern Australia. Entomol Exp Appl 92:179–189
Weeks AR, Hoffmann AA (2000) Competitive interactions between two pest species of earth mites, Halotydeus destructor and Penthaleus major (Acarina: Penthaleidae). J Econ Entomol 93:1183–1191
Weeks A, Fripp Y, Hoffmann A (1995) Genetic structure of Halotydeus destructor and Penthaleus major populations in Victoria (Acari: Penthaleidae). Exp Appl Acarol 19:633–646
Weeks AR, Turelli M, Hoffmann AA (2000) Dispersal patterns of pest earth mites (Acari: Penthaleidae) in pastures and crops. J Econ Entomol 93:1415–1423
Weiss MJ, McDonald G (1998) European earwig, Forficula auricularia L. (Dermaptera: Forficulidae), as a predator of the redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) (Acarina: Penthaleidae). Aust J Entomol 37:183–185
Wickham H (2016) ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-018-0331-2
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by funding from the Grains Research Development Corporation and the Commonwealth Scientific Industrial Research Organisation, and would not have been possible without the time and assistance from numerous agronomists and farmers. We also thank Garry McDonald for preliminary work and Xuan Cheng for technical advice. Thanks to the anonymous reviewers whose comments on this manuscript were very valuable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douglas, J., Umina, P., Macfadyen, S. et al. Field associations of first generation densities of the pest mites Halotydeus destructor and Penthaleus major in pasture. Exp Appl Acarol 76, 487–506 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-018-0331-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-018-0331-2