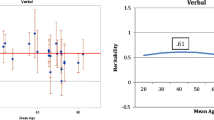
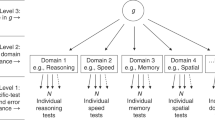
Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuthnott K, Frank J (2000) Trail making test, part B as a measure of executive control: validation using a set-switching paradigm. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 22(4):518–528
Ardila A, Pineda D, Rosselli M (2000) Correlation between intelligence test scores and executive function measures. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 15:495–513
Baddeley A (1986) Working memory. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Baddeley A (1990) Human memory: theory and practice. Erlbaum, London
Benton AL, Hamsher KS (1976) Multilingual aphasia examination: manual of instruction. University of Iowa, Iowa City
Bryan J, Luszcz MA (2000) Measurement of executive function: consideration for detecting adult age differences. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 22(1):40–55
Bugaiska A, Clarys D, Jarry, C, Taconnat L, Tapia G, Vanneste S, Isingrini M (2006) The effect of aging in recollective experience: the processing speed and executive functioning hypothesis. Conscious Cogn 16:797–808
Bunce D, Macready A (2005) Processing speed, executive, and age difference in remembering and knowing. Quart J Exp Psychol 58A(1):155–168
Cirulli ET, Kasperavičiūtė D, Attix DK, Need AC, Ge D, Gibson G, Goldstein DB (2010) Common genetic variation and performance on standardized cognitive tests. Eur J Hum Genet 18(7):815–820
Delis DC, Kaplan E, Kramer JH (2001) Executive function system: examiner’s manual. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, pp 91–103
Finkel D, Pedersen NL, McGue M, McClearn GE (1995a) Heritability of cognitive abilities in adult twins: comparison of Minnesota and Swedish data. Behav Genet 25:421–431
Finkel D, Pedersen NL, McGue M (1995b) Genetic influence on memory performance in adulthood: comparison of Minnesota and Swedish data. Psychol Aging 10:437–446
Fjell AM, Westlye LT, Amlien E, Espeseth T, Reinvang I, Raz N, Agartz I, Salat DH, Greve DN, Fischl B, Dale AM, Walhovd KB (2009) High consistency of regional cortical thinning in aging across multiple samples. Cereb Cortex 19:2001–2012
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state” a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Friedman NP, Miyake A, Corley RP, Young SE, DeFries JC, Hewitt JK (2006) Not all executive functions are related to intelligence. Psychol Sci 17(2):172–179
Friedman NP, Miyake A, Young SE, DeFries JC, Corley RP, Hewitt JK (2008) Individual differences in executive functions are almost entirely genetic in origin. J Exp Psychol Gen 137(2):201–225
Giubilei F, Medda E, Fagnani C, Bianchi V, De Carolis A, Salvetti M, Sepe-Monti M, Stazi MA (2008) Heritability of neurocognitive functioning in the elderly: evidence from an Italian twin study. Age Aging. doi:10.1093/ing/afn132
Head D, Rodrigue KM, Kennedy KM, Raz N (2008) Neuroanantomical and cognitive mediators of -related differences in episodic memory. Neuropsychology 22(4):491–507
Henry JD, von Hippel W, Baynes K (2009) Social inappropriateness, executive control, and aging. Psychol Aging 24(1):239–244
Huizinga M, Dolan CV, van der Molan MW (2006) Related change in executive function: developmental trends and a latent variable analysis. Neuropsychologia 44(11):2017–2036
Johnson W, Bouchard TJJr, Segal NL, Keyes M, Samuels J. (2003) The Stroop Color-Word Test: genetic and environmental influences: Reading, mental ability, and personality correlates. Journal of Educational Psychology 95:58-65
Kimberg DY, Farah MJ (1993) A unified account of cognitive impairments following frontal lobe dam: the role of working memory in complex, organised behavior. J Exp Psychol Gen 122(4):411–428
Lansbergen MM, Kenemans JL, van Engeland H (2007) Stroop interference and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychology 21(2):251–262
Lee T, Mosing MA, Henry JD, Trollor JN, Lammel A, Ames A, Martin NG, Wright MJ, Sachdev PS (2011) Genetic influences on five measures of processing speed and their covariation with general cognitive ability in the elderly: the older Australian twin study. Behav Genet. doi:10.1007/s10519-011-9474-1
Lessov-Schlaggar CN, Swan GE, Reed T, Wolf PA, Carmelli D (2007) Longitudinal genetic analysis of executive function in elderly men. Neurobiol Aging 28:1759–1768
Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW (2004) Neuropsychological assessment (4th edn). Oxford University Press Inc., New York
Luciano M, Gow AJ, Harris SE, Hayward C, Allerhand M, Starr JM, Visscher PM (2009) Cognitive ability at 11 and 70 years, information processing speed, and APOE variation: the Lothian birth cohort 1936 study. Psychol Aging 24(1):129–138
McClearn GE, Johansson B, Berg S, Pedersen NL, Ahern F, Petrill SA, Plomin R (1997) Substantial genetic influence on cognitive abilities in twins 80 or more years old. Science 276:1560–1563
McGue M, Christensen K (2001) The heritability of cognitive functioning in very old adults: evidence from Danish twins d 75 years and older. Psychol Aging 16(2):272–280
