Abstract
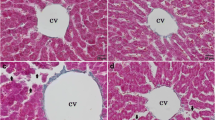
The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effect of 3-alkynyl selenophene (3-ASP) on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and 2-nitropropane (2-NP) in rats. On the first day of treatment, the animals received 3-ASP (25 mg/kg, p.o.). On the second day, the rats received CCl4 (1 mg/kg, i.p.) or 2-NP (100 mg/kg, p.o.). Twenty-four hours after CCl4 or 2-NP administration, the animals were euthanized, and their plasma and liver were removed for biochemical and histological analyses. The histological analysis revealed extensive injury in the liver of CCl4-exposed and 2-NP-exposed rats, which was attenuated by 3-ASP. 3-ASP significantly attenuated (1) the increase in plasmatic aspartate and alanine aminotransferase activities and lipid peroxidation levels induced by CCl4 and 2-NP; (2) the inhibition of δ-aminolevulinic dehydratase activity caused by 2-NP; and (3) the decrease in ascorbic acid (AA) levels and catalase (CAT) activity caused by CCl4. AA levels and CAT activity remained unaltered in the liver of rats exposed to 2-NP. The protective effect of 3-ASP on acute liver injury induced by CCl4 and 2-NP in rats was demonstrated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol. 1984;105:121–6.
Alves D, Luchese C, Nogueira CW, Zeni G. Electrophilic cyclization of (Z)-selenoenynes: synthesis and reactivity of 3-iodoselenophenes. J Org Chem. 2007;72:6726–34.
Arteel GE, Sies H. The biochemistry of selenium and the glutathione system. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2001;10:153–8.
Bock A, Forchammer JH, Leinfelder W, Sawers G, Vepreck B, Zinnia F. Selenocysteine: the 21st amino acid. Mol Microbiol. 1991;5:515–20.
Borges LP, Borges VC, Moro AV, Nogueira CW, Rocha JBT, Zeni G. Protective effect of diphenyl diselenide on acute liver damage induced by 2-nitropropane in rats. Toxicology. 2005;210:1–8.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principles of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Brattin WJ, Glende Jr EAJ, Recknagel RO. Pathological mechanisms in carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Free Radic Biol Med. 1985;1:27–38.
Chaterrjee TK. Medicinal plants with hepatoprotective properties. Herbal options. Calcutta: Books and Applied Allied (P) Ltd.; 2000. p. 143.
Clauson GA. Mechanism of carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 1989;8:104–12.
Dougherty JJ, Hoekstra WG. Stimulation of lipid peroxidation in vivo by injected selenite and lack of stimulation by selenate. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982;169:209–15.
Hafeman DG, Hoekstra WG. Protection against carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation in the rat by dietary vitamin E, selenium, and methionine as measured by ethane evolution. J Nutr. 1997;107:656–65.
Hung MY, Fu TY, Shih PH, Lee CP, Du-Zhong GCY. Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. leaves inhibits CCl4-induced hepatic damage in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006;44:1424–31.
Ianăş O, Olinescu R, Bădescu I, Simionescu L, Popovici D. The influence of “selenium organicum” upon the hepatic function of carbon tetrachloride poisoned rats. Rom J Intern Med. 1995;33:113–20.
Jacques-Silva MC, Nogueira CW, Broch LC, Rocha JBT. Diphenyl diselenide and ascorbic acid changes deposition of selenium and ascorbic acid in brain of mice. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;88:119–25.
Jain A, Soni M, Deb L, Jain A, Rout SP, Gupta VB, et al. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of ethanolic and aqueous extracts of Momordica dioica Roxb. leaves. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;115:61–6.
Kiso Y, Tohkin Ino H, Hatori M, Sakamoto T, Namba T. Mechanism of antihepatotoxic activity of glycyrrhizin: effect of free radical generation and lipid peroxidation. Planta Med. 1984;50:298–302.
Lewis TR, Ulrich CE, Busey WM. Subchronic inhalation toxicity of nitromethane and 2-nitropropane. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979;2:233–49.
May SW. Selenium-based pharmacological agents: an up date. Expert Opin Invest Drugs. 2002;11:1261–9.
Meotti FC, Stangherlin EC, Zeni G, Nogueira CW, Rocha JBT. Protective role of aryl and alkyl diselenides on lipid peroxidation. Environ Res. 2004;94:276–82.
Murugesan P, Muthusamy T, Balasubramania K, Arunakaran J. Effects of vitamins C and E on steroidogenic enzymes mRNA expression in polychlorinated biphenyl (Aroclor 1254) exposed adult rat Leydig cells. Toxicology. 2007;232:170–82.
