Abstract
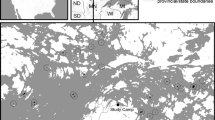
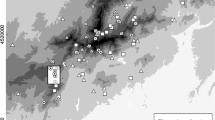
A number of studies analysing the structure of butterfly communities on Mediterranean islands have confirmed the well-established pattern of a current decrease in species richness in island communities. However, these studies generally lack quantitative data on butterfly population densities across habitats and over time. This precludes testing the hypotheses of ecological release, niche expansion and density compensation in island populations and their links to the presence of fewer competitors and/or predators. Here we use long-term monitoring data on butterfly populations from five sites on Menorca (Balearic Islands) and 20 sites from continental Catalonia (NE Spain) to test several hypotheses regarding island biogeography. We first confirm that island butterfly assemblages are not only impoverished versions of their continental counterparts but also have an over-representation of habitat generalists and highly mobile species. On the other hand, we did not find a consistent phenomenon of niche expansion and density compensation was only found for Celastrina argioulus and Gonepteryx cleopatra. Given the absence of habitat specialists on islands and the severe population declines taking place amongst specialist species on mainland Catalonia in the past two decades, we expected to detect more positive trends in island butterfly communities. Instead, we noted widespread declines, comparable to those previously recorded on the continent. Both the extension of the summer drought on Menorca and general habitat degradation due to the abandonment of cattle and sheep grazing may be responsible for these general declines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audusseau H, Le Vaillant M, Janz N, Nylin S, Karlsson B, Schmucki R (2017) Species range expansion constrains the ecological niches of resident butterflies. J Biogeogr 44:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12787
Carnicer J, Stefanescu C, Vila R, Dincă V, Font X, Peñuelas J (2013) A unified framework for diversity gradients: the adaptive trait continuum. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 22:6–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2012.00762.x
Chao A, Gotelli NJ, Hsieh TC, Sander EL, Ma KH, Colwell RK, Ellison AM (2014) Rarefaction and extrapolation with Hill numbers: a framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecol Monogr 84:45–67
Cox GW, Ricklefs RE (1977) Species diversity and ecological release in Caribbean land bird faunas. Oikos 28:113–122. https://doi.org/10.2307/3543330
Dapporto L, Dennis RLH (2007) Species richness, rarity and endemicity on Italian offshore islands: complementary signals from island-focused and species-focused analyses. J Biogeogr 35:664–674. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2007.01812.x
Dapporto L, Dennis RLH (2008) Island size is not the only consideration. Ranking priorities for the conservation of butterflies on Italian offshore islands. J Insect Conserv 12:237–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-008-9150-9
Dapporto L, Dennis RLH (2009) Conservation biogeography of large Mediterranean islands. Butterfly impoverishment, conservation priorities and inferences for an ecologica “island paradigm”. Ecography 32:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.16000-0587.2008.05600.x
Dapporto L, Dennis RLH (2013) The generalist-specialist continuum: testing predictors for distribution and trends in british butterflies. Biol Conserv 157:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2012.09.016
Dapporto L, Cini A, Menchetti M, Voda R, Bonelli S, Casacci LP, Dinca V, Scalercio S, Hinojosa JC, Biermann H, Forbicioni L, Mazzantini U, Venturi L, Zanichelli F, Balleto E, Shreeve TG, Dennis RLH, Vila R (2017) Rise and fall of insland butterfly diversity: understanding genetic differentiation and extinction in a highly diverse archipelago. Divers Distrib 23:1169–1181. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12610
Dennis RLH, Shreeve TG (1996) Butterflies on British and Irish offshore islands. Gem Publishing Company, Oxfordshire
Dennis RLH, Donato B, Sparks TH, Pollard E (2000) Ecological correlates of island incidence and geographical range among British butterflies. Biodivers Conserv 9:343–359. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008924329854
Dennis RLH, Hardy PB, Dapporto L (2012) Nestedness in island faunas: novel insights into island biogeography through butterfly community profiles of colonization ability and migration capacity. J Biogeogr 39:1412–1426. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2012.02698.x
Diamond JM (1975) Assembly of species communities. In: Cody ML, Diamond JM (eds) Ecology and evolution of communities. Belknap-Harvard Press, Cambridge, pp 342–444
