Abstract
Purpose
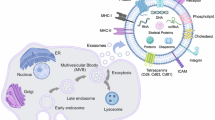
The interaction between malignant cells and surrounding healthy tissues is a critical factor in the metastatic progression of breast cancer (BC). Extracellular vesicles, especially exosomes, are known to be involved in inter-cellular communication during cancer progression. In the study presented herein, we aimed to evaluate the role of circulating plasma exosomes in the metastatic dissemination of BC and to investigate the underlying molecular mechanisms of this phenomenon.
Methods
Exosomes isolated from plasma of healthy female donors were applied in various concentrations into the medium of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines. Motility and invasive properties of BC cells were examined by random migration and Transwell invasion assays, and the effect of plasma exosomes on the metastatic dissemination of BC cells was demonstrated in an in vivo zebrafish model. To reveal the molecular mechanism of interaction between plasma exosomes and BC cells, a comparison between un-treated and enzymatically modified exosomes was performed, followed by mass spectrometry, gene ontology, and pathway analysis.
Results
Plasma exosomes stimulated the adhesive properties, two-dimensional random migration, and transwell invasion of BC cells in vitro as well as their in vivo metastatic dissemination in a dose-dependent manner. This stimulatory effect was mediated by interactions of surface exosome proteins with BC cells and consequent activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling in the tumor cells.
Conclusions
Plasma exosomes have a potency to stimulate the metastasis-promoting properties of BC cells. This pro-metastatic property of normal plasma exosomes may have impact on the course of the disease and on its prognosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menard JA, Cerezo-Magana M, Belting M (2018) Functional role of extracellular vesicles and lipoproteins in the tumour microenvironment. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser 373 (1737). https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0480
Green TM, Alpaugh ML, Barsky SH, Rappa G, Lorico A (2015) Breast cancer-derived extracellular vesicles: characterization and contribution to the metastatic phenotype. BioMed Res Int 2015:634865. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/634865
Harris DA, Patel SH, Gucek M, Hendrix A, Westbroek W, Taraska JW (2015) Exosomes released from breast cancer carcinomas stimulate cell movement. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0117495. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117495
Luga V, Wrana JL (2013) Tumor-stroma interaction: revealing fibroblast-secreted exosomes as potent regulators of Wnt-planar cell polarity signaling in cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 73(23):6843–6847. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1791
Gernapudi R, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Wolfson B, Roy S, Duru N, Eades G, Yang P, Zhou Q (2015) Targeting exosomes from preadipocytes inhibits preadipocyte to cancer stem cell signaling in early-stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 150(3):685–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3326-2
Lin R, Wang S, Zhao RC (2013) Exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote migration through Wnt signaling pathway in a breast cancer cell model. Mol Cell Biochem 383(1–2):13–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1746-z
Jang JY, Lee JK, Jeon YK, Kim CW (2013) Exosome derived from epigallocatechin gallate treated breast cancer cells suppresses tumor growth by inhibiting tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and M2 polarization. BMC Cancer 13:421. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-421
Chow A, Zhou W, Liu L, Fong MY, Champer J, Van Haute D, Chin AR, Ren X, Gugiu BG, Meng Z, Huang W, Ngo V, Kortylewski M, Wang SE (2014) Macrophage immunomodulation by breast cancer-derived exosomes requires Toll-like receptor 2-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Sci Rep 4:5750. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05750
