Abstract
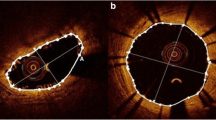
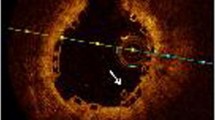
Implantation of a coronary stent results in a mechanical enlargement of the coronary lumen with stretching of the surrounding atherosclerotic plaque. Using intravascular ultrasound virtual-histology (IVUS-VH) we examined the temporal changes in composition of the plaque behind the struts (PBS) following the implantation of the everolimus eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold (BVS). Using IVUS-VH and dedicated software, the composition of plaque was analyzed in all patients from the ABSORB B trial who were imaged with a commercially available IVUS-VH console (s5i system, Volcano Corporation, Rancho Cordova, CA, USA) post-treatment and at 6-month follow-up. This dedicated software enabled analysis of the PBS after subtraction of the VH signal generated by the struts. The presence of necrotic core (NC) in contact with the lumen was also evaluated at baseline and follow-up. IVUS-VH data, recorded with s5i system, were available at baseline and 6-month follow-up in 15 patients and demonstrated an increase in both the area of PBS (2.45 ± 1.93 mm2 vs. 3.19 ± 2.48 mm2, P = 0.005) and the external elastic membrane area (13.76 ± 4.07 mm2 vs. 14.76 ± 4.56 mm2, P = 0.006). Compared to baseline there was a significant progression in the NC (0.85 ± 0.70 mm2 vs. 1.21 ± 0.92 mm2, P = 0.010) and fibrous tissue area (0.88 ± 0.79 mm2 vs. 1.15 ± 1.05 mm2, P = 0.027) of the PBS. The NC in contact with the lumen in the treated segment did not increase with follow-up (7.33 vs. 6.36%, P = 0.2). Serial IVUS-VH analysis of BVS-treated lesions at 6-month demonstrated a progression in the NC and fibrous tissue content of PBS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moses JW, Leon MB, Popma JJ, Fitzgerald PJ, Holmes DR, O’Shaughnessy C, Caputo RP, Kereiakes DJ, Williams DO, Teirstein PS, Jaeger JL, Kuntz RE (2003) Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery. N Engl J Med 349(14):1315–1323. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035071349/14/1315[pii]
Finn AV, Nakazawa G, Joner M, Kolodgie FD, Mont EK, Gold HK, Virmani R (2007) Vascular responses to drug eluting stents: importance of delayed healing. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(7):1500–1510. doi:ATVBAHA.107.144220[pii]10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.144220
Joner M, Finn AV, Farb A, Mont EK, Kolodgie FD, Ladich E, Kutys R, Skorija K, Gold HK, Virmani R (2006) Pathology of drug-eluting stents in humans: delayed healing and late thrombotic risk. J Am Coll Cardiol 48(1):193–202. doi:S0735-1097(06)01109-0[pii]10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.042
Wilson GJ, Nakazawa G, Schwartz RS, Huibregtse B, Poff B, Herbst TJ, Baim DS, Virmani R (2009) Comparison of inflammatory response after implantation of sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents in porcine coronary arteries. Circulation 120(2):141–149, 141–142. doi:CIRCULATIONAHA.107.730010 [pii]10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.730010
Kim SW, Mintz GS, Hong YJ, Pakala R, Park KS, Pichard AD, Satler LF, Kent KM, Suddath WO, Waksman R, Weissman NJ (2008) The virtual histology intravascular ultrasound appearance of newly placed drug-eluting stents. Am J Cardiol 102(9):1182–1186. doi:S0002-9149(08)00567-5[pii]10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.03.054
Sarno G, Onuma Y, Garcia HM, Garg S, Regar E, Thuesen L, Dudek D, Veldhof S, Dorange C, Ormiston JA, Serruys PW (2010) Ivus radiofrequency analysis in the evaluation of the polymeric struts of the bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting device during the bioabsorption process. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 5:627–632. doi:10.1002/ccd.22332
Kubo T, Maehara A, Mintz GS, Garcia-Garcia HM, Serruys PW, Suzuki T, Klauss V, Sumitsuji S, Lerman A, Marso SP, Margolis MP, Margolis JR, Foster MC, De Bruyne B, Leon MB, Stone GW (2010) Analysis of the long-term effects of drug-eluting stents on coronary arterial wall morphology as assessed by virtual histology intravascular ultrasound. Am Heart J 159(2):271–277. doi:S0002-8703(09)00880-1 [pii]10.1016/j.ahj.2009.11.008
Serruys PW, Ormiston JA, Onuma Y, Regar E, Gonzalo N, Garcia-Garcia HM, Nieman K, Bruining N, Dorange C, Miquel-Hebert K, Veldhof S, Webster M, Thuesen L, Dudek D (2009) A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system (absorb): 2-year outcomes and results from multiple imaging methods. Lancet 373(9667):897–910. doi:S0140-6736(09)60325-1[pii]10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60325-1
Ormiston JA, Serruys PW, Regar E, Dudek D, Thuesen L, Webster MW, Onuma Y, Garcia-Garcia HM, McGreevy R, Veldhof S (2008) A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system for patients with single de novo coronary artery lesions (absorb): a prospective open-label trial. Lancet 371(9616):899–907. doi:S0140-6736(08)60415-8[pii]10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60415-8
Hausmann D, Lundkvist AJ, Friedrich GJ, Mullen WL, Fitzgerald PJ, Yock PG (1994) Intracoronary ultrasound imaging: intraobserver and interobserver variability of morphometric measurements. Am Heart J 128(4):674–680
Nair A, Kuban BD, Tuzcu EM, Schoenhagen P, Nissen SE, Vince DG (2002) Coronary plaque classification with intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. Circulation 106(17):2200–2206
