Abstract
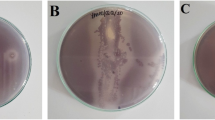
Actinomycetes from marine habitats are relatively unexplored. They are reported as potential sources of novel bacterial species. In this current study, 16 strains of bacteria were isolated using Actinomycetes Isolation Agar medium. Two strains showed antibacterial activity against the shrimp pathogens, Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Among them, only 1 strain was found to have potent antibacterial properties. This strain was designated as Bacillus licheniformis VIT02. The crude bioactive compounds obtained from Bacillus licheniformis were extracted and identified using FTIR and GC–MS analyses. The data revealed that the phenolic bioactive compound, phenol,2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl), and ester compound, propanoic acid, 2-Hydroxy-, Ethyl Ester, (S) have antimicrobial properties, and hence, can be used as potent antimicrobial drugs after performing further studies. The in vivo pathogenicity in Macrobrachium rosenbergii was investigated against A. hydrophila for 120 h. After 120 h of exposure, 34% of mortality was observed at the highest concentration of 106 A. hydrophila. The in vivo treatment using the bioactive compound from the isolated strain B. licheniformis was performed against A. hydrophila in M. rosenbergii. The shrimp challenged with A. hydrophila when treated with 25 µL of bioactive compounds extracted from B. licheniformis showed 90% of survival up to 15 days of exposure. A survey of literature revealed that this could be the first study reporting the treatment of A. hydrophila infection in M. rosenbergii using the bioactive compounds from marine Actinomycete, Bacillus licheniformis VIT02. The histopathological analysis revealed that there was difference between the infected and the treated groups when compared with the control. The results indicated that the crude bioactive compound revealed potent disease resistance capacity against A. hydrophila in M. rosenbergii.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdolnabi S, Salwany MYI, Daud HM, Mariana SD, Abdelhadi YM (2015). Pathogenicity of Aermonas hydrophila in giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii, cultured in East Malaysia. Iran J Fish Sci. 14(1): 232–245. http://dorl.net/dor/20.1001.1.15622916.2015.14.1.18.5
Al-rubaye TS, Risan MH, Al-Rubaye D (2020) Gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy analysis of bioactive compounds from Streptomyces spp isolated from Tigris river sediments in Baghdad city. J Biotech Res Cent 14(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.24126/jobrc.2020.14.1.590
Azhar N, Yudiati E, Subagiyo, Alghazeer R (2021) Producing active secondary metabolite against pathogenic Vibrio spp. by actinobacteria-sodium alginate co-culture. Ilmu Kelaut Indones J Mar Sci 26:254–264. https://doi.org/10.14710/ik.ijms.26.4.254-264
Balachandran C, Duraipandiyan V, Balakrishna K, Ignacimuthu S (2012) Petroleum and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) degradation and naphthalene metabolism in Streptomyces sp. (ERI-CPDA-1) isolated from oil contaminated soil. Bioresour Technol 112:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.059
Barakat KM, Beltagy EA (2015) Bioactive phthalate from marine streptomyces Ruber EKH2 against virulent fish pathogens. Egypt J Aquat Res 41:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2015.03.006
Barka EA, Vatsa P, Sanchez L, Gaveau-Vaillant N, Jacquard C et al (2016) Taxonomy, physiology, and natural products of actinobacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 80(1):1–43. https://doi.org/10.1128/2FMMBR.00019-15
Chaudhary HS, Yadav J, Shrivastava AR, Singh S, Singh AK, Gopalan N (2013) Antibacterial activity of Actinomycetes isolated from different soil samples of Sheopur (A city of central India). J Adv Pharm Tech Res 4(2):1–6. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-4040.111528
Cheesbrough M (2010) Adaptive or specific immune response, district laboratory in tropical countries. Cambridge University Press, Cape Town, South Africa, p 11
Daigham GE, Mahfouz AY (2020) Isolation, characterization, and screening of actinomycetes producing bioactive compounds from Egyptian soil. Egypt Pharmaceut J 19(4):381–390. https://doi.org/10.4103/epj.epj_44_20
Devi DP, Hareesh K, Reddy MS (2015) Enhancement of growth potentials in freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii through supplementation of probiotic diets of Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 3(2):124–131
Dholakiya RN, Kumar R, Mishra A, Mody KH, Jha B (2017) Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of novel actinobacteria strain isolated from gulf of Khambhat. Gujarat Front Microbiol 8:2420. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02420
Duke JUS (1992). Dr. Duke’s Phytochem. Ethanobotanical databases; Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA
El Karkouri A, Assou SA, El Hassouni M (2019) Isolation and screening of actinomycetes producing antimicrobial substances from an extreme Moroccan biotope. Pan Afr Med J 33:1–9. https://doi.org/10.11604/2Fpamj.2019.33.329.19018