Whiteside TL (2017) Exosomes in cancer: another mechanism of tumor-induced immune suppression. Adv Exp Med Biol 1036:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67577-0_6
Rana S, Malinowska K, Zoller M (2013) Exosomal tumor microRNA modulates premetastatic organ cells. Neoplasia 15(3):281–295
Costa-Silva B, Aiello NM, Ocean AJ, Singh S, Zhang H, Thakur BK, Becker A, Hoshino A, Mark MT, Molina H, Xiang J, Zhang T, Theilen TM, Garcia-Santos G, Williams C, Ararso Y, Huang Y, Rodrigues G, Shen TL, Labori KJ, Lothe IM, Kure EH, Hernandez J, Doussot A, Ebbesen SH, Grandgenett PM, Hollingsworth MA, Jain M, Mallya K, Batra SK, Jarnagin WR, Schwartz RE, Matei I, Peinado H, Stanger BZ, Bromberg J, Lyden D (2015) Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat Cell Biol 17(6):816–826. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3169
Hoshino A, Costa-Silva B, Shen TL, Rodrigues G, Hashimoto A, Tesic Mark M, Molina H, Kohsaka S, Di Giannatale A, Ceder S, Singh S, Williams C, Soplop N, Uryu K, Pharmer L, King T, Bojmar L, Davies AE, Ararso Y, Zhang T, Zhang H, Hernandez J, Weiss JM, Dumont-Cole VD, Kramer K, Wexler LH, Narendran A, Schwartz GK, Healey JH, Sandstrom P, Labori KJ, Kure EH, Grandgenett PM, Hollingsworth MA, de Sousa M, Kaur S, Jain M, Mallya K, Batra SK, Jarnagin WR, Brady MS, Fodstad O, Muller V, Pantel K, Minn AJ, Bissell MJ, Garcia BA, Kang Y, Rajasekhar VK, Ghajar CM, Matei I, Peinado H, Bromberg J, Lyden D (2015) Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 527(7578):329–335. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15756
Ochieng J, Pratap S, Khatua AK, Sakwe AM (2009) Anchorage-independent growth of breast carcinoma cells is mediated by serum exosomes. Exp Cell Res 315(11):1875–1888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.03.010
Almendros I, Khalyfa A, Trzepizur W, Gileles-Hillel A, Huang L, Akbarpour M, Andrade J, Farre R, Gozal D (2016) Tumor cell malignant properties are enhanced by circulating exosomes in sleep apnea. Chest 150(5):1030–1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2016.08.1438
Khalyfa A, Almendros I, Gileles-Hillel A, Akbarpour M, Trzepizur W, Mokhlesi B, Huang L, Andrade J, Farre R, Gozal D (2016) Circulating exosomes potentiate tumor malignant properties in a mouse model of chronic sleep fragmentation. Oncotarget 7(34):54676–54690. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10578
Genna A, Lapetina S, Lukic N, Twafra S, Meirson T, Sharma VP, Condeelis JS, Gil-Henn H (2018) Pyk2 and FAK differentially regulate invadopodia formation and function in breast cancer cells. J Cell Biol 217(1):375–395. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201702184
Thery C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, Clayton A (2006) Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471143030.cb0322s30
Samsonov R, Burdakov V, Shtam T, Radzhabova Z, Vasilyev D, Tsyrlina E, Titov S, Ivanov M, Berstein L, Filatov M, Kolesnikov N, Gil-Henn H, Malek A (2016) Plasma exosomal miR-21 and miR-181a differentiates follicular from papillary thyroid cancer. Tumour Biol 37(9):12011–12021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5065-3
Shtam T, Kovalev R, Varfolomeeva E, Makarov E, Kil Y, Filatov M (2013) Exosomes are natural carriers of exogenous siRNA to human cells in vitro. Cell Commun Signal 11:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-11-88
Alamri Y, Vogel R, MacAskill M, Anderson T (2016) Plasma exosome concentration may correlate with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement 4:107–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dadm.2016.08.002
Shtam T, Samsonov R, Kamyshinsky R, Pantina R, Verlov N, Vasiliev A, Konevega A, Malek A (2017) Exosomes: Some approaches to cancer diagnosis and therapy. AIP Conference Proceedings 1882 (1), 020066