Franzén M, Betzholtz PE (2012) Species traits predict island occupancy in noctuid moths. J Insect Conserv 16:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-011-9401-z
Herrando S, Brotons L, Anton M, Páramo F, Villero D, Titeux N, Quesada J, Stefanescu C (2015) Assessing impacts of land abandonment on Mediterranean biodiversity using indicators based on bird and butterfly monitoring data. Environ Conserv 43:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0376892915000260
Hsieh TC, Ma KH, Chao A (2016) iNext: an R package for rarefaction and extrapolation of species diversity (Hill numbers). Methods Ecol Evol 7:1451–1456. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12613
Jansà A, Homar V, Romero R, Alonso S, Guijarro JA, Ramis C (2017) Extension of summer climatic conditions into spring in the Western Mediterranean area. Int J Climatol 37:1938–1950. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4824
Jiménez-Valverde A, Hortal J (2003) Las curvas de acumulación de especies y la necesidad de evaluar la calidad de los inventarios biológicos. Revista ibérica de aracnología 8:151–161
John E, Cottle N, McArthur A, Makris C (2008) Eastern Mediterranean migrations of Pieris rape (Linnaeus, 1758) (Lepidoptera: Pieridae): observations in Cyprus, 2001 and 2007. Entomol Gaz 59:71–78
Julliard R, Clavel J, Devictor V, Jiguet F, Couvet D (2006) Spatial segregation of specialists and generalists in bird communities. Ecol Lett 9(11):1237–1244
Lomolino MV, Riddle BR, Brown JH (2006) Biogeography. Sianuer Associates, Sunderland
MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (1967) The theory of island biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Magurran AE (2004) Measuring biological diversity. Blackwell Science Ltd., Oxford
Melero Y, Stefanescu C, Pino J (2016) General declines in Mediterranean butterflies over the last two decades are modulated by species traits. Biol Conserv 201:336–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2016.07.029
Olivier A (1993) The butterflies of the Greek island of Ródos: taxonomy, faunistics, ecology and phenology. Vlaamse Vereniging voor Entomologie, Antwerpen
Pannekoek J, van Strien AJ (2001) TRIM 3 manual (trends & indices for monitoring data). Statistics Netherlands, Voorburg
Piechnik DA, Lawler SP, Martinez ND (2008) Food-web assembly during a classic biogeographic study: species’ “trophic breadth” corresponds to colonization order. Oikos 117:665–674. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2008.15915.x
Polis GA, Hurd DS (1995) Extraordinary high spider densities on islands: flow of energy from the marine to terrestrial food webs and the absence of predators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4382–4386. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.10.4382
Pollard E, Yates TJ (1993) Monitoring butterflies for ecology and conservation: the British butterfly monitoring scheme. Springer, Berlin
Polus E, Vandewoestijne S, Choutt J, Baguette M (2007) Tracking the effects of one century of habitat loss and fragmentation on calcareous grassland butterfly communities. Biodivers Conserv 16:3423–3436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-006-9008-y
Potts SG, Biesmeijer JC, Kremen C, Neumann P, Schweiger O, Kunin WE (2010) Global pollinator declines: trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol Evol 25:345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2010.01.007
Ribeiro SP, Borges PAV, Gaspar C, Melo C, Serrano A, Amaral J, Aguilar C, Genage A, Quartau JA (2005) Canopy insect herbivore diversity and distribution in the native forests of the Azores: key host plant species in a highly generalist insect community. Ecography 28:315–330. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0906-7590.2005.04104.x
Schmucki R, Pe’er G, Roy DB, Stefanescu C, Van Swaay CAM, Oliver TH, Kuussaari M, van Strien AJ, Ries L, Settele J, Musche M, Carnicer J, Schweiger O, Brereton T, Harpke A, Heliölä J, Kühn E, Julliard R (2015) A regionally informed abundance index for supporting integrative analyses across butterfly monitoring schemes. J Appl Ecol 53:501–510. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12561
Schoener TW, Spiller DA (1987) High population persistence in a system with high turnover. Nature 330:474–477. https://doi.org/10.1038/330474a0
Shaw MR, Stefanescu C, van Nouhuys S (2009) Parasitism of European butterflies (Hesperioidea and Papilionoidea). In: Settele J, Shreeve TG, Konvicka M, van Dyck H (eds) Ecology of butterflies in Europe. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 130–156
Sparks TH, Dennis RLH, Croxton PJ, Cade M (2007) Increased migration of Lepidoptera linked to climate change. Eur J Entomol 104:139–143. https://doi.org/10.14411/eje.2007.019
