Abstract
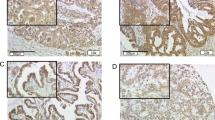
We previously identified a correlation between estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) and the candidate tumour suppressor gene Forkhead Box P1 (FOXP1), whose nuclear protein expression in breast tumours was associated with improved patient survival. However, the expression pattern of FOXP1 in normal breast tissue is more reminiscent of the second receptor, ERβ, which has an emerging role as a tumour suppressor in breast cancer and critically may underlie the ability of some ERα-negative tumours to respond to tamoxifen. In a series of 283 breast cancers, in which ERα-positive tumours were treated with tamoxifen, the nuclear expression of ERβ correlated significantly with ERα (p = 0.004), low-tumour grade (p = 0.008) and nuclear FOXP1 (p = 0.01). High-grade tumours exhibited significantly more cytoplasmic ERβ than the low-grade tumours (p = 0.006). Regression analysis demonstrated that FOXP1 expression was most closely related to nuclear ERβ (p = 0.021). Neither, nuclear or cytoplasmic ERβ expression demonstrated prognostic significance. FOXP1 is not estrogen regulated and silencing FOXP1 expression, using siRNA, did not affect ERα, ERβ or progesterone receptor expression, suggesting ER and FOXP1 co-expression may reflect a common regulatory mechanism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang B, Weidenfeld J, Lu MM et al (2004) Foxp1 regulates cardiac outflow tract, endocardial cushion morphogenesis and myocyte proliferation and maturation. Development 131(18):4477–4487
Banham AH, Beasley N, Campo E et al (2001) The FOXP1 winged helix transcription factor is a novel candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p. Cancer Res 61(24):8820–8829
Fox SB, Brown P, Han C et al (2004) Expression of the forkhead transcription factor FOXP1 is associated with estrogen receptor alpha and improved survival in primary human breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 10(10):3521–3527
Bieche I, Lidereau R (1995) Genetic alterations in breast cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 14(4):227–251
Martinez A, Walker RA, Shaw JA et al (2001) Chromosome 3p allele loss in early invasive breast cancer: detailed mapping and association with clinicopathological features. Mol Pathol 54(5):300–306
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Sivridis E et al (2006) Loss of expression and nuclear/cytoplasmic localization of the FOXP1 forkhead transcription factor are common events in early endometrial cancer: relationship with estrogen receptors and HIF-1alpha expression. Mod Pathol 19(1):9–16
Banham AH, Boddy J, Launchbury R et al (2007) Expression of the forkhead transcription factor FOXP1 is associated both with hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) and the Androgen receptor in prostate cancer but is not directly regulated by Androgens or hypoxia. Prostate 67(10):1091–1098
Ali S, Coombes RC (2002) Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2(2):101–112
Murphy LC, Watson PH (2006) Is oestrogen receptor-beta a predictor of endocrine therapy responsiveness in human breast cancer? Endocr Relat Cancer 13(2):327–334
Speirs V, Walker RA (2007) New perspectives into the biological and clinical relevance of oestrogen receptors in the human breast. J Pathol 211(5):499–506
Gruvberger-Saal SK, Bendahl PO, Saal LH et al (2007) Estrogen receptor beta expression is associated with tamoxifen response in ERalpha-negative breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13(7):1987–1994
McGuire WL (1975) Current status of estrogen receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer 36(2):638–644
(1998) Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet 351(9114):1451–1467
Speirs V, Skliris GP, Burdall SE et al (2002) Distinct expression patterns of ER alpha and ER beta in normal human mammary gland. J Clin Pathol 55(5):371–374
Elston C (1987) Grading of invasive carcinoma of the breast. In: Page D, Anderson T (eds) Diagnostic histopathology of the breast. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 300–311
Couse JF, Korach KS (1999) Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev 20(3):358–417
Liu MM, Albanese C, Anderson CM et al (2002) Opposing action of estrogen receptors alpha and beta on cyclin D1 gene expression. J Biol Chem 277(27):24353–24360
Pajer P, Pecenka V, Kralova J et al (2006) Identification of potential human oncogenes by mapping the common viral integration sites in avian nephroblastoma. Cancer Res 66(1):78–86
Speirs V, Carder PJ, Lane S et al (2004) Oestrogen receptor beta: what it means for patients with breast cancer. Lancet Oncol 5(3):174–181
Speirs V, Parker M, Green A et al (2006) Progress towards unlocking the secrets of oestrogen receptor beta in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 8(Suppl 2):P24
Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S et al (2007) Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev 87(3):905–931
Skliris GP, Munot K, Bell SM et al (2003) Reduced expression of oestrogen receptor beta in invasive breast cancer and its re-expression using DNA methyl transferase inhibitors in a cell line model. J Pathol 201(2):213–220
Zhao C, Lam EW, Sunters A et al (2003) Expression of estrogen receptor beta isoforms in normal breast epithelial cells and breast cancer: regulation by methylation. Oncogene 22(48):7600–7606
Kim SJ, Kim TW, Lee SY et al (2004) CpG methylation of the ERalpha and ERbeta genes in breast cancer. Int J Mol Med 14(2):289–293
Rody A, Holtrich U, Solbach C et al (2005) Methylation of estrogen receptor beta promoter correlates with loss of ER-beta expression in mammary carcinoma and is an early indication marker in premalignant lesions. Endocr Relat Cancer 12(4):903–916
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by funding from the Breast Cancer Campaign, Cancer Research UK, Tenovus and the Leukaemia Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bates, G.J., Fox, S.B., Han, C. et al. Expression of the forkhead transcription factor FOXP1 is associated with that of estrogen receptorβ in primary invasive breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111, 453–459 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9812-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9812-4