Shtam T, Samsonov R, Volnitskiy A, Kamyshinsky R, Verlov N, Kniazeva M, Korobkina E, Orehov A, Vasiliev A, Konevega A, Malek A (2018) Isolation of extracellular micro-vesicles from cell culture medium: comparative evaluation of methods. Biomeditsinskaia Khimiia 64(1):23–30. https://doi.org/10.18097/PBMC20186401023
Egorov VV, Lebedev DV, Shaldzhyan AA, Sirotkin AK, Gorshkov AN, Mirgorodskaya OA, Grudinina NA, Vasin AV, Shavlovsky MM (2014) A conservative mutant of a proteolytic fragment produced during fibril formation enhances fibrillogenesis. Prion 8(5):369–373. https://doi.org/10.4161/19336896.2014.983745
Nečas D, Klapetek P (2012) Gwyddion: an open-source software for SPM data analysis. Cent Eur J Phys 10(1):181–188
Wisniewski JR, Zougman A, Nagaraj N, Mann M (2009) Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat Methods 6(5):359–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1322
Naryzhny S, Zgoda V, Kopylov A, Petrenko E, Kleist O, Archakov A (2017) Variety and dynamics of proteoforms in the human proteome: aspects of markers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Proteomes 5 (4). https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes5040033
Naryzhny S, Maynskova M, Zgoda V, Archakov А (2017) Zipf’s law in proteomics. J Proteom Bioinform 10:79–84
Ishihama Y, Oda Y, Tabata T, Sato T, Nagasu T, Rappsilber J, Mann M (2005) Exponentially modified protein abundance index (emPAI) for estimation of absolute protein amount in proteomics by the number of sequenced peptides per protein. Mole Cell Proteom 4(9):1265–1272. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M500061-MCP200
Ishihama Y, Schmidt T, Rappsilber J, Mann M, Hartl FU, Kerner MJ, Frishman D (2008) Protein abundance profiling of the Escherichia coli cytosol. BMC Genom 9:102. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-102
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 37(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn923
Nakaya A, Katayama T, Itoh M, Hiranuka K, Kawashima S, Moriya Y, Okuda S, Tanaka M, Tokimatsu T, Yamanishi Y, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M, Goto S (2013) KEGG OC: a large-scale automatic construction of taxonomy-based ortholog clusters. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Database issue):D353–D357. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1239
Schaefer CF, Anthony K, Krupa S, Buchoff J, Day M, Hannay T, Buetow KH (2009) PID: the pathway interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res 37: D674-D679. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn653
Croft D, Mundo AF, Haw R, Milacic M, Weiser J, Wu G, Caudy M, Garapati P, Gillespie M, Kamdar MR, Jassal B, Jupe S, Matthews L, May B, Palatnik S, Rothfels K, Shamovsky V, Song H, Williams M, Birney E, Hermjakob H, Stein L, D’Eustachio P (2014) The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D472–D477. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1102
Malek A, Catapano CV, Czubayko F, Aigner A (2010) A sensitive polymerase chain reaction-based method for detection and quantification of metastasis in human xenograft mouse models. Clin Exp Metastasis 27(4):261–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-010-9324-1
The Transwell Migration Assay (2017) J Vis Exp
White RM, Sessa A, Burke C, Bowman T, LeBlanc J, Ceol C, Bourque C, Dovey M, Goessling W, Burns CE, Zon LI (2008) Transparent adult zebrafish as a tool for in vivo transplantation analysis. Cell Stem Cell 2(2):183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2007.11.002
Lotvall J, Hill AF, Hochberg F, Buzas EI, Di Vizio D, Gardiner C, Gho YS, Kurochkin IV, Mathivanan S, Quesenberry P, Sahoo S, Tahara H, Wauben MH, Witwer KW, Thery C (2014) Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: a position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles 3:26913. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.26913
Shtam T, Naryzhny S, Kopylov A, Petrenko E, Samsonov R, Kamyshinsky R, Zabrodskaya Y, Nikitin D, Sorokin M, Buzdin A, Malek A (2018) Functional properties of circulating exosomes mediated by surface-attached plasma proteins. J Hematol 7(4):149–153
