Abstract
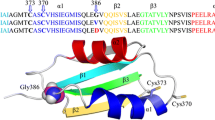
The Menkes (ATP7A) P1B-type ATPase is a transmembrane copper-translocating protein. It contains six similar high-affinity metal-binding domains (MBDs) in the N-terminal cytoplasmic tail that are important for sensing intracellular copper and regulating ATPase function through the transfer of copper between domains. Molecular characterization of copper-binding and transfer is predominantly dependent on NMR structures derived from E. coli expression systems. A limitation of these models is the exclusion of post-translational modifications. We have previously shown that the third copper-binding domain, MBD3, uniquely contains two phosphorylated residues: Thr-327, which is phosphorylated only in the presence of elevated copper; and Ser-339, which is constitutively phosphorylated independent of copper levels. Here, using molecular dynamic simulations, we have incorporated these phosphorylated residues into a model based on the NMR structures of MBD3. Our data suggests that constitutively phosphorylated Ser-339, which is in a loop facing the copper-binding site, may facilitate the copper transfer process by exposing the CxxC copper-binding region of MBD3. Copper-induced phosphorylation of Thr327 is predicted to stabilize this change in conformation. This offers new molecular insights into how cell signaling (phosphorylation) can affect MBD structure and dynamics and how this may in turn affect copper-binding and thus copper-translocation functions of ATP7A.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achila D, Banci L, Bertini I, Bunce J, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Huffman DL (2006) Structure of human Wilson protein domains 5 and 6 and their interplay with domain 4 and the copper chaperone HAM in copper uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:5729–5734
Anastassopoulou I, Banci L, Bertini I, Cantini F, Katsari E, Rosato A (2004) Solution structure of the Apo and copper(I)-loaded human metallochaperone HAH1. Biochemistry 43:13046–13053
Arnesano F, Banci L, Bertini I, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Molteni E, Huffman DL, O’Halloran TV (2002) Metallochaperones and metal-transporting ATPases: a comparative analysis of sequences and structures. Genome Res 12:255–271
Baker NA, Sept D, Holst MJ, McCammon JA (2001) The adaptive multilevel finite element solution of the Poisson-Boltzmann equation on massively parallel computers. IBM J Res Dev 45:427–438
Banci L, Bertini I, Cantini F, DellaMalva N, Herrmann T, Rosato A, Wurthrich K (2006a) Solution structure and intermolecular interactions of the third metal-binding domain of ATP7A, the Menkes disease protein. J Biol Chem 281:29141–29147
Banci L, Bertini I, Cantini F, Felli IC, Gonnelli L, Hadjiliadis N, Pierattelli R, Rosato A, Voulgaris P (2006b) The Atx1-Ccc2 complex is a metal-mediated protein–protein interaction. Nat Chem Biol 2:367–368
Banci L, Bertini I, Cantini F, Della-Malva N, Migliardi M, Rosato A (2007) The different intermolecular interactions of the soluble copper-binding domains of the Menkes protein, ATP7A. J Biol Chem 282:23140–23146
Banci L, Bertini I, Cantini F, Rosenzweig AC, Yatsunyk LA (2008) Metal binding domains 3 and 4 of the Wilson disease protein: solution Structure and interaction with the copper(I) chaperone HAH1. Biochemistry 47:7423–7429
Banci L, Bertini I, Calderone V, Della-Malva N, Felli IC, Neri S, Pavelkova A, Rosato A (2009) Copper(I)-mediated protein–protein interactions result from suboptimal interaction surfaces. Biochem J 422:37–42
Banci L, Bertini I, McGreevy KS, Rosato A (2010a) Molecular recognition in copper trafficking. Nat Prod Rep 27:695–710
Banci L, Bertini I, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Kozyreva T, Zovo K, Palumaa P (2010b) Affinity gradients drive copper to cellular destinations. Nature 465:645–648
Banci L, Bertini I, Cantini F, Inagaki S, Migliardi M, Rosato A (2010c) The binding mode of ATP revealed by the solution structure of the N-domain of human ATP7A. J Biol Chem 285:2537–2544
Bartee MY, Ralle M, Lutsenko S (2009) The loop connecting metal-binding domains 3 and 4 of ATP7B is a target of a kinase-mediated phosphorylation. Biochemistry 48:5573–5581
Boal AK, Rosenzweig AC (2009) Structural biology of copper trafficking. Chem Rev 109:4760–4779
Braiterman L, Nyasae L, Guo Y, Bustos R, Lutsenko S, Hubbard A (2009) Apical targeting and Golgi retention signals reside within a 9-amino acid sequence in the copper-ATPase, ATP7B. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296:G433–G444
Brooks BR, Bruccoleri RE, Olafson BD, States DJ, Swaminathan S, Karplus M (1983) CHARMM - A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J Comput Chem 4:187–217
Cater MA, Forbes J, La Fontaine S, Cox D, Mercer JFB (2004) Intracellular trafficking of the human Wilson protein: the role of the six N-terminal metal-binding sites. Biochem J 380:805–813
Dmitriev O, Tsivkovskii R, Abildgaard F, Morgan CT, Markley JL, Lutsenko S (2006) Solution structure of the N-domain of Wilson disease protein: distinct nucleotide-binding environment and effects of disease mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:5302–5307
Forbes JR, Hsi G, Cox DW (1999) Role of the copper-binding domain in the copper transport function of ATP7B, the P-type ATPase defective in Wilson disease. J Biol Chem 274:12408–12413
Gitschier J, Moffat B, Reilly D, Wood WI, Fairbrother WJ (1998) Solution structure of the fourth metal-binding domain from the Menkes copper-transporting ATPase. Nat Struct Biol 5:47–54
