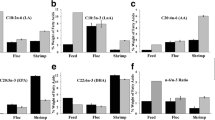
Abstract
Feeding strategies have a significant impact on growth and water quality in shrimp farming. Feed management also affects shrimp health, survival, and yields. All these factors contribute to production cost-effectiveness and the commercial shrimp industry sustainability. The effect of feeding frequency and two aquafeed cooking processes (extrusion and pelleting) on shrimp performance and water quality parameters was studied under controlled conditions in a 60-day trial with juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei fed once (10:00 h); twice (10:00 h, 12:00 h); four (10:00 h, 12:00 h, 15:00 h, 18:00 h) and six (10:00 h, 12:00 h, 15:00 h, 18:00 h, 21:00 h, 24:00 h) times/day frequencies. No statistical differences (p > 0.05) in growth rate, survival or feed efficiency were observed within pelleted feed treatments at any of the frequencies tested. Growth rate was significantly higher (p < 0.05) with extruded feed when administered once or twice in daylight (10:00–12:00 h). However, at such frequencies, growth was achieved at the cost of water quality and feed conversion ratio. At higher frequencies (six times a day) with extruded diets, the results in water quality suggest a reduction in total ammonia nitrogen and nitrite-nitrogen levels as frequency increased. The outcomes suggest that extruded feed with daylight feeding has the potential to improve growth rate, and an increased frequency could represent a suitable strategy to preserve water quality. The present research is the first to show that the extrusion process improves water quality; thus, extruded feeds could reduce effluent pollution impact and improve shrimp farming sustainability.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aalimahmoudi M, Reyshahri A, Bavarsad SS, Maniat M (2016) Effects of feeding frequency on growth, feed conversion ratio, survival rate and water quality of white leg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei, Boone, 1931). Int J Fish Aquat Stud 4(3):293–297
Aguiñaga-Cruz JA, Sainz-Hernández JC, García-Rodríguez LD, García-Ulloa M, García-Gutiérrez C, Montoya-Mejía M (2019) Trypsin polymorphism and modulation in Penaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931): a review. Latin Am J Aquat Res 47(5):723–732. https://doi.org/10.3856/vol47-issue5-fulltext-1
Amirkolaie AK, Verreth JAJ, Schrama JW (2006) Effect of gelatinization degree and inclusion level of dietary starch on the characteristics of digesta and faeces in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus (L)). Aquaculture 260(1–4):194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.06.039
An W, He H, Dong X, Tan B, Yang Q, Chi S, Zhang S, Liu H, Yang Y (2020) Regulation of growth, fatty acid profiles, hematological characteristics and hepatopancreatic histology by different dietary n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids levels in the first stages of juvenile Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac Rep 17:100321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100321
Arnold S, Smullen R, Briggs M, West M, Glencross B (2016) The combined effect of feed frequency and ration size of diets with and without microbial biomass on the growth and feed conversion of juvenile Penaeus monodon. Aquac Nutr 22(6):1340–1347. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12338
Bardera G, Usman N, Owen M, Pountney D, Sloman KA, Alexander ME (2019) The importance of behaviour in improving the production of shrimp in aquaculture. Rev Aquac 11(4):1104–1132. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12282
Basto-Silva C, Serra CR, Castro C, Nóvoa GS, Oliva-Tales A, Capilla E, Guerreiro I (2022) Effects of Feeding Frequency and Dietary Protein/Carbohydrate Ratios on Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Intestinal Functionality and Health. Aquac Nutr 2022:8435786. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8435786
Booth MA, Allan GL, Evans AJ, Gleeson VP (2002) Effects of steam pelleting or extrusion on digestibility and performance of silver perch Bidyanus bidyanus Aquac Res 33(14):1163–1173. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2109.2002.00773.x
Bortone BE (2017) Performance of aquafeed ingredients in extrusion cooking. Glob Aquac Advocate 1–6
Bortone BE (2018) Twin screw technology for better extruded feeds. Glob Aquac Advocate 7–13
Boyd BCE (2021) A low feed conversion ratio is the primary indicator of efficient aquaculture. Glob Aquac Advocate 1–5
Bray WA, Lawrence AL, Leung-Trujillo JR (1994) The effect of salinity on growth and survival of Penaeus vannamei, with observations on the interaction of IHHN virus and salinity. Aquaculture 122(2–3):133–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(94)90505-3
Casillas-Hernández R, Nolasco-Soria H, Lares-Villa F, García-Galano T, Carrillo-Farnes O, Vega-Villasante F (2006) Ritmo circadiano de la actividad enzimática digestiva del camarón blanco Litopenaeus vannamei y su efecto en el horario de alimentación. Rev Latinoam Recur Naturales 2(2):55–64