Purushothaman A, Bandari SK, Liu J, Mobley JA, Brown EE, Sanderson RD (2016) Fibronectin on the surface of myeloma cell-derived exosomes mediates exosome-cell interactions. J Biol Chem 291(4):1652–1663. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.686295
Sung BH, Ketova T, Hoshino D, Zijlstra A, Weaver AM (2015) Directional cell movement through tissues is controlled by exosome secretion. Nat Commun 6:7164. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8164
Luga V, Zhang L, Viloria-Petit AM, Ogunjimi AA, Inanlou MR, Chiu E, Buchanan M, Hosein AN, Basik M, Wrana JL (2012) Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell 151(7):1542–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.024
Lakkaraju A, Rodriguez-Boulan E (2007) Cell biology: caught in the traffic. Nature 448(7151):266–267. https://doi.org/10.1038/448266a
Mu W, Rana S, Zoller M (2013) Host matrix modulation by tumor exosomes promotes motility and invasiveness. Neoplasia 15(8):875–887
Koliha N, Heider U, Ozimkowski T, Wiemann M, Bosio A, Wild S (2016) Melanoma affects the composition of blood cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Front Immunol 7:282. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00282
Sung BH, Weaver AM (2017) Exosome secretion promotes chemotaxis of cancer cells. Cell Adhesi Migr 11(2):187–195. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336918.2016.1273307
Gan L, Meng J, Xu M, Liu M, Qi Y, Tan C, Wang Y, Zhang P, Weng W, Sheng W, Huang M, Wang Z (2017) Extracellular matrix protein 1 promotes cell metastasis and glucose metabolism by inducing integrin beta4/FAK/SOX2/HIF-1alpha signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.363
Naik MU, Naik TU, Summer R, Naik UP (2017) Binding of CIB1 to the αIIb tail of αIIbβ3 is required for FAK recruitment and activation in platelets. PloS one 12(5):e0176602. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176602
Keasey MP, Jia C, Pimentel LF, Sante RR, Lovins C, Hagg T (2018) Blood vitronectin is a major activator of LIF and IL-6 in the brain through integrin-FAK and uPAR signaling. J Cell Sci. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.202580
Li CL, Yang D, Cao X, Wang F, Hong DY, Wang J, Shen XC, Chen Y (2017) Fibronectin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via activation of calpain. Oncol Lett 13(5):3889–3895. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.5896
Hu C, Wen J, Gong L, Chen X, Wang J, Hu F, Zhou Q, Liang J, Wei L, Shen Y, Zhang W (2017) Thrombospondin-1 promotes cell migration, invasion and lung metastasis of osteosarcoma through FAK dependent pathway. Oncotarget 8(44):75881–75892. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17427
Lawson C, Lim ST, Uryu S, Chen XL, Calderwood DA, Schlaepfer DD (2012) FAK promotes recruitment of talin to nascent adhesions to control cell motility. J Cell Biol 196(2):223–232. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201108078
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by RFBR (grant numbers 15-54-12380 and 18-015-00289), by Russian Science Foundation (grant number 17-14-01416), by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (ID RFMEFI62117 × 0017) (to Anastasia Malek), as well as by the Israel Cancer Association and Estee Lauder Companies (grant number 20180089), by the Israel Cancer Research Foundation (grant number 17-902-AG), and by the Israel Science Foundation (grant number 1462/17) (to Hava Gil-Henn).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The design of study has been approved by Ethical Committee of N.N. Petrov National Medical Research Center of Oncology. All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration. All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shtam, T., Naryzhny, S., Samsonov, R. et al. Plasma exosomes stimulate breast cancer metastasis through surface interactions and activation of FAK signaling. Breast Cancer Res Treat 174, 129–141 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-018-5043-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-018-5043-0