Abstract
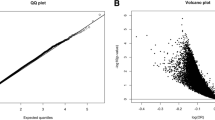
Aberrant DNA methylation is a key feature of breast carcinoma. We aimed to test the association between breast cancer risk and epigenome-wide methylation in DNA from peripheral blood. Nested case–control study within the prospective Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study. DNA was extracted from before-diagnosis blood samples (420 incident cases and matched controls). Methylation was measured with the Illumina Infinium Human Methylation 450 BeadChip array. Odds ratio (OR) for epigenome-wide methylation, quantified as the mean beta values across the CpGs, in relation to breast cancer risk were estimated using conditional logistic regression. Overall, the OR for breast cancer was 0.42 (95 % CI 0.20–0.90) for the top versus bottom quartile of epigenome-wide DNA methylation and the OR for a one standard deviation increment was 0.69 (95 % CI 0.50–0.95; test for linear trend, p = 0.02). Epigenome-wide DNA methylation of CpGs within functional promoters was associated with an increased risk, whereas epigenome-wide DNA methylation of genomic regions outside promoters was associated with decreased risk (test for heterogeneity, p = 0.0002). The increased risk associated with epigenome-wide DNA methylation in functional promoters did not vary by time between blood collection and diagnosis, whereas the inverse association with epigenome-wide DNA methylation outside functional promoters was strongest when the interval from blood collection to diagnosis was less than 5 years and weakest for the longest interval. Epigenome-wide methylation in DNA extracted from peripheral blood collected before diagnosis may have potential utility as markers of breast cancer risk and for early detection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Das PM, Singal R (2004) DNA methylation and cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(22):4632–4642
Kulis M, Esteller M (2010) DNA methylation and cancer. Adv Genet 70:27–56
Phillips, T (2008) The role of methylation in gene expression. Nat Educ 1(1):116
Wilson AS, Power BE, Molloy PL (2007) DNA hypomethylation and human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1775(1):138–162
Hinshelwood RA, Clark SJ (2008) Breast cancer epigenetics: normal human mammary epithelial cells as a model system. J Mol Med (Berl) 86(12):1315–1328
Jovanovic J, Ronneberg JA, Tost J, Kristensen V (2010) The epigenetics of breast cancer. Mol Oncol 4(3):242–254
Kristiansen S, Jorgensen LM, Guldberg P, Soletormos G (2013) Aberrantly methylated DNA as a biomarker in breast cancer. Int J Biol Markers 28(2):141–150
Szyf M (2012) DNA methylation signatures for breast cancer classification and prognosis. Genome Med 4(3):26
Fang F, Turcan S, Rimner A, Kaufman A, Giri D, Morris LG et al (2011) Breast cancer methylomes establish an epigenomic foundation for metastasis. Sci Transl Med 3(75):75ra25
Zhuang J, Jones A, Lee SH, Ng E, Fiegl H, Zikan M et al (2012) The dynamics and prognostic potential of DNA methylation changes at stem cell gene loci in women’s cancer. PLoS Genet 8(2):e1002517
Xu Z, Bolick SC, DeRoo LA, Weinberg CR, Sandler DP, Taylor JA (2013) Epigenome-wide association study of breast cancer using prospectively collected sister study samples. J Natl Cancer Inst 105(10):694–700
Shenker, N.S., S. Polidoro, K. van Veldhoven, C. Sacerdote, F. Ricceri, M.A. Birrell, et al. (2012).Epigenome-wide association study in the european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC-Turin) identifies novel genetic loci associated with smoking. Human Mol Genet p. dds488
Anjum S, Fourkala E-O, Zikan M, Wong A, Gentry-Maharaj A, Jones A et al (2014) A BRCA1-mutation associated DNA methylation signature in blood cells predicts sporadic breast cancer incidence and survival. Genome Med 6(6):47
Fackler MJ, Malone K, Zhang Z, Schilling E, Garrett-Mayer E, Swift-Scanlan T et al (2006) Quantitative multiplex methylation-specific PCR analysis doubles detection of tumor cells in breast ductal fluid. Clin Cancer Res 12(11 Pt 1):3306–3310
Hoque MO, Feng Q, Toure P, Dem A, Critchlow CW, Hawes SE et al (2006) Detection of aberrant methylation of four genes in plasma DNA for the detection of breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(26):4262–4269
Horvath S, Zhang Y, Langfelder P, Kahn RS, Boks MP, van Eijk K et al (2012) Aging effects on DNA methylation modules in human brain and blood tissue. Genome Biol 13(10):R97
Lim U, Flood A, Choi SW, Albanes D, Cross AJ, Schatzkin A et al (2008) Genomic methylation of leukocyte DNA in relation to colorectal adenoma among asymptomatic women. Gastroenterology 134(1):47–55
