Abstract
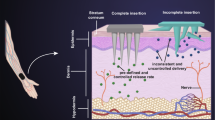
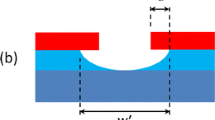
High density electrodes are a new frontier for biomedical implants. Increasing the density and the number of electrodes used for the stimulation of retinal ganglion cells is one possible strategy for enhancing the quality of vision experienced by patients using retinal prostheses. The present work presents an integration strategy for a diamond based, high density, stimulating electrode array with a purpose built application specific integrated circuit (ASIC). The strategy is centered on flip-chip bonding of indium bumps to create high count and density vertical interconnects between the stimulator ASIC and an array of diamond neural stimulating electrodes. The use of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) housing prevents cross-contamination of the biocompatible diamond electrode with non-biocompatible materials, such as indium, used in the microfabrication process. Micro-imprint lithography allowed edge-to-edge micro-scale pattering of the indium bumps on non-coplanar substrates that have a form factor that can conform to body organs and thus are ideally suited for biomedical applications. Furthermore, micro-imprint lithography ensures the compatibility of lithography with the silicon ASIC and aluminum contact pads. Although this work focuses on 256 stimulating diamond electrode arrays with a pitch of 150 μm, the use of indium bump bonding technology and vertical interconnects facilitates implants with tens of thousands electrodes with a pitch as low as 10 μm, thus ensuring validity of the strategy for future high acuity retinal prostheses, and bionic implants in general.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Bajaj, D. Akin, A. Gupta, D. Sherman, B. Shi, O. Auciello, R. Bashir, Biomed. Microdevices 9, 787 (2007)
C.A. Curcio, K.A. Allen, J. Comp. Neurol. 300, 5 (1990)
N.C. Das, M. Taysing-Lara, K.A. Olver, F. Kiamilev, J.P. Prineas, J.T. Olesberg, E.J. Koerperick, L.M. Murray, T.F. Boggess, IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 32, 9 (2009)
K. Ganesan, D.J. Garrett, A. Ahnood, M.N. Shivdasani, W. Tong, A.M. Turnley, K. Fox, H. Meffin, S. Prawer, Biomaterials 35, 908 (2014)
D.J. Garrett, K. Ganesan, A. Stacey, K. Fox, H. Meffin, S. Prawer, J. Neural Eng. 9, 016002 (2012)
R.A. Green, N.H. Lovell, G.G. Wallace, L.A. Poole-Warren, Biomaterials 29, 3393 (2008)
T. Guenther, C.W.D. Dodds, N.H. Lovell, G.J. Suaning in 2011 Annu. Int. Conf. Ieee Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 6717–6720 (2011)
T. Guenther, N.H. Lovell, G.J. Suaning, Expert. Rev. Med. Dev. 9, 33 (2012)
A.E. Hadjinicolaou, R.T. Leung, D.J. Garrett, K. Ganesan, K. Fox, D.A.X. Nayagam, M.N. Shivdasani, H. Meffin, M.R. Ibbotson, S. Prawer, B.J. O’Brien, Biomaterials 33, 5812 (2012)
H. Hämmerle, K. Kobuch, K. Kohler, W. Nisch, H. Sachs, M. Stelzle, Biomaterials 23, 797 (2002)
J. John, L. Zimmermann, P. D. Moor, C. V. Hoof, Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 531, 202 (2004)
Y.S. Kim, K.Y. Suh, H.H. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 2285 (2001)
M. Laroussi, F. Leipold, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 233, 81 (2004)
W. Lin, Y.C. Lee, IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 22, 592 (1999)
N.L. Opie, L.N. Ayton, N.V. Apollo, K. Ganesan, R.H. Guymer, C.D. Luu, Artif. Organs 38, E82 (2014)
P.J.Love, A.W. Hoffman, D.J. Gulbransen, M.P. Murray, K.J. Ando, N.J. Therrien, J.P. Rosbeck, R.S. Holcombe, 134–143 (2004).
J.D. Plessis, W.J. Pugh, A. Judefeind, J. Hadgraft, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 15, 63 (2002)
A. Santos, M.S. Humayun, E. de Juan Jr. et al., Arch. Ophthalmol. 115, 511 (1997)
C. Sekirnjak, P. Hottowy, A. Sher, W. Dabrowski, A.M. Litke, E.J. Chichilnisky, J. Neurosci. 28, 4446 (2008)
W. Tong, K. Fox, K. Ganesan, A.M. Turnley, O. Shimoni, P.A. Tran, A. Lohrmann, T. McFarlane, A. Ahnood, D.J. Garrett, H. Meffin, N.M. O’Brien-Simpson, E.C. Reynolds, S. Prawer, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 43, 135 (2014)
N. Tran, S. Bai, J. Yang, H. Chun, O. Kavehei, Y. Yang, V. Muktamath, D. Ng, H. Meffin, M. Halpern, E. Skafidas, IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 49, 751 (2014)
Z. Zhang, C.P. Wong, IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 27, 515 (2004)
D. Zhou, and E. Greenbaum, Implantable neural prostheses 2: techniques and engineering approaches (Springer Science & Business Media, 2010)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the ARC through its Special Research Initiative (SRI) in Bionic Vision Science and Technology grant to Bionic Vision Australia (BVA). This work was performed in part at the NSW Node of the Australian National Fabrication Facility. NVA is supported by an MMI-CSIRO PhD scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahnood, A., Escudie, M.C., Cicione, R. et al. Ultrananocrystalline diamond-CMOS device integration route for high acuity retinal prostheses. Biomed Microdevices 17, 50 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-9952-y
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-9952-y