Garcia-Garcia HM, Gonzalo N, Pawar R, Kukreja N, Dudek D, Thuesen L, Ormiston JA, Regar E, Serruys PW (2009) Assessment of the absorption process following bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting stent implantation: temporal changes in strain values and tissue composition using intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. A substudy of the absorb clinical trial. EuroIntervention 4(4):443–448
Serruys PW, Onuma Y, Ormiston JA, De Bruyne B, Regar E, Dudek D, Thuesen L, Smith P, Chevalier B, McClean D, Koolen J, Windecker S, Whitbourn R, Meredith I, Dorange C, Veldhof S, Miquel-Hebert K, Rapoza R, Garcia Garcia HM (2010) Evaluation of the second generation of a bioresorbable everolimus drug-eluting vascular scaffold for treatment of de novo coronary artery stenosis: 6-month clinical and imaging outcomes. Circulation (in press)
Virmani R, Liistro F, Stankovic G, Di Mario C, Montorfano M, Farb A, Kolodgie FD, Colombo A (2002) Mechanism of late in-stent restenosis after implantation of a paclitaxel derivate-eluting polymer stent system in humans. Circulation 106(21):2649–2651
Klugherz BD, Llanos G, Lieuallen W, Kopia GA, Papandreou G, Narayan P, Sasseen B, Adelman SJ, Falotico R, Wilensky RL (2002) Twenty-eight-day efficacy and phamacokinetics of the sirolimus-eluting stent. Coron Artery Dis 13(3):183–188
Carter AJ, Aggarwal M, Kopia GA, Tio F, Tsao PS, Kolata R, Yeung AC, Llanos G, Dooley J, Falotico R (2004) Long-term effects of polymer-based, slow-release, sirolimus-eluting stents in a porcine coronary model. Cardiovasc Res 63(4):617–624. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.04.029S0008636304002019[pii]
Aoki J, Abizaid AC, Serruys PW, Ong AT, Boersma E, Sousa JE, Bruining N (2005) Evaluation of four-year coronary artery response after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation using serial quantitative intravascular ultrasound and computer-assisted grayscale value analysis for plaque composition in event-free patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 46(9):1670–1676. doi:S0735-1097(05)01846-2[pii]10.1016/j.jacc.2005.06.076
Tsuchida K, Piek JJ, Neumann FJ, van der Giessen WJ, Wiemer M, Zeiher AM, Grube E, Haase J, Thuesen L, Hamm CW, Veldhof S, Dorange C, Serruys PW (2005) One-year results of a durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent in de novo coronary narrowings (the spirit first trial). EuroIntervention 1(3):266–272. doi:EIJV1I3A44[pii]
Aoki J, Colombo A, Dudek D, Banning AP, Drzewiecki J, Zmudka K, Schiele F, Russell ME, Koglin J, Serruys PW (2005) Peristent remodeling and neointimal suppression 2 years after polymer-based, paclitaxel-eluting stent implantation: insights from serial intravascular ultrasound analysis in the taxus ii study. Circulation 112(25):3876–3883. doi:CIRCULATIONAHA.105.558601[pii]10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.558601
Onuma Y, Serruys P, den Heijer P, Joesoef KS, Duckers H, Regar E, Kukreja N, Tanimoto S, Garcia-Garcia HM, van Beusekom H, van der Giessen W, Nishide T (2009) Mahoroba, first-in-man study: 6-month results of a biodegradable polymer sustained release tacrolimus-eluting stent in de novo coronary stenoses. Eur Heart J 30(12):1477–1485. doi:ehp127[pii]10.1093/eurheartj/ehp127
Verheye S, Martinet W, Kockx MM, Knaapen MW, Salu K, Timmermans JP, Ellis JT, Kilpatrick DL, De Meyer GR (2007) Selective clearance of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques by autophagy. J Am Coll Cardiol 49(6):706–715. doi:S0735-1097(06)02888-9[pii]10.1016/j.jacc.2006.09.047
Martinet W, Verheye S, De Meyer GR (2007) Everolimus-induced mtor inhibition selectively depletes macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques by autophagy. Autophagy 3(3):241–244. doi:3711[pii]
Onuma Y, Serruys PW, Perkins L, Okamura T, Gonzalo N, Garcia HM, Regar E, Kamberi M, Powers JC, Rapoza R, van Beusekom H, van der Giessen W, Virmani R Intracoronary optical coherence tomography (oct) and histology at 1 month, at 2, 3 and 4 years after implantation of everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in a porcine coronary artery model: an attempt to decipher the human oct images in the absorb trial. Circulation (in press)
Rodriguez-Granillo GA, Serruys PW, Garcia-Garcia HM, Aoki J, Valgimigli M, van Mieghem CA, McFadden E, de Jaegere PP, de Feyter P (2006) Coronary artery remodelling is related to plaque composition. Heart 92(3):388–391. doi:hrt.2004.057810[pii]10.1136/hrt.2004.057810
Rodriguez-Granillo GA, Vaina S, Garcia-Garcia HM, Valgimigli M, Duckers E, van Geuns RJ, Regar E, van der Giessen WJ, Bressers M, Goedhart D, Morel MA, de Feyter PJ, Serruys PW (2006) Reproducibility of intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis: implications for the design of longitudinal studies. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 22(5):621–631. doi:10.1007/s10554-006-9080-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brugaletta, S., Garcia-Garcia, H.M., Garg, S. et al. Temporal changes of coronary artery plaque located behind the struts of the everolimus eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 27, 859–866 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-010-9724-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-010-9724-y