Miyake A, Friedman NP, Emerson MJ, Witzki AH, Howerter A, Wr TD (2000) The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: a latent variable analysis. Cogn Psychol 41:49–100
Mosocovitch M, Winocur G. (1992) The neuropsychology of memory and aging. In FIM Craik, TA Salthouse (eds), The handbook of aging and cognition, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, pp 315–372
Neale MC (2005) Twin studies: software and algorithms. Encyclopedia of life sciences. Wiley. www.els.net
Neale MC, Boker SM, Xie G, Maes HH (2002) Mx: statistical modeling. VA 23298: Department of Psychiatry VCU Box 900126, Richmond
Nelson HE, Willison JR (1991). National adult reading test (NART): Test manual, 2nd edn. NFER-Nelson, Windsor
Pedersen NL, Plomin R, Nesselroade J, McClearn GE (1992) A quantitative genetic analysis of cognitive abilities during the second half of the life span. Psychol Sci 3:346–352
Peper JS, Brouwer RM, Boomsma DI, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol (2001) Genetic influences on human brain structure: a review of brain imaging studies in twins. Human Brain Mapping 28:464–473
Plomin R, Pedersen NL, Lichtenstein P, Mcclearn GE (1994) Variability and stability in cognitive abilities are largely genetic later in life. Behav Genet 24:207–215
Purcell S (2008) Statistical methods in behavioral genetics. In: Plomin R, Defries JC, McClearn GE, McGuffin P. Behavioral Genetics, 5th edn. Worth Publishers and WH Freeman & Co, New York
Raz N, Gunning-Dixon FM, Head D, Dupuis JH, Acker JD (1998) Neuroanatomical correlates of cognitive aging: evidence from structural magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropsychology 12:95–114
Reitan RM, Wolfson D (1985) The Halstead-Reitan neuropsychological test battery: theory and interpretation. Neuropsychology Press, Tucson
Rey A (1964) L’examen clinique en psychologie. Presses Universitaires de France, Paris
Sachdev PS, Brodaty H, Reppermund S, Kochan NA, Trollor JN, Draper B, Memory and Aging Study Team (2010) Methodology and baseline medical and neuropsychiatric characteristics of an elderly epidemiological non-demented cohort of Australians aged 70–90 years. Int Psychogeriatr 22(8):1248–1264
Sachdev PS, Lammel A, Trollor JN, Lee T, Wright MJ, Ames D, Wen W, Martin NG, Brodaty H, Schofield PR, The OATS research team (2009) A comprehensive neuropsychiatric study of elderly twins: the older Australian Twins study. Twin Res Hum Genet 12(6):573–582
Salthouse TA (1996) The processing-speed theory of adult age differences in cognition. Psychol Bull 103:403–428
Salthouse TA (2005) Relations between cognitive abilities and measures of executive functioning. Neuropsychology 19(4):532–545
Shallice T (1988) From neuropsychology to mental structure. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sivan AB, Spreen O (1996) Der Benton-Test, 7th edn. Hans Huber, Berne
Smith EE, Jonides J (1999) Storage and executive processes in the frontal lobes. Science 283:1657–1661
Snow WG, Weinstock J (1990) Sex differences among non-brain-damaged adults on the Spinath Weschsler audlt intelligence scales: a review of the literature. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 12(6):873–886
Stins JF, van Baal GCM, Polderman TJC, Verhulst FC, Boomsma DI (2004) Heritability of Stroop and flanker performance in 12-year old children. BMC Neuroscience 5:49
Swan GE, Carmelli D (2002) Evidence of genetic mediation of executive control: a study of aging male twins. J Gerontol 57B(2):133–143
Taylor J (2007) Heritability of Wisconsin card sorting test (WCST) and stroop color-word test performance in normal individuals: implications for the search for endophenotypes. Twin Res Hum Genet 10(6):829–834
Walsh KW (1985) Understanding brain damage: a primer of neuropsychological evaluation. Churchill Livingstone, Longman Group Limited
Wechsler (1981) Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Wechsler D (1987) Wechsler Memory Scale-Revised manual. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Wechsler D (1997) Adult intelligence scale, 3rd edn. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
West RL (1996) An application of prefrontal cortex function theory to cognitive aging. Psychol Bull 120:272–292
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (ID 401162), and facilitated with access to the Australian Twin Registry, a national research resource supported by an Enabling Grant (ID 310667) from the National Health and Medical Research Council, and administered by The University of Melbourne. We would like to thank the OATS Research Team (www.brainage.med.unsw.edu.au) for their contribution to this study, and most of all, we would like to thank the twins and the informants for their participation in the OATS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Michael Lyons.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, T., Mosing, M.A., Henry, J.D. et al. Genetic Influences on Four Measures of Executive Functions and Their Covariation with General Cognitive Ability: The Older Australian Twins Study. Behav Genet 42, 528–538 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-012-9526-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-012-9526-1