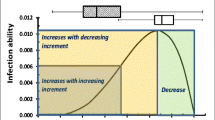
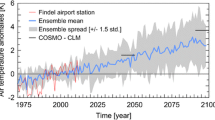
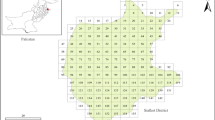
Abstract
Rice is the most rapidly growing staple food in Africa and although rice production is steadily increasing, the consumption is still out-pacing the production. In Tanzania, two important diseases in rice production are leaf blast caused by Magnaporthe oryzae and bacterial leaf blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. The objective of this study was to quantify rice yield losses due to these two important diseases under a changing climate. We found that bacterial leaf blight is predicted to increase causing greater losses than leaf blast in the future, with losses due to leaf blast declining. The results of this study indicate that the effects of climate change on plant disease can not only be expected to be uneven across diseases but also across geographies, as in some geographic areas losses increase but decrease in others for the same disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson PK, Cunningham AA, Patel NG, Morales FJ, Epstein PR, Daszak P (2004) Emerging infectious diseases of plants: pathogen pollution, climate change and agrotechnology drivers. Trends Ecol Evol 19(10):535–544. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2004.07.021. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169534704002186
Barreiro-Hurle J (2012) Analysis of incentives and disincentives for rice in the United Republic of Tanzania. Technical note series, MAFAP, FAO, Rome
Bivand R, Keitt T, Rowlingson B (2014) rgdal: Bindings for the Geospatial Data Abstraction Library. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rgdal, , R package version 0.8-16
Boko M, Niang I, Nyong A, Vogel C, Githeko A, Medany M, Osman-Elasha B, Tabo R, Yanda P (2007) Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, chap Africa, 433–467
Bouman B, Kropff M, Tuong T, Woperies M, ten Berge H, van Laar H (2001) ORYZA2000: modeling lowland rice. International Rice Research Institute, and Wageningen: Wageningen University and Research Center, Suite 1009, Pacific Bank Building, 6776 Ayala Avenue, Makati City, Philippines
Chakraborty S, Newton AC (2011) Climate change, plant diseases and food security: an overview. Plant Pathol 60(1):2–14. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02411.x
Coakley SM, Scherm H, Chakraborty S (1999) Climate change and plant disease management. Annu Rev Phytopathol 37(1):399–426. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.37.1.399. pMID: 11701829
Diagne A, Amovin-Assagba E, Futakuchi K, Wopereis M (2013) Realizing Africa’s rice promise, CAB International, Nosworthy Way, Wallingford, Oxfordshire OX10 8DE, UK, chap Estimation of cultivated area, number of farming households and yield for major rice-growing environments in Africa, 35–45
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2015) CROPCALENDAR. Crop calendar (Database). Webpage, http://data.fao.org/ref/2ca1cadd-9ee2-42ee-84d4-34473f2508fa.html?version=1.0 http://data.fao.org/ref/2ca1cadd-9ee2-42ee-84d4-34473f2508fa.html?version=1.0
Foundation PS (2014) The Python Language Reference. Python Software Foundation, https://docs.python.org/2/
Garrett KA, Dendy SP, Frank EE, Rouse MN, Travers SE (2006) Climate change effects on plant disease: Genomes to ecosystems. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44(1):489–509. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.070505.143420. pMID: 16722808
Geng S, de Vries FWP, Supit I (1986) A simple method for generating daily rainfall data. Agric For Meteorol 36(4):363–376. 10.1016/0168-1923(86)90014-6. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0168192386900146
Haefele SM, Saito K, N’Diaye KM, Mussgnug F, Nelson A, Wopereis MCS (2013) Realizing Africa’s rice promise, CAB International, Nosworthy Way, Wallingford, Oxfordshire OX10 8DE, UK, chap Increasing Productivity Through Improved Nutrient Use in Africa, 205–264
Hijmans RJ (2014) raster: Geographic data analysis and modeling. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster, R package version 2.2-31
Hijmans RJ, Forbes GA, Walker TS (2000) Estimating the global severity of potato late blight with GIS-linked disease forecast models. Plant Pathol 49(6):697–705. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3059.2000.00511.x