Nogueira CW, Zeni G, Rocha JBT. Organoselenium and organotellurium compounds: toxicology and pharmacology. Chem Rev. 2004;104:6255–85.
Nogueira CW, Borges LP, Souza AC. Oral administration of diphenyl diselenide potentiates hepatotoxicity induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. J Appl Toxicol. 2009;29:156–64.
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979;95:351–8.
Ohta Y, Sasaki E, Nishida K, Kongo M, Hayashi T, Nagata M, et al. Inhibitory effect of Oren-gedoku-to (Huanglian-Jie-Du-Tang) extract on hepatic triglyceride accumulation with the progression of carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 1998;61:75–80.
Ohta Y, Kongo-Nishimura M, Matsura T, Yamada K, Kitagawa A, Kishikawa T. Melatonin prevents disruption of hepatic reactive oxygen species metabolism in rats treated with carbon tetrachloride. J Pineal Res. 2004;36:10–7.
Plaa GL, Charbonneau M. Detection and evaluation of chemically induced liver injury. In: Principles and methods of toxicology. New York: Raven Press. 1989; 399-628.
Porcíuncula LO, Rocha JBT, Boeck CR, Vendite D, Souza DO. Ebselen prevents excitotoxicity provoked by glutamate in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2001;299:217–20.
Prediger P, Moro AV, Nogueira CW, Savegnago L, Rocha JBT, Zeni G. Palladium-catalyzed Suzuki cross-coupling of 2-haloselenophenes: synthesis of 2-arylselenophenes, 2, 5-diarylselenophenes, and 2-arylselenophenyl ketones. J Org Chem. 2006;71:3786–92.
Recknagel RO, Glende Jr EA, Dolak JA, Waller RL. Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;43:139–54.
Reitman S, Frankel S. A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957;28:56–63.
Rocha JBT, Pereira ME, Emanuelli T, Christofari RS, Souza DO. Effect of treatment with mercury chloride and lead acetate during the second stage of rapid postnatal brain growth on delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALA-D) activity in brain, liver kidney and blood of suckling rats. Toxicology. 1995;100:27–37.
Rocha JBT, Gabriel D, Zeni G, Posser T, Siqueira L, Nogueira CW, et al. Ebselen and diphenyl diselenide change biochemical hepatic responses to overdosage with paracetamol. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;19:255–61.
Roscher E, Ziegler-Skylakakis K, Andrae U. Involvement of different pathways in the genotoxicity of nitropropanes in cultured mammalian cells. Mutagenesis. 1990;5:375–80.
Sassa S. Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase assay. Enzyme. 1982;28:133–45.
Schewe T. Molecular actions of ebselen—an antiinflammatory antioxidant. Gen Pharmacol. 1995;26:1153–69.
Shiah HS, Lee WS, Juang SH, Hong PC, Lung CC, Chang CJ, et al. Mitochondria-mediated and p53-associated apoptosis induced in human cancer cells by a novel selenophene derivative, D-501036. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;73:610–9.
Thabrew MI, Joice PDTM, Rajatissa WA. A comparative study of the efficacy of Pavetta indica and Osbeckia octandra in the treatment of liver dysfunction. Planta Med. 1987;53:239–41.
Wang H, Wei W, Wang NP, Gui SY, Wu L, Sun WY, et al. Melatonin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrogenesis in rats via inhibition of oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2005;77:1902–15.
Wang T, Sun N, Zhang W, Li H, Lua G, Yuan B, et al. Protective effects of dehydrocavidine on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;117:300–8.
Wilhelm EA, Jesse CR, Bortolatto CF, Nogueira CW, Savegnago L. Anticonvulsant and antioxidant effects of 3-alkynyl selenophene in 21-day-old rats on pilocarpine model of seizures. Brain Res Bull. 2009a;79:281–7.
Wilhelm EA, Jesse CR, Roman SS, Nogueira CW, Savegnago L. Hepatoprotective effect of 3-alkynyl selenophene on acute liver injury induced by d-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide. Exp Mol Pathol. 2009b;87:20–6.
Wolf PL. Biochemical diagnosis of liver diseases. Ind J Clin Biochem. 1999;14:59–90.
Zitting A, Savolainen H, Nickels J. Acute effects of 2-nitropropane on rat liver and brain. Toxicol Lett. 1981;9:237–46.
Acknowledgements
Financial support by FAPERGS, CAPES, and CNPq is gratefully acknowledged. C.W.N. and E.A.W. are recipients of CNPq fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilhelm, E.A., Jesse, C.R., Prigol, M. et al. 3-Alkynyl selenophene protects against carbon-tetrachloride-induced and 2-nitropropane-induced hepatic damage in rats. Cell Biol Toxicol 26, 569–577 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-010-9164-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-010-9164-4