Chamberlain GW (2004) Extruded shrimp feeds reemerge. Glob Aquac Advocate 8–12
Chen S, Shi C, Migaud H, Song C, Mu C (2022) Light spectrum impacts on growth, Molting, and oxidative stress response of the mud crab Scylla paramamosain Front Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.840353
Daniel N (2018) A review on replacing fish meal in aqua feeds using plant protein sources. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 6(2):164–179
DeMan JM, Finley JW, Hurst WJ, Lee CY (2018) Principles of food chemistry. Springer, Cham
FAO (2020) El estado mundial de la pesca y la acuacultura. Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura. https://www.fao.org/3/ca9231es/ca9231es.pdf Accessed 14 Sept 2021
FAO (2022) Extruded shrimp feeds improve performance, so why are they not more popular? Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura. https://www.fao.org/3/cb9078en/cb9078en.pdf Accessed 19 Apr 2022
Gao S, Jin J, Liu H, Han D, Zhu X, Yang Y, Xie S (2019) Effects of pelleted and extruded feed of different ingredients particle sizes on feed quality and growth performance of gibel carp (Carassius gibelio var. CAS V). Aquaculture 511:734236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734236
Gilannejad N, Rønnestad I, Lai F, Olderbakk-Jordal AE, Gottlieb Almeida AP, Martínez-Rodríguez G, Moyano FJ, Yúfera M (2021) Daily rhythms of intestinal cholecystokinin and pancreatic proteases activity in senegalese sole juveniles with diurnal and nocturnal feeding. Comp Biochem Physiol - Part A: Mol Integr Physiol 253:110868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.110868
Glencross B, Hawkins W, Evans D, Rutherford N, McCafferty P, Dods K, Hauler R (2011) A comparison of the effect of diet extrusion or screw-press pelleting on the digestibility of grain protein products when fed to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 312(1–4):154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.12.025
Hardy RW, Barrows FT (2002) Diet formulation and manufacture. In: RW, Hardy (eds) Fish Nutrition, 3rd edn. Academic, London, pp 505–600
Haws M, Boyd C (2001) Métodos para mejorar la camaronicultura en Centroamérica. Universidad Centroamericana, Managua, p 5
Hindley JPR (1975) Effects of endogenous and some exogenous factors on the activity of the juvenile banana prawn Penaeus merguiensis Mar Biol 29(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395521
Hoyos JL, Villada HS, Fernández A, Ortega-Toro R (2017) Physical quality of extruded aquafeeds. Effect of formulation and processing conditions. Información Tecnológica 28(5):101–114. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-07642017000500012
Jescovitch LN, Ullman C, Rhodes M, Davis DA (2018) Effects of different feed management treatments on water quality for Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Aquac Res 49(1):526–531. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13483
Kamarudin MS, de Cruz CR, Saad CR, Romano N, Ramezani-Fard E (2018) Effects of extruder die head temperature and pre-gelatinized taro and broken rice flour level on physical properties of floating fish pellets. Anim Feed Sci Technol 236:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.12.007
Kanmani N, Romano N, Ebrahimi M, Nurul Amin SM, Kamarudin MS, Karami A, Kumar V (2018) Improvement of feed pellet characteristics by dietary pre-gelatinized starch and their subsequent effects on growth and physiology in tilapia. Food Chem 239:1037–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.061
Kavalek M, Plachy V (2019) Feed Extrusion: A way to increase efficiency. All about feed. https://www.allaboutfeed.net/animal-feed/feed-processing/feed-extrusion-a-way-to-increase-efficiency/ Accessed 14 Sept 2021
Kawamura G, Uy Bagarinao T, Syallinaz Seniman N, Seok-Kian Yong A, Lim LS (2018) Comparative morphology and function of feeding appendages in food intake behaviour of the whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, and the giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Borneo J Mar Sci Aquac 2:26–39
Lin YC, Chen JC (2001) Acute toxicity of ammonia on Litopenaeus vannamei Boone juveniles at different salinity levels. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 259(1):109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0981(01)00227-1
Lin YC, Chen JC (2003) Acute toxicity of nitrite on Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) juveniles at different salinity levels. Aquaculture 224(1–4):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00220-5
Liu T, Zhang G, Feng Y, Kong C, Larbi C, Huang X, Hua X (2019) Dietary soybean antigen impairs growth and health through stress-induced non-specific immune responses in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:124–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.09.062
Merican Z (2020) Aquafeeds in 2019: pulled by market demand. Aquac Asia Pac Mag 16(3):1–7
Misra CK, Sahu NP, Jain KK (2002) Effect of extrusion processing and steam pelleting diets on pellet durability, water absorption and physical response of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 15(9):1354–1358. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2002.1354