Elliah P, Ramana T, Bapi Raju KVVS, Sujatha P, Uma Sankar AM (2004) Investigation on marine actinomycetes from Bay of Bengal near Karnataka coast of Andra Pradesh. Asian J Microbiol Biotechnol Environ Sci 6(1):53–56
Gebreyohannes G, Moges F, Sahile S, Raja N (2013) Isolation and characterization of potential antibiotic producing actinomycetes from water and sediments of Lake Tana. Ethiopia Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 3(6):426–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2221-1691(13)60092-1
Gopinath BV, Vootla PK, Jyothi R, Reddy SK (2013a) Antimicrobial activity of actinomycetes isolated from coal mine soils of Godavari Belt Region, A.P. India Asia J Exp Biol Sci 4:518–523
Gopinath BV, Vootla PK, Jyothi R, Reddy SK (2013) Antimicrobial activity of Actinomycetes isolated from coal mine soils of Godavari Belt Region AP India Asia. J Exp Biol Sci 4(4):518–523
Hindu SV, Thanigaivel S, Vijayakumar S, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A, Thomas J (2018) Effect of microencapsulated probiotic Bacillus vireti 01-polysaccharide extract of Gracilaria folifera with alginate-chitosan on immunity, antioxidant activity and disease resistance of Macrobrachium rosenbergii against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 73:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.12.007
Ibnouf EO, Aldawsari MF, Waggiallah HA (2022) Isolation and extraction of some compounds that act as antimicrobials from actinomycetes. Saudi J Biol Sci 29(8):103352. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.sjbs.2022.103352
Imada C, Masuda S, Kobayashi T, Hamada-Sato N, Nakashima T (2010) Isolation and characterization of marine and terrestrial Actinomycetes using a medium supplemented with NaCl. Actinomycetologica 24(1):12–17. https://doi.org/10.3209/saj.SAJ240104
Kumar PS, Duraipandiyan V, Ignacimuthu S (2014) Isolation, screening and partial purification of antimicrobial antibiotics from soil Streptomyces sp SCA7. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 30(9):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kjms.2014.05.006
Kumar V, Bisht GS, Gusain O (2013) Terrestrial actinomycetes from diverse locations of Uttarakhand, India: Isolation and screening for their antibacterial activity. Iran J Microbiol 5(3): 299–308. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3895571/
Majhi R (2019). Screening of antibiotic producing Actinomycetes for antibiosis from soil of Sunsari, Nepal. Dissertation, Tribhuvan University, Dharan, Nepal.
Malviya MK, Pandey A, Sharma A, Tiwari SC (2013) Characterization and identifification of actinomycetes isolated from “fifired Plots” under shifting cultivation in Northeast Himalaya. India Ann Microbiol 63:561–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0504-x
Manimaran M, Rajkumar T, Vimal S, Taju G, Majeed SA et al (2018) Antiviral activity of 9(10H)- acridanone extracted from marine streptomyces Fradiae Strain VITMK2 in Litopenaeus vannamei infected with white spot syndrome virus. Aquaculture 488:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.01.032
Mondal H, Thomas J (2022) Isolation and characterization of a novel Actinomycete isolated from marine sediments and its antibacterial activity against fish pathogens. Antibiotics 11:1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111546
Mondal H, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A, Thomas J (2021) Viral infections in cultured fish and shrimps: current status and treatment methods. Aquac Int 30:227–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-021-00795-2
Muiru WM, Mutitu EW, Mukunya DM (2008) Identification of selected Actinomycetes isolates and characterization of their antibiotic metabolites. J Biol Sci 8(6):1021–1026. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2008.1021.1026
Newman SG (2007). Antibiotics in aquaculture. Is responsible use possible? Available online: https://www.globalseafood.org/advocate/antibiotics-in-aquaculture-is-responsible-use-possible/. Accessed 28 Sept 2022
Nonomura H (1974) Key for classification and identification of 458 species of the Streptomycetes included in ISP. J Ferment Technol (formerly Known) 52:78–92
Oskay M (2009) Antifungal and antibacterial compounds from Streptomyces strains. African J Biotechnol 8(13):3007–3017
Pepper IL, Garba CP (2004) Environmental microbiology, 2nd edn. Elsevier Acadamic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 37–49
Rajaram SK, Ahmad P, Keerthana SSS, Cressida PJ, Moorthy IG et al (2020) Extraction and purification of an antimicrobial bioactive element from lichen associated Streptomyces olivaceus LEP7 against wound inhabiting microbial pathogens. JKSUS 32(3):2009–2015
Rajkumar T, Manimaran M, Taju G, Vimal S, Majeed SA et al. (2018) Antiviral viral compound from Streptomyces ghanaensis like strain against white spot 2 syndrome virus (WSSV) of shrimp. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/340265
Ramalingam V, Rajaram R (2016) Antioxidant activity of 1-hydroxy-1-norresistomycin derived from Streptomyces variabilis KP149559 and evaluation of its toxicity against zebra fish Danio rerio. RSC Adv 6:16615–16623. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA22558B
Rasool U, Hemalatha S (2017) Diversified role and applications of marine actinomycetes in the field of biology. World Sci News 74:1–14