Stefanescu C (1997) Butterflies and moths recorded at sea off Eivissa and Barcelona (Western Mediterranean) in October 1996. Boll Soc Hist Nat Balears 40:51–56
Stefanescu C (2001) The nature of migration in the red admiral butterfly Vanessa atalanta: evidence from the population ecology in its southern range. Ecol Entom 26:525–536. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2311.2001.00347.x
Stefanescu C, Carnicer J, Peñuelas J (2011a) Determinants of species richness in generalist and specialist Mediterranean butterfly: the negative synergistic forces of climate and habitat change. Ecography 34:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.2010.06264.x
Stefanescu C, Torre I, Jubany J, Páramo F (2011b) Recent trends in butterfly populations from north-east Spain and Andorra in the light of habitat and climate change. J Insect Conserv 15:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-010-9325-z
Thomas JA (2016) Butterfly communities under threat. Science 353:216–218. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf8838
Thomas JA, Simcox DJ, Hovestadt T (2011) Evidence based conservation of butterflies. J Insect Conserv 15:241–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-010-9341-z
van Strien AJ, Pannekoek J, Gibbons DW (2010) Indexing European bird population trends using results of national monitoring schemes: a trial of a new method. Bird Study 48(2):200–213
van Swaay CAM, Nowicki P, Settele J, van Strien AJ (2008) Butterfly monitoring in Europe: methods, applications and perspectives. Biodivers Conserv 17:3455–3469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-008-9491-4
Van Swaay C, van Strien A, Aghababyan K, Astrom S, Botham M, Brereton T et al (2016) The European butterfly indicator for grassland species 1990-2015. Report VS2016.019. De Vlinderstichting, Wageningen
Voda R, Dapporto L, Dinca V, Vila R (2015) Why do cryptic species tend not to co-occur? A case study on two cryptic pairs of butterflies. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0117802. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117802
Voda R, Dapporto L, Dinca V, Shreeve TG, Khaldi M, Barech G, Rebbas K, Sammut P, Scalercio H, Hebert PDN, Vila R (2016) Historical and contemporary factors generate unique butterfly communities on islands. Sci Rep 6:28828. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28828
Warren MS, Hill JK, Thomas JA, Asher J, Fox R, Huntley B, Roy DB, Telfer MG, Jeffcoate S, Harding P, Jeffcoate G, Willis SG, Greatorex-Davies JN, Moss D, Thomas CD (2001) Rapid responses of British butterflies to opposing forces of climate and habitat change. Nature 414:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/35102054
Whittaker RJ, Fernández-Palacios JM (2007) Island biogeography: ecology, evolution, and conservation. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Whittaker RJ, Schmitt SF, Jones SH, Partomihardjo T, Bush MB (1998) Stand biomass and tree mortality from permanent forest plots on Krakatau, Indonesia, 1989–1995 1. Biotropica 30:519–529. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7429.1998.tb00092.x
Wiens JJ, Ackerly DD, Allen AP, Anacker B, Buckley LB, Cornell HV, Damschen EI, Davies TJ, Grytnes JA, Harrison SP, Hawkins BA, Holt RD, McCain CM, Stephens PR (2010) Niche conservatism as an emerging principle in ecology and conservation biology. Ecol Lett 13:1310–1324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01515.x
Williamson M (1981) Island populations. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Zhang Ch, Harpke A, Kühn E, Páramo F, Settele J, Stefanescu C, Wiemers M, Zhang Y, Schweiger O (2018) Applicability of butterfly transect counts to estimate species richness in different parts of the palearctic region. Ecol Indic 95:735–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.08.027
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the CBMS volunteers who have carried out the counts during all these years. This research would not have been possible without them. We would also specifically like to thank the Socio-environmental Observatory of Menorca, the Natural Park of S’Albufera des Grau and Menorca Agency Biosphere Reserve for their support for the Menorcan recording stations. Yolanda Melero, Ferran Páramo and Andreu Ubach assisted in data analysis and organisation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Frank Chambers.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colom, P., Carreras, D. & Stefanescu, C. Long-term monitoring of Menorcan butterfly populations reveals widespread insular biogeographical patterns and negative trends. Biodivers Conserv 28, 1837–1851 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-019-01764-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-019-01764-1