Hijmans RJ, Savary S, Pangga R, Aunario J (2009) cropsim: Simulation modeling of crops and their diseases. R package version 0.2.0-5
Institute (2011) ArcGIS Desktop: Release 10. Environmental Systems Research Institute, Redlands
Jones P, Thornton P, Heinke J (2009) Generating characteristic daily weather data using downscaled climate model data from the IPCC’s Fourth Assessment Report
Juroszek P, von Tiedemann A (2011) Potential strategies and future requirements for plant disease management under a changing climate. Plant Pathol 60(1):100–112. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02410.x
Kermack W, McKendrick A (1927) A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc R Soc Lond 115:700–721
Kim KH, Cho J, Lee YH, Lee WS (2015) Predicting potential epidemics of rice leaf blast and sheath blight in south korea under the RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 climate change scenarios using a rice disease epidemiology model, EPIRICE. Agric For Meteorol 203(0):191–207. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.01.011. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016819231500012X
Liu J, Williams JR, Wang X, Yang H (2009) Using MODAWEC to generate daily weather data for the EPIC model. Environ Model Softw 24(5):655–664. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2008.10.008. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364815208001904
Luck J, Spackman M, Freeman A, Trebicki P, Griffiths W, Finlay K, Chakraborty S (2011) Climate change and diseases of food crops. Plant Pathol 60 (1):113–121. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02414.x
Madden L, Hughes G, van den Bosch F (2007) The study of plant disease epidemics. The American Phytopathological Society. APS Press, St. Paul
Madden LV (2006) Botanical epidemiology: some key advances and its continuing role in disease management. Eur J Plant Pathol 115(1):3–23. doi:10.1007/s10658-005-1229-5
Meertens H, Ndege L, Lupeja P (1999) The cultivation of rainfed, lowland rice in Sukumaland, Tanzania. Agric Ecosyst Environ 76(1):31–45. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(99)00073-0
Parry M, Rosenzweig C, Iglesias A, Livermore M, Fischer G (2004) Effects of climate change on global food production under {SRES} emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Glob Environ Chang 14(1):53–67. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2003.10.008. climate Change. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959378003000827
Pautasso M, Dehnen-Schmutz K, Holdenrieder O, Pietravalle S, Salama N, Jeger M J, Lange E, Hehl-Lange S (2010) Plant health and global change – some implications for landscape management. Biol Rev 85(4):729–755. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.2010.00123.x
Peng S, Huang J, Sheehy JE, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Zhong X, Centeno GS, Khush GS, Cassman KG (2004) Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(27):9971–9975. 10.1073/pnas.0403720101. http://www.pnas.org/content/101/27/9971.full.pdf
Portmann FT, Siebert S, Döll P (2010) MIRCA2000—global monthly irrigated and rainfed crop areas around the year 2000: A new high-resolution data set for agricultural and hydrological modeling. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 24(1). doi:10.1029/2008GB003435
R Core Team (2014) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, http://www.R-project.org/
Ripley B, Lapsley M (2013) RODBC: ODBC Database Access. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RODBC, R package version 1.3-10
Rowhani P, Lobell DB, Linderman M, Ramankutty N (2011) Climate variability and crop production in Tanzania. Agric For Meteorol 151(4):449–460. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.12.002. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168192310003357
Saito K, Nelson A, Zwart S, Niang A, Sow A, Yoshida H, Wopereis M (2013) Realizing Africa’s rice promise, CAB International, Nosworthy Way, Wallingford, Oxfordshire OX10 8DE, UK, chap Towards a better understanding of biophysical determinants of yield gaps and potential expansion of rice area in Africa, 188–203
Savary S, Willocquet L, Elazegui FA, Teng PS, Van Du P, Zhu D, Tang Q, Huang S, Lin X, Singh HM, Srivastava RK (2000) Rice pest constraints in tropical Asia: Characterization of injury profiles in relation to production situations. Plant Dis 84(3):341–356. doi:10.1094/PDIS.2000.84.3.341