Pufulete M, Al-Ghnaniem R, Leather AJ, Appleby P, Gout S, Terry C et al (2003) Folate status, genomic DNA hypomethylation, and risk of colorectal adenoma and cancer: a case control study. Gastroenterology 124(5):1240–1248
Hsiung DT, Marsit CJ, Houseman EA, Eddy K, Furniss CS, McClean MD et al (2007) Global DNA methylation level in whole blood as a biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 16(1):108–114
Moore LE, Pfeiffer RM, Poscablo C, Real FX, Kogevinas M, Silverman D et al (2008) Genomic DNA hypomethylation as a biomarker for bladder cancer susceptibility in the Spanish bladder cancer study: a case–control study. Lancet Oncol 9(4):359–366
Brennan K, Garcia-Closas M, Orr N, Fletcher O, Jones M, Ashworth A et al (2012) Intragenic ATM methylation in peripheral blood DNA as a biomarker of breast cancer risk. Cancer Res 72(9):2304–2313
Choi JY, James SR, Link PA, McCann SE, Hong CC, Davis W et al (2009) Association between global DNA hypomethylation in leukocytes and risk of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 30(11):1889–1897
Delgado-Cruzata L, Wu HC, Perrin M, Liao Y, Kappil MA, Ferris JS et al (2012) Global DNA methylation levels in white blood cell DNA from sisters discordant for breast cancer from the New York site of the breast cancer family registry. Epigenetics 7(8):868–874
Xu X, Gammon MD, Hernandez-Vargas H, Herceg Z, Wetmur JG, Teitelbaum SL et al (2012) DNA methylation in peripheral blood measured by LUMA is associated with breast cancer in a population-based study. FASEB J 26(6):2657–2666
Sandoval J, Heyn H, Moran S, Serra-Musach J, Pujana MA, Bibikova M et al (2011) Validation of a DNA methylation microarray for 450,000 CpG sites in the human genome. Epigenetics 6(6):692–702
Clark C, Palta P, Joyce CJ, Scott C, Grundberg E, Deloukas P et al (2012) A comparison of the whole genome approach of MeDIP-seq to the targeted approach of the Infinium Human Methylation450 BeadChip((R)) for methylome profiling. PLoS One 7(11):e50233
Houseman EA, Accomando WP, Koestler DC, Christensen BC, Marsit CJ, Nelson HH et al (2012) DNA methylation arrays as surrogate measures of cell mixture distribution. BMC Bioinform 13:86
Chen YA, Lemire M, Choufani S, Butcher DT, Grafodatskaya D, Zanke BW et al (2013) Discovery of cross-reactive probes and polymorphic CpGs in the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 microarray. Epigenetics 8(2):203–209
Laird PW (2003) The power and the promise of DNA methylation markers. Nat Rev Cancer 3(4):253–266
Woo HD, Kim J (2012) Global DNA hypomethylation in peripheral blood leukocytes as a biomarker for cancer risk: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 7(4):e34615
Ostertag EM, Kazazian HH Jr (2001) Biology of mammalian L1 retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 35:501–538
Hoffmann MJ, Schulz WA (2005) Causes and consequences of DNA hypomethylation in human cancer. Biochem Cell Biol 83(3):296–321
Horard B, Eymery A, Fourel G, Vassetzky N, Puechberty J, Roizes G et al (2009) Global analysis of DNA methylation and transcription of human repetitive sequences. Epigenetics 4(5):339–350
Wu HC, Wang Q, Yang HI, Tsai WY, Chen CJ, Santella RM (2012) Global DNA methylation levels in white blood cells as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma risk: a nested case–control study. Carcinogenesis 33(7):1340–1345
Riboli E, Kaaks R (1997) The EPIC project: rationale and study design. European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Int J Epidemiol 26(suppl 1):S6
Michailidou, K, Hall P, Gonzalez-Neira A, Ghoussaini M, Dennis J, Milne RL et al (2013) Large-scale genotyping identifies 41 new loci associated with breast cancer risk. Nat Genet 45(4):353–361
Severi G, Byrnes GB, Hopper JL (2008) Five genetic variants associated with prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 358(25):2739–2740
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the many thousands of Melbourne residents who continue to participate in the Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study, the original investigators, program managers and the diligent team who recruited the participants and who continue working on follow-up. The methylation measures were conducted by the Australian Genome Research Facility (AGRF) in Melbourne. This work was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council (Grant number 1011618); and the Victorian Breast Cancer Research Consortium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Severi, G., Southey, M.C., English, D.R. et al. Epigenome-wide methylation in DNA from peripheral blood as a marker of risk for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 148, 665–673 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3209-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3209-y