Greenough M, Pase L, Voskoboinik I, Petris MJ, O’Brien AW, Camakaris J (2004) Signals regulating trafficking of Menkes (MNK; ATP7A) copper-translocating P-type ATPase in polarized MDCK cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C1463–C1471
Groban ES, Narayanan A, Jacobson MP (2006) Conformational changes in protein loops and helices induced by post-translational phosphorylation. PLoS Comput Biol 2:238–250
Guo Y, Nyasae L, Braiterman LT, Hubbard AL (2005) NH2-terminal signals in ATP7B Cu-ATPase mediate its Cu-dependent anterograde traffic in polarized hepatic cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289:G904–G916
Holt BTO, Merz KM (2007) Insights into Cu(I) exchange in HAH1 using quantum mechanical and molecular simulations. Biochemistry 46:8816–8826
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14:33–38
Huster D, Lutsenko S (2003) The distinct roles of the N-terminal copper-binding sites in regulation of catalytic activity of the Wilson’s Disease protein. J Biol Chem 278:32212–32218
Kaplan JH, Lutsenko S (2009) Copper transport in mammalian cells: special care for a metal with special needs. J Biol Chem 284:25461–25465
Lamb AL, Wernimont AK, Pufahl RA, O’Halloran TV, Rosenzweig AC (2000) Crystal structure of the second domain of the human copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase. Biochemistry 39:1589–1595
LeShane ES, Shinde U, Walker JM, Barry AN, Blackburn NJ, Ralle M, Lutsenko S (2010) Interactions between copper-binding sites determine the redox status and conformation of the regulatory N-terminal domain of ATP7B. J Biol Chem 285:6327–6336
Morin I, Gudin S, Mintz E, Cuillel M (2009) Dissecting the role of the N-terminal metal-binding domains in activating the yeast copper ATPase in vivo. FEBS J 276:4483–4495
Narayanan A, Jacobson MP (2009) Computational studies of protein regulation by post-translational phosphorylation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19:156–163
Petris MJ, Voskoboinik I, Cater M, Smith K, Kim BE, Llanos RM, Strausak D, Camakaris J, Mercer JFB (2002) Copper-regulated trafficking of the Menkes disease copper ATPase is associated with formation of a phosphorylated catalytic intermediate. J Biol Chem 277:46736–46742
Phillips JC, Braun R, Wang W, Gumbart J, Tajkhorshid E, Villa E, Chipot C, Skeel RD, Kale L, Schulten K (2005) Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J Comput Chem 26:1781–1802
Rodriguez-Granillo A, Crespo A, Wittung-Stafshede P (2009) Conformational dynamics of metal-binding domains in Wilson disease protein: molecular insights into selective copper transfer. Biochemistry 48:5849–5863
Rodriguez-Granillo A, Crespo A, Wittung-Stafshede P (2010) Interdomain interactions modulate collective dynamics of the metal-binding domains in the Wilson disease protein. J Phys Chem B 114:1836–1848
Singleton WCJ, McInnes KT, Cater MA, Winnall WR, McKirdy R, Yu Y, Taylor PE, Ke BX, Richardson DR, Mercer JFB, La Fontaine S (2010) Role of Glutaredoxin1 and Glutathione in regulating the activity of the copper-transporting P-type ATPases, ATP7A and ATP7B. J Biol Chem 285:27111–27121
Strausak D, La Fontaine S, Hill J, Firth SD, Lockhart PJ, Mercer JFB (1999) The role of GMXCXXC metal binding sites in the copper-induced redistribution of the Menkes protein. J Biol Chem 274:11170–11177
Strausak D, Howie MK, Firth SD, Schlicksupp A, Pipkorn R, Multhaup G, Mercer JFB (2003) Kinetic analysis of the interaction of the copper chaperone Atox1 with the metal binding sites of the Menkes protein. J Biol Chem 278:20821–20827
Veldhuis N, Gaeth A, Pearson R, Gabriel K, Camakaris J (2009a) The multi-layered regulation of copper translocating P-type ATPases. Biometals 22:177–190
Veldhuis NA, Valova VA, Gaeth AP, Palstra N, Hannan KM, Michell BJ, Kelly LE, Jennings I, Kemp BE, Pearson RB, Robinson PJ, Camakaris J (2009b) Phosphorylation regulates copper-responsive trafficking of the Menkes copper transporting P-type ATPase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:2403–2412
Voskoboinik I, Mar J, Strausak D, Camakaris J (2001) The regulation of catalytic activity of the Menkes copper-translocating P-type ATPase—role of high affinity copper- binding sites. J Biol Chem 276:28620–28627
Voskoboinik I, Mar J, Camakaris J (2003) Mutational analysis of the Menkes copper P-type ATPase (ATP7A). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301:488–494
Wernimont AK, Huffman DL, Lamb AL, O’Halloran TV, Rosenzweig AC (2000) Structural basis for copper transfer by the metallochaperone for the Menkes/Wilson disease proteins. Nat Struct Biol 7:766–771
Yatsunyk LA, Rosenzweig AC (2007) Cu(I) binding and transfer by the N-terminus of the Wilson disease protein. J Biol Chem 282:8622–8631
Acknowledgments
The authors were supported by a NHMRC project grant (NV, JC). R.B.P is supported by a NHMRC Senior Research Fellowship. RCJD acknowledges the CR Roper Fellowship fund for salary support. The authors are also grateful to the Victorian Life Science Computational Initiative (VLSCI), which dedicated computational time to this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
N. A. Veldhuis and M. J. Kuiper contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veldhuis, N.A., Kuiper, M.J., Dobson, R.C.J. et al. In silico modeling of the Menkes copper-translocating P-type ATPase 3rd metal binding domain predicts that phosphorylation regulates copper-binding. Biometals 24, 477–487 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9410-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9410-0