Savary S, Nelson A, Sparks AH, Willocquet L, Duveiller E, Mahuku G, Forbes G, Garrett KA, Hodson D, Padgham J, Pande S, Sharma M, Yuen J, Djurle A (2011) International agricultural research tackling the effects of global and climate changes on plant diseases in the developing world. Plant Dis 95 (10):1204–1216. doi:10.1094/PDIS-04-11-0316
Savary S, Nelson A, Willocquet L, Pangga I, Aunario J (2012) Modeling and mapping potential epidemics of rice diseases globally. Crop Prot 34(0):6–17. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2011.11.009. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261219411003656
Seck P, Toure A, Coulibaly J, Diagne A, Wopereis M (2013) Realizing Africa’s rice promise, CAB International, Nosworthy Way, Wallingford, Oxfordshire OX10 8DE, UK, chap Africa’s rice economy before and after the 2008 rice crisis, 24–34
Sere Y, Fargette D, Abo M, Wydra K, Bimerew M, Onasanya A, Akator S (2013) Realizing Africa’s rice promise, CAB International, Nosworthy Way, Wallingford, Oxfordshire OX10 8DE, UK, chap Managing the major diseases of rice in Africa, 213–228
Sparks AH, Forbes GA, Hijmans RJ, Garrett KA (2014) Climate change may have limited effect on global risk of potato late blight. Glob Chang Biol 20 (12):3621–3631. doi:10.1111/gcb.12587
Stevens RB (1960) Plant Pathology, an Advanced Treatise, vol 3. Academic Press, New York, pp 357–429
Sutherst RW, Constable F, Finlay KJ, Harrington R, Luck J, Zalucki MP (2011) Adapting to crop pest and pathogen risks under a changing climate. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Clim Chang 2(2):220–237. doi:10.1002/wcc.102
Thornton PK, Jones PG, Alagarswamy G, Andresen J (2009) Spatial variation of crop yield response to climate change in East Africa. Glob Environ Chang 19(1):54–65. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.08.005. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959378008000812
Verdier V, Cruz CV, Leach JE (2012) Controlling rice bacterial blight in Africa: Needs and prospects. J Biotechnol 159(4):320–328. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.09.020. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168165611005578
Willocquet L, Savary S, Fernandez L, Elazegui F, Teng P (2000) Development and evaluation of a multiple-pest, production situation specific model to simulate yield losses of rice in tropical Asia. Ecol Model 131(2–3):133–159. 10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00271-4. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304380000002714
Willocquet L, Savary S, Fernandez L, Elazegui F, Castilla N, Zhu D, Tang Q, Huang S, Lin X, Singh H, Srivastava R (2002) Structure and validation of RICEPEST, a production situation-driven, crop growth model simulating rice yield response to multiple pest injuries for tropical Asia. Ecol Model 153(3):247–268. doi:10.1016/S0304-3800(02)00014-5. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304380002000145
Willocquet L, Elizegui FA, Castilla N, Fernandez L, Fischer KS, Peng S, Ten PS, Srivastava RK, Singh HM, Zhu D, Savary S (2004) Research priorities for rice management in tropical Asia: A simulation analysis of yield losses and management efficiencies. Phytopathology 94:672–682
Yoshida S (1981) Fundamentals of Rice Science. The International Rice Research Institute, PO Box 933, Metro Manila, Philippines
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors wish to acknowledge J.K. Aunario and M. Noel for their assistance in running models and gathering data used in this study. The authors were funded in part by the Mitigating the Impact of Climate Change On Rice Disease resistance in East Africa (MICCORDEA) project financed by Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ), by the Consultative Group for International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) Consortium Research Programs (CRP) Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS) and Global Rice Science Partnership (GRiSP).
The first two authors contributed equally to this work are listed alphabetically.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duku, C., Sparks, A.H. & Zwart, S.J. Spatial modelling of rice yield losses in Tanzania due to bacterial leaf blight and leaf blast in a changing climate. Climatic Change 135, 569–583 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1580-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1580-2