Ravi L, Kannabiran K (2018) Extraction and identification of Gancidin W from marine Streptomyces sp. VITLGK012. Indian J Pharm Sci 80(6):1093–1099. https://doi.org/10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000460
Saadoun I, Hameed KM, Moussauui A (1999) Characterization and analysis of antibiotic activity of some aquatic actinomycetes. Microbios 99(394):173–179
Sanglier JJ, Haag H, Huck TA, Fehr T (1996) Review of actinomycetes compounds: 1990e1995. Expert Opin Invest Drugs 5:207–223
Sapkota A, Thapa A, Budhathoki A, Sainju M, Shrestha P et al (2020) Isolation, characterization, and screening of antimicrobial-producing actinomycetes from soil samples. Int J Microbiol 2020:2716584. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2716584
Selvameenal L, Radhakrishnan M, Balagurunathan R (2009) Antibiotic pigment from desert soil Actinomycetes; biological activity, purification and chemical screening. Indian J Pharm Sci 71(5):499–504. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474x.58174
Selvan GP, Ravikumar S, Ramu A, Neelakandan P (2012) Antagonistic activity of marine sponge associated Streptomyces sp. against isolated fish pathogens. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 2:S724–S728. https://doi.org/10.1016/2FS2222-1808(12)60252-7
Setyati WA, Pringgenies D, Soenardjo N, Pramesti R (2021) Actinomycetes of secondary metabolite producers from mangrove sediments Central Java Indonesia. Vet World. 14(10):2620–2624. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2021.2620-2624
Singh V, Haque S, Singh H, Verma J, Vibha K et al (2016) Isolation, screening, and identification of novel isolates of Actinomycetes from India for antimicrobial applications. Front Microbiol 7:1921. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01921
Somasundaram S, Nagarajan S, Ayyachamy VK, Babu N (2020). Screening of bioactive compounds from marine Actinomycetes. Int J Sci Pharma Res. Conference: National Conference on Unearth the new frontiers in life sciences (NCUFS’19). At Coimbatore, India
Talbot GH, Bradley J, Edwards JE, Gilbert D, Scheld M et al (2006) Bad bugs need drugs: an update of the development pipeline from the antimicrobial task force of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 42(5):657–668. https://doi.org/10.1086/499819
Tankeshwar A (2022) Sulphide indole motility (SIM) medium: principle, procedure, and results. In: Biochemical tests. Microbe online. https://microbeonline.com/sulfide-indole-motility-sim-medium/
Thanigaivel S, Vijayakumar S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N, Thomas J (2014) Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of Chaetomorpha antennina against shrimp pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture 433:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.07.003
Thirumurugan D, Vijayakumar R (2013) A potent fish pathogenic bacterial killer Streptomyces sp isolated from the soils of East Coast Region. South India. J Coast Life Med 1(3):175–180. https://doi.org/10.12980/JCLM.1.2013C1086
Trenozhnikova L, Azizan A (2018) Discovery of actinomycetes from extreme environments with potential to produce novel antibiotics. Cent Asian J Glob Health 7(1):337. https://doi.org/10.5195/cajgh.2018.337
Undabarrena A, Beltrametti F, Claverías FP, González M, Moore ERB et al (2016) Exploring the diversity and antimicrobial potential of marine Actinobacteria from the Comau Fjord in Northern Patagonia. Chile Front Microbiol 7:1135. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01135
Valanarasu M, Duraipandiyan V, Agastian P, Ignacimuthu S (2009) In vitro antimicrobial activity of Streptomyces spp ERI-3 isolated from Western Ghats rock soil (India). J de Mycologie Me’dicale 19(1):22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2008.12.002
Valli S, Suvathi SS, Aysha OS, Nirmala P, Vinoth KP et al (2012) Antimicrobial potential of Actinomycetes species isolated from marine environment. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(6):469–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60078-1
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to VIT Vellore for providing the required facilities to carry out this work.
Funding
We hereby declare that there was no funding for this research work
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Formal analysis, methodology, validation, and writing the original draft were performed by Haimanti Mondal. Conceptualization, investigation, supervision, and validation of the manuscript were done by John Thomas. Review was performed by Natarajan Chandrasekaran and editing of the manuscript was done by Amitava Mukherjee. All authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling editor: Raja Sudhakaran
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, H., Chandrasekaran, N., Mukherjee, A. et al. Antibacterial activity of Bacillus licheniformis isolated from marine sediments and its effect in treating Aeromonas hydrophila infection in freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquacult Int 31, 3071–3093 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-023-01121-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-023-01121-8