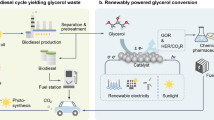
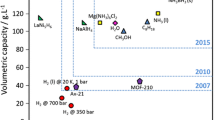
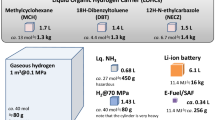
Abstract
A new immobilisate of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is described in which all components for the reaction, i.e. enzyme, the coenzyme NADP+, the buffer and other cofactors (trace elements), are immobilized together. It is an all-inclusive catalyst. The support is a cheap, commercially-available, superabsorbent polymer. The immobilisation is easy to achieve. The superabsorbed ADH is, even when dried, a stable and storable catalyst for at least five weeks at −18°C. Asymmetric reductions of the prochiral ketones, acetophenone, 4-acetylpyridine and ethyl acetoacetate, with a superabsorbed ADH from Lactobacillus brevis (ADH 002) and a superabsorbed ADH from Thermoanaerobicum sp. (ADH 005) in 2-propanol as both the organic solvent and the cofactor-regenerating substrate are given. Yields of chiral (R) and (S)-alcohols from 97–100% were achieved within 18 to 48 h with enantiomeric excesses of >99%. The superabsorbed ADH was easily separated by filtration and could be reused at least four times.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amotz S (1970) Unlösliches enzymatisches reaktives material. DE Patent 1959169, 4 June 1970
Hartdegen FJ, Swann WE (1980) Immobilization of biological materials with polyurethane polymers. US Patent 4,237,229, 2 Dec 1980
Hildebrand F, Lütz S (2006) Immobilization of alcohol dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus brevis and its application in a plug-flow reactor. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 17:3219–3225
Hischer T, Steinsiek S, Ansorge-Schumacher MB (2006) Use of polyvinyl alcohol cryogels for the compartmentation of biocatalyzed reactions in non-aqueous media. Biocatal Biotransformation 24(6):437–442
Hummel W, Riebel B (1997) Alkohol-dehydrogenase und deren Verwendung zur enzymatischen Herstellung chiraler Hydroxyverbindungen. DE Patent 19610984, 25 Sep 1997
Hussain W, Pollard DJ, Truppo M, Lye GJ (2008) Enzymatic ketone reductions with co-factor recycling: Improved reactions with ionic liquid co-solvents. J Mol Catal B: Enzym 55:19–29
Jeromin GE (2008) Immobilisierung von Alkoholdehydrogenasen und deren Coenzyme sowie Verwendung des Immobilisats. DE Patent 102008038 326.0, 19 Aug 2008
Jeromin GE, Bertau M (2005) Bioorganikum, Praktikum der Biokatalyse. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Metrangolo-Ruiz De Temiño D, Hartmeier W, Ansorge-Schumacher MB (2005) Entrapment of the alcohol dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus kefir in polyvinyl alcohol for the synthesis of chiral hydrophobic alcohols in organic solvents. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:3–9
Miethe P,Voss H, Gruber R, Poetzsch H (1989) Verfahren zur biokatalytischen Herstellung schlecht wasserlöslicher Substanzen mit integrierter extraktiver Aufarbeitung. EP Patent 0347873, 27 Dec 1989
Peschko C, Stohrer J (2005) Enzymatic method for the enantioselective reduction of keto compounds. EP Patent 1568780, 10 Feb 2005
Pfaller R, Schneider C (2007) Production of (S)-2-Butanol by oxidative racemate resolution. US Patent 0207529 A1, 23 Feb 2007
Pfaller R, Stohrer J (2007) Method for the enzymatic production of chiral alcohols. US Patent Application 0212766 A1, 13 Sep 2007
Tschaen DM, Abramson L, Cai D, Desmond R, Dolling U-H, Frey L, Karady S, Shi Y-J, Verhoeven TR (1995) Asymmetric synthesis of MK-0499. J Org Chem 60:4324–4330
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Kompetenzplattform Bioengineering Jülich (KOPF), financed by the Ministry for Innovation, Science, Research and Technology of North-Rhine Westphalia (Ministerium für Innovation, Wissenschaft, Forschung und Technologie des Landes Nordrhein-Westfalen (MIWFT- NRW)), GC-analytics were made by Dr. Andrea Butzen from Julich Chiral Solutions GmbH and enzyme activities were produced by Robert Kuss of the Aachen University of Applied Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeromin, G.E. Superabsorbed alcohol dehydrogenase—a new catalyst for asymmetric reductions. Biotechnol Lett 31, 1717–1721 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0062-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0062-x