Abstract
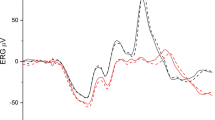
The electroretinogram is a widely used objective measure of visual function. The best characterised feature of the full-field dark-adapted flash ERG, is the earliest corneal negativity, the a-wave, which primarily reflects photoreceptoral responses. However, recent studies in humans and primates show that there are post-receptoral contributions to the a-wave. It is not clear if such contributions exist in the rat a-wave. We consider this issue in the rat a-wave, using intravitreal application of pharmacological agents that isolate post-receptoral ON-pathways and OFF-pathways. In anaesthetised adult long Evans rats, we show that the ON-pathway (2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid, APB sensitive) makes negligible contribution to the a-wave. In contrast, CNQX (6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione) or PDA (cis-piperidine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid) sensitive mechanisms modify the a-wave in two ways. First, for bright luminous energies, OFF-pathway inhibition (CNQX or PDA) results in a 22% reduction to the early phase of the leading edge of the a-wave up to 14 ms. Second, OFF-pathway inhibition removed a corneal negativity that resides between the a-wave trough and the b-wave onset.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERG:
-
Electroretinogram
- APB:
-
2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid
- CNQX:
-
6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione
- PDA:
-
cis-piperidine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid
References
Jamison JA, Bush RA, Lei B, Sieving PA (2001) Characterization of the rod photo response isolated from the dark-adapted primate ERG. Vis Neurosci 18:445–455
Robson JG, Saszik SM, Ahmed J, Frishman LJ (2003) Rod and cone contributions to the a-wave of the electroretinogram of the macaque. J Physiol 547:509–530
Robson JG, Frishman LJ (1996) Photoreceptor and bipolar cell contributions to the cat electroretinogram: a kinetic model for the early part of the flash response. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis 13:613–622
Naarendorp F, Williams GE (1999) The d-wave of the rod electroretinogram of rat originates in the cone pathway. Vis Neurosci 16:91–105
Weymouth AE, Vingrys AJ (2008) Rodent electroretinography: methods for extraction and interpretation of rod and cone responses. Prog Retin Eye Res 27:1–44
Lyubarsky AL, Daniele LL, Pugh EN Jr (2004) From candelas to photoisomerizations in the mouse eye by rhodopsin bleaching in situ and the light-rearing dependence of the major components of the mouse ERG. Vision Res 44:3235–3251
Bui BV, Fortune B (2004) Ganglion cell contributions to the rat full-field electroretinogram. J Physiol 555:153–173
Nguyen CT, Bui BV, Sinclair AJ, Vingrys AJ (2007) Dietary omega 3 fatty acids decrease intraocular pressure with age by increasing aqueous outflow. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:756–762
Tsai TI, Bui BV, Vingrys AJ (2009) Dimethyl sulphoxide dose-response on rat retinal function. Doc Ophthalmol 119:199–207
Berkowitz BA, Lukaszew RA, Mullins CM, Penn JS (1998) Impaired hyaloidal circulation function and uncoordinated ocular growth patterns in experimental retinopathy of prematurity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 39:391–396
Saszik SM, Robson JG, Frishman LJ (2002) The scotopic threshold response of the dark-adapted electroretinogram of the mouse. J Physiol 543:899–916
Fulton AB, Rushton WA (1978) Rod ERG of the mudpuppy: effect of dim red backgrounds. Vision Res 18:785–792
Green DG, Kapousta-Bruneau NV (1999) A dissection of the electroretinogram from the isolated rat retina with microelectrodes and drugs. Vis Neurosci 16:727–741
Jeffery G, Darling K, Whitmore A (1994) Melanin and the regulation of mammalian photoreceptor topography. Eur J Neurosci 6:657–667
Bui BV, Sinclair AJ, Vingrys AJ (1998) Electroretinograms of albino and pigmented guinea-pigs (Cavia porcellus). Aust N Z J Ophthalmol 26(Suppl 1):S98–S100
Quraishi S, Gayet J, Morgans CW, Duvoisin RM (2007) Distribution of group-III metabotropic glutamate receptors in the retina. J Comp Neurol 501:931–943
Hood DC, Birch DG (1994) Rod phototransduction in retinitis pigmentosa: estimation and interpretation of parameters derived from the rod a-wave. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:2948–2961
Lamb TD, Pugh ENJ (1992) A quantitative account of the activation steps involved in phototransduction in amphibian photoreceptors. J Physiol 449:719–758
Shiells RA, Falk G (1999) Contribution of rod, on-bipolar, and horizontal cell light responses to the ERG of dogfish retina. Vis Neurosci 16:503–511
Hanitzsch R, Karbaum R, Lichtenberger T (1998) Do horizontal cells contribute to the rabbit ERG? Doc Ophthalmol 97:57–66
Acknowledgments
NHMRC CJ Martin Postdoctoral Fellowship (BVB), NHMRC project grant 400127 (BVB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, T.M., Tsai, T.I., Vingrys, A.J. et al. Post-receptoral contributions to the rat scotopic electroretinogram a-wave. Doc Ophthalmol 122, 149–156 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-011-9269-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10633-011-9269-y