Molina C, Cadena E, Orellana F (2000) Alimentación de camarones en relación a la actividad enzimática como una respuesta natural al ritmo circadiano y ciclo de muda. In: Cruz -Suárez, LE, Ricque-Marie, D, Tapia-Salazar, M, Olvera-Novoa, MA y Civera-Cerecedo. R (eds). Avances en Nutrición Acuícola V. Memorias del V Simposium Internacional de Nutrición Acuícola. Mérida, Yucatán, México. Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León. Monterrey, Nuevo León, México, pp 358–380
Molina-Poveda C, Espinoza-Ortega M (2019) La extrusión mejora las características nutricionales del alimento y contribuye a la preservación del medio acuícola. Aquacultura, 131 Guayaquil-Ecuador pp 77–81
Napaumpaiporn T, Churchid N, Taparhudee W (2013) Study on the efficiency of three different feeding techniques in the culture of Pacific White shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Kasetsart Univ Fish Res Bull 37(2):8–16
NRC (2011) Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. National Academy Press, Washington DC
Nunes AJP, Goddard S, Gesteira TCV (1996) Feeding activity patterns of the southern brown shrimp Penaeus subtilis under semi-intensive culture in NE Brazil. Aquaculture 144(4):371–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(96)01297-5
Nunes AJP, Sabry-Neto H, da Silva FHP, de Oliveira-Neto AR, Masagounder K (2018) Multiple feedings enhance the growth performance and feed efficiency of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei when fed a low-fish meal amino acid-supplemented diet. Aquacult Int 27(2):337–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-018-0330-7
Peixoto S, Soares R, Silva JF, Hamilton S, Morey A, Davis DA (2020a) Acoustic activity of Litopenaeus vannamei fed pelleted and extruded diets. Aquaculture 525:735307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735307
Peixoto S, Soares R, Allen Davis D (2020b) An acoustic based approach to evaluate the effect of different diet lengths on feeding behavior of Litopenaeus vannamei Aquac Eng 91:102114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2020.102114
Ponce-Palafox J, Martinez-Palacios CA, Ross LG (1997) The effects of salinity and temperature on the growth and survival rates of juvenile white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei, Boone, 1931. Aquaculture 157(1–2):107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(97)00148-8
Pontes CS, Arruda MDF (2005) Comportamento de Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) (Crustacea, Decapoda, Penaeidae) em função da oferta do alimento artificial nas fases clara e escura do período de 24 horas. Rev Brasileira Zoologia 22(3):648–652
Pontes CS, Arruda MDF, De Lara Menezes AA, De Lima PP (2006) Daily activity pattern of the marine shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone 1931) juveniles under laboratory conditions. Aquac Res 37(10):1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2006.01519.x
Pontes CS, De Lima PP, Arruda MF (2008) Feeding responses of juvenile shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) fed at different frequencies under laboratory conditions. Aquac Res 39(13):1416–1422. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02011.x
Reymond H, Lagardére JP (1990) Feeding rhythms and food of Penaeus japonicus bate (Crustacea, Penaeidae) in salt marsh ponds; role of halophilic entomofauna. Aquaculture 84:125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(90)90343-L
Robertson L, Wrence ALL, Castille FL (1993) Effect of feeding frequency and feeding time on growth of Penaeus vannamei (Boone). Aquac Res 24(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.1993.tb00823.x
Romano N, Kumar V (2019) Starch gelatinization on the physical characteristics of aquafeeds and subsequent implications to the productivity in farmed aquatic animals. Rev Aquac 11(4):1271–1284. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12291
Rout RK, Bandyopadhyay S (1999) A comparative study of shrimp feed pellets processed through cooking extruder and meat mincer. Aquac Eng 19(2):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8609(98)00034-X
Sedgwick RW (1979) Effect of ration size and feeding frequency on the growth and food conversion of juvenile Penaeus merguiensis de Man. Aquaculture 16(4):279–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(79)90069-3
Sick LV, White D, Baptist G (1973) The effect of duration of feeding, amount of food, light intensity, and animal size on rate of ingestion of pelleted food by juvenile penaeid shrimp. Prog Fish-Cult 35(1):22–26. https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8659(1973)35[22:TEODOF]2.0.CO;2
Smith DM, Burford MA, Tabrett SJ, Irvin SJ, Ward LR (2002) The effect of feeding frequency on water quality and growth of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Aquaculture 207(1–2):125–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00757-8
Soares R, Peixoto S, Galkanda-Arachchige HSC, Davis DA (2021) Growth performance and acoustic feeding behavior of two size classes of Litopenaeus vannamei fed pelleted and extruded diets. Aquacult Int 29(1):399–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00636-8
Tacon AGJ (2003) Trial finds extruded feeds superior to steamed pellets. Glob Aquac Advocate 6:44–45
Tacon AGJ, Cody JJ, Conquest LD, Divakaran S, Forster IP, Decamp OE (2002) Effect of culture system on the nutrition and growth performance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) fed different diets. Aquacult Nutr 8(2):121–137. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2095.2002.00199.x
Velasco M, Lawrence AL, Castille FL (1999) Effect of variations in daily feeding frequency and ration size on growth of shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone), in zero-water exchange culture tanks. Aquaculture 179(1–4):141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00158-1
Venou B, Alexis MN, Fountoulaki E, Haralabous J (2009) Performance factors, body composition and digestion characteristics of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) fed pelleted or extruded diets. Aquacult Nutr 15(4):390–401. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2008.00603.x
Vidal NP, Roman L, Swaraj VJS, Ragavan KV, Simsek S, Rahimi J, Kroetsch B, Martinez MM (2022) Enhancing the nutritional value of cold-pressed oilseed cakes through extrusion cooking. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 77:102956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2022.102956
Weldon A, Davis DA, Rhodes M, Reis J, Stites W, Ito P (2021) Feed management of Litopenaeus vannamei in a high density biofloc system. Aquaculture 544:737074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737074
Welker TL, Overturf K, Snyder S, Liu K, Abernathy J, Frost J, Barrows FT (2018) Effects of feed processing method (extrusion and expansion-compression pelleting) on water quality and growth of rainbow trout in a commercial setting. J Appl Aquac 30(2):97–124. https://doi.org/10.1080/10454438.2018.1433095
Woumbo CY, Kuate D, Klang MJ, Womeni HM (2021) Valorization of Glycine max (Soybean) Seed waste: Optimization of the Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE) and characterization of polyphenols from soybean meal using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). J Chem 2021:4869909. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4869909
Xu H, Li X, Sun W, Chen J, Gao Q, Shuai K, Leng X (2017) Effects of different feeding rates of extruded and pelleted feeds on growth and nutrient retention in channel catfish. Aquacult Int 25(3):1361–1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-017-0119-0
Yan M, Wang W, Huang X, Wang X, Wang Y (2020) Interactive effects of dietary cholesterol and phospholipids on the growth performance, expression of immune-related genes and resistance against Vibrio alginolyticus in white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Fish Shellfish Immunol 97:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.11.048
Zhang P, Zhang X, Li J, Gao T (2009) Effect of salinity on survival, growth, oxygen consumption and ammonia-N excretion of juvenile whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei Aquac Res 40(12):1419–1427. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2009.02240.x
Zhu M, Long X, Wu S (2018) Effects of dietary trehalose on the growth performance and nonspecific immunity of white shrimps (Litopenaeus vannamei). Fish Shellfish Immunol 78:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.04.035
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Ecuadorian Secretary of Higher Education, Science, Technology, and Innovation support for providing the scholarship for Manuel Espinoza (Contract 063-2012). The authors also express their gratitude to Gisis S.A., as well as Libertad Jiménez, Saul Zamora, and Sandra de La Paz Reyes for the technical support during the feeding trial, and Diana Fischer for English language edition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Manuel Espinoza-Ortega, Roberto Civera-Cerecedo, Miguel Jover-Cerdá; Methodology: Manuel Espinoza-Ortega, Roberto Civera-Cerecedo, Miguel Jover-Cerdá; Formal analysis: César Molina-Poveda, Roberto Civera-Cerecedo, Miguel Jover-Cerdá; Investigation: Manuel Espinoza-Ortega, Roberto Civera-Cerecedo; Writing - original draft preparation: Manuel Espinoza-Ortega, Roberto Civera-Cerecedo; Writing - review and editing: César Molina-Poveda, Roberto Civera-Cerecedo, Miguel Jover-Cerdá; Supervision: César Molina-Poveda, Roberto Civera-Cerecedo, Miguel Jover-Cerdá. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Gavin Burnell
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Espinoza-Ortega, M., Molina-Poveda, C., Jover-Cerdá, M. et al. Feeding frequency effect on water quality and growth of Litopenaeus vannamei fed extruded and pelleted diets. Aquacult Int 32, 413–429 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-023-01166